Regulation of growth signalling and cell cycle by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genes
- PMID: 15566428
- PMCID: PMC2517533
- DOI: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00407.x
Regulation of growth signalling and cell cycle by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genes
Abstract
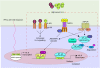
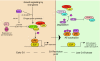
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is the primary aetiological agent of at least three malignancies associated with HIV infection and immunosuppression: Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma and multicentric Castleman's disease. KSHV encodes proteins that deregulate key checkpoints in the signalling pathways governing cell proliferation, which may ultimately contribute to the virus' oncogenic potential. To alter cellular signalling associated with proliferation, these viral proteins function like growth factor ligands/receptors, signal transduction proteins, transcription factors and cell cycle regulators. This review focuses on the mechanisms by which some KSHV-encoded proteins activate signalling pathways and cell proliferation and their role in the pathogenesis of KSHV-driven mechanisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The pleiotropic effects of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus.J Pathol. 2006 Jan;208(2):187-98. doi: 10.1002/path.1904. J Pathol. 2006. PMID: 16362980 Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)/human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) as a tumour virus.Herpes. 2003 Dec;10(3):72-7. Herpes. 2003. PMID: 14759339 Review.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV8): key aspects of epidemiology and pathogenesis.AIDS Rev. 2003 Oct-Dec;5(4):222-9. AIDS Rev. 2003. PMID: 15012001 Review.
-
Distinct expression of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded proteins in Kaposi's sarcoma and multicentric Castleman's disease.Pathol Int. 2006 Oct;56(10):617-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2006.02017.x. Pathol Int. 2006. PMID: 16984619
-
G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator.Nature. 1998 Jan 1;391(6662):86-9. doi: 10.1038/34193. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9422510
Cited by
-
Activation of DNA Damage Response Induced by the Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpes Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jun 1;17(6):854. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060854. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27258263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatinization of the KSHV Genome During the KSHV Life Cycle.Cancers (Basel). 2015 Jan 14;7(1):112-42. doi: 10.3390/cancers7010112. Cancers (Basel). 2015. PMID: 25594667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KSHV/HHV-8 and HIV infection in Kaposi's sarcoma development.Infect Agent Cancer. 2007 Feb 2;2:4. doi: 10.1186/1750-9378-2-4. Infect Agent Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17270056 Free PMC article.
-
Primary effusion lymphoma: current perspectives.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Jun 28;11:3747-3754. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S167392. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29988764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of AIDS-Associated Kaposi Sarcoma: A Functional Genomics Approach.Front Genet. 2020 Jan 24;10:1376. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01376. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32038721 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An J, Lichtenstein AK, Brent G, Rettig MB. The Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) induces cellular interleukin 6 expression: role of the KSHV latency-associated nuclear antigen and the AP1 response element. Blood. 2002;99:649–654. - PubMed
-
- An J, Sun Y, Rettig MB. Transcriptional coactivation of c-Jun by the KSHV-encoded LANA. Blood. 2003a;103:222–228. - PubMed
-
- An J, Sun Y, Sun R, Rettig MB. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoded vFLIP induces cellular IL-6 expression: the role of the NF-kappaB and JNK/AP1 pathways. Oncogene. 2003b;22:3371–3385. 10.1038/sj.onc.1206407. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Jaffe ES, Chang Y, et al. Angiogenesis and hematopoiesis induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded interleukin-6. Blood. 1999;93:4034–4043. - PubMed
-
- Aoki Y, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T, Tosato G. Receptor engagement by viral interleukin-6 encoded by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Blood. 2001a;98:3042–3049. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

