SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 are required for juvenile development and the production of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 15466488
- PMCID: PMC522987
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1231804
SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 are required for juvenile development and the production of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis
Abstract
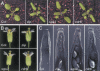
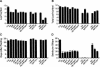
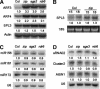
Higher plants undergo a transition from a juvenile to an adult phase of vegetative development prior to flowering. Screens for mutants that undergo this transition precociously produced alleles of two genes required for posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS)--SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING3 (SGS3) and SUPPRESSOR OF GENE SILENCING2(SGS2)/SILENCING DEFECTIVE1 (SDE1)/RNA-DEPENDENT POLYMERASE6 (RDR6). Loss-of-function mutations in these genes have a phenotype similar to that of mutations in the Argonaute gene ZIPPY (ZIP). Epistasis analysis suggests that ZIP, SGS3, SGS2/SDE1/RDR6, and the putative miRNA export receptor, HASTY (HST), operate in the same pathway(s). Microarray analysis revealed a small number of genes whose mRNA is increased in ZIP, SGS3, and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 mutants, as well as genes that are up-regulated in SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 mutants, but not in ZIP mutants. One of these latter genes (At5g18040) is silenced posttranscriptionally in trans by the sRNA255 family of endogenous, noncoding, small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The increase in At5g18040 mRNA in SGS3 and SGS2/SDE1/RDR6 mutants is attributable to the absence of sRNA255-like siRNAs in these mutants. These results demonstrate a role for endogenous siRNAs in the regulation of gene expression, and suggest that PTGS plays a central role in the temporal control of shoot development in plants.
Copyright 2004 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Figures
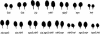



Similar articles
-
Geminivirus VIGS of endogenous genes requires SGS2/SDE1 and SGS3 and defines a new branch in the genetic pathway for silencing in plants.Plant J. 2004 Jun;38(6):1004-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02103.x. Plant J. 2004. PMID: 15165191
-
Genetic interaction between the AS1-AS2 and RDR6-SGS3-AGO7 pathways for leaf morphogenesis.Plant Cell Physiol. 2006 Jul;47(7):853-63. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcj057. Epub 2006 May 13. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16699177
-
DRB4-dependent TAS3 trans-acting siRNAs control leaf morphology through AGO7.Curr Biol. 2006 May 9;16(9):927-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.03.035. Curr Biol. 2006. PMID: 16682354
-
MicroRNA-dependent trans-acting siRNA production.Sci STKE. 2005 Sep 6;2005(300):pe43. doi: 10.1126/stke.3002005pe43. Sci STKE. 2005. PMID: 16145017 Review.
-
The function of RNAi in plant development.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:165-70. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.030. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381293 Review.
Cited by
-
The Whys and Wherefores of Transitivity in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 31;11:579376. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.579376. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32983223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel DICER-LIKE1 siRNAs Bypass the Requirement for DICER-LIKE4 in Maize Development.Plant Cell. 2015 Aug;27(8):2163-77. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00194. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Plant Cell. 2015. PMID: 26209554 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as master regulators of the plant NB-LRR defense gene family via the production of phased, trans-acting siRNAs.Genes Dev. 2011 Dec 1;25(23):2540-53. doi: 10.1101/gad.177527.111. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 22156213 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of small RNAs in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35306. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035306. Epub 2012 Apr 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22514725 Free PMC article.
-
The origin and effect of small RNA signaling in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2012 Aug 9;3:179. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2012.00179. eCollection 2012. Front Plant Sci. 2012. PMID: 22908024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso J.M., Stepanova, A.N., Leisse, T.J., Kim, C.J., Chen, H., Shinn, P., Stevenson, D.K., Zimmerman, J., Barajas, P., Cheuk, R., et al. 2003. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301: 653-657. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V., Lee, R.C., Lavanway, A., Williams, P.T., and Jewell, D. 2003b. MicroRNAs and other tiny endogenous RNAs in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 13: 807-818. - PubMed
-
- Banks J.A., Masson, P., and Fedoroff, N. 1988. Molecular mechanisms in the developmental regulation of the maize Suppressor-mutator transposable element. Genes & Dev. 2: 1364-1380. - PubMed
-
- Beclin C., Boutet, S., Waterhouse, P., and Vaucheret, H. 2002. A branched pathway for transgene-induced RNA silencing in plants. Curr. Biol. 12: 684-688. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
