The Fos-related antigen Fra-1 is an activator of bone matrix formation
- PMID: 15229648
- PMCID: PMC514946
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600282
The Fos-related antigen Fra-1 is an activator of bone matrix formation
Abstract
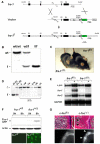
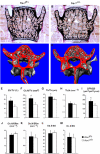
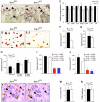
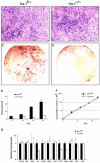
Ectopic expression of the transcription factor Fra-1 in transgenic mice leads to osteosclerosis, a bone disorder characterized by increased bone mass. The molecular basis for this phenotype is unknown and Fra-1 functions cannot be studied by a conventional loss-of-function approach, since fra-1-knockout mice die in utero likely due to placental defects. Here we show that the lethality of fra-1-knockout mice can be rescued by specific deletion of Fra-1 only in the mouse embryo and not in the placenta. Mice lacking Fra-1 (fra-1(delta/delta)) are viable and develop osteopenia, a low bone mass disease. Long bones of fra-1(delta/delta) mice appear to have normal osteoclasts but express reduced amounts of bone matrix components produced by osteoblasts and chondrocytes such as osteocalcin, collagen1a2 and matrix Gla protein. The gene for matrix Gla protein seems to be a specific target of Fra-1 since its expression was markedly increased in the long bones of fra-1-transgenic mice. These results uncover a novel function of Fra-1 in regulating bone mass through bone matrix production by osteoblasts and chondrocytes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased bone formation and osteosclerosis in mice overexpressing the transcription factor Fra-1.Nat Med. 2000 Sep;6(9):980-4. doi: 10.1038/79676. Nat Med. 2000. PMID: 10973316
-
Increased bone formation in mice lacking plasminogen activators.J Bone Miner Res. 2003 Jul;18(7):1167-76. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.7.1167. J Bone Miner Res. 2003. PMID: 12854826
-
Normal mineralization and nanostructure of sclerotic bone in mice overexpressing Fra-1.Bone. 2004 May;34(5):776-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2004.01.004. Bone. 2004. PMID: 15121008
-
Contribution of genetically modified mouse models to the elucidation of bone physiology.Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1999 Dec;66(12):728-35. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1999. PMID: 10649609 Review.
-
Energy regulation by the skeleton.Nutr Rev. 2008 Apr;66(4):229-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2008.00027.x. Nutr Rev. 2008. PMID: 18366536 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of Orai1 alters expression of multiple genes during osteoclast and osteoblast maturation.Cell Calcium. 2012 Dec;52(6):488-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 31. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 23122304 Free PMC article.
-
Control of bone formation by the serpentine receptor Frizzled-9.J Cell Biol. 2011 Mar 21;192(6):1057-72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201008012. Epub 2011 Mar 14. J Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21402791 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis.Cell Discov. 2024 Jul 2;10(1):71. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00689-6. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 38956429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone, inflammation, and inflammatory bowel disease.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011 Dec;9(4):251-7. doi: 10.1007/s11914-011-0077-9. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2011. PMID: 21935582 Review.
-
Water extract of Rumex crispus prevents bone loss by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and inducing osteoblast mineralization.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Oct 26;17(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1986-7. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 29070038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amling M, Priemel M, Holzmann T, Chapin K, Rueger JM, Baron R, Demay MB (1999) Rescue of the skeletal phenotype of vitamin D receptor-ablated mice in the setting of normal mineral ion homeostasis: formal histomorphometric and biomechanical analyses. Endocrinology 140: 4982–4987 - PubMed
-
- Behrens A, Haigh J, Mechta-Grigoriou F, Nagy A, Yaniv M, Wagner EF (2003) Impaired intervertebral disc formation in the absence of Jun. Development 130: 103–109 - PubMed
-
- Boyle WJ, Simonet WS, Lacey DL (2003) Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature 423: 337–342 - PubMed
-
- Chung KY, Agarwal A, Uitto J, Mauviel A (1996) An AP-1 binding sequence is essential for regulation of the human alpha2(I) collagen (COL1A2) promoter activity by transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem 271: 3272–3278 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

