Latent membrane protein 2A inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
- PMID: 14747535
- PMCID: PMC369507
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.78.4.1697-1705.2004
Latent membrane protein 2A inhibits transforming growth factor-beta 1-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
Abstract
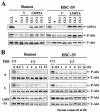
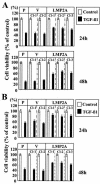
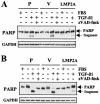
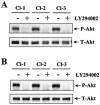
Latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) blocks B-cell receptor signal transduction in vitro by binding the Syk and Lyn protein tyrosine kinases. As well as blocking B-cell signal transduction, LMP2A has been shown to activate the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-K)/Akt pathway, which acts as a survival signal in both B cells and epithelial cells. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) is a multifunctional cytokine that plays important roles in regulating cell growth and differentiation in many biological systems. The loss of the growth-inhibitory response to the TGF-beta 1 signal is found in many cancers and is widely thought to promote tumor development. In this study, we found that LMP2A induced the phosphorylation of Akt (serine 473) in Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Ramos and in gastric carcinoma cell line HSC-39 and partially enhanced cell viability following TGF-beta 1 treatment. In addition, LMP2A partially inhibited TGF-beta 1-induced DNA fragmentation and cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). In the presence of LY294002, an inhibitor of PI3-K, the LMP2A-mediated inhibitory effects on TGF-beta 1-induced DNA fragmentation and cleavage of PARP were alleviated. Furthermore, LMP2A did not alter the levels of expression of type I and type II TGF-beta 1 receptors. Taken together, these results suggest that LMP2A may inhibit TGF-beta 1-mediated apoptosis through activation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A mediates transformation through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3-K/Akt Pathway.J Virol. 2007 Sep;81(17):9299-306. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00537-07. Epub 2007 Jun 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17582000 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A activates beta-catenin signaling in epithelial cells.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(22):12276-84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.22.12276-12284.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14581564 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-6 inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathways.J Biol Chem. 1999 Aug 13;274(33):23013-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.33.23013. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10438468
-
Latent membrane protein-1 induces cyclin D2 expression, pRb hyperphosphorylation, and loss of TGF-beta 1-mediated growth inhibition in EBV-positive B cells.J Immunol. 1995 Aug 1;155(3):1047-56. J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7636179
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I inhibits transcriptional responses of transforming growth factor-beta by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent suppression of the activation of Smad3 but not Smad2.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 3;278(40):38342-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304583200. Epub 2003 Jul 21. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12876289
Cited by
-
Growth regulation of simian and human AIDS-related non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cell lines by TGF-beta1 and IL-6.BMC Cancer. 2007 Feb 26;7:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-7-35. BMC Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17324269 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A alters in vivo and in vitro models of B-cell anergy, but not deletion, in response to autoantigen.J Virol. 2005 Jun;79(12):7355-62. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.12.7355-7362.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15919890 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Malignancies: Roles of Viral Oncoproteins in Carcinogenesis.Front Oncol. 2018 Aug 2;8:265. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00265. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30116721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif of latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) in Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A-induced cell transformation.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):5189-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03714-13. Epub 2014 Feb 19. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24554661 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-barr virus and the pathogenesis of T and NK lymphoma: a mystery unsolved.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2012 Dec;7(4):276-84. doi: 10.1007/s11899-012-0136-z. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2012. PMID: 22983913 Review.
References
-
- Brunet, A., A. Bonni, M. J. Zigmond, M. Z. Lin, P. Juo, L. S. Hu, M. J. Anderson, K. C. Arden, J. Blenis, and M. E. Greenberg. 1999. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857-868. - PubMed
-
- Cardone, M. H., N. Roy, H. R. Stennicke, G. S. Salvesen, T. F. Franke, E. Stanbridge, S. Frisch, and J. C. Reed. 1998. Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282:1318-1321. - PubMed
-
- Chen, R. H., M. C. Chang, Y. H. Su, Y. T. Tsai, and M. L. Kuo. 1999. Interleukin-6 inhibits transforming growth factor-beta-induced apoptosis through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase / Akt and signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 274:23013-23019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

