SVA elements are nonautonomous retrotransposons that cause disease in humans
- PMID: 14628287
- PMCID: PMC1180407
- DOI: 10.1086/380207
SVA elements are nonautonomous retrotransposons that cause disease in humans
Abstract
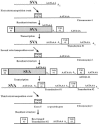
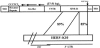
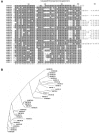
L1 elements are the only active autonomous retrotransposons in the human genome. The nonautonomous Alu elements, as well as processed pseudogenes, are retrotransposed by the L1 retrotransposition proteins working in trans. Here, we describe another repetitive sequence in the human genome, the SVA element. Our analysis reveals that SVA elements are currently active in the human genome. SVA elements, like Alus and L1s, occasionally insert into genes and cause disease. Furthermore, SVA elements are probably mobilized in trans by active L1 elements.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Engineered SVA Trans-mobilization Assay.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1400:203-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3372-3_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26895056
-
The non-autonomous retrotransposon SVA is trans-mobilized by the human LINE-1 protein machinery.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Feb;40(4):1666-83. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr863. Epub 2011 Nov 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22053090 Free PMC article.
-
Retrotransposition of marked SVA elements by human L1s in cultured cells.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Sep 1;20(17):3386-400. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr245. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21636526 Free PMC article.
-
Active human retrotransposons: variation and disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012 Jun;22(3):191-203. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2012.02.006. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2012. PMID: 22406018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrotransposal integration of mobile genetic elements in human diseases.J Hum Genet. 1998;43(2):77-84. doi: 10.1007/s100380050045. J Hum Genet. 1998. PMID: 9621510 Review.
Cited by
-
Benchmarking computational tools for polymorphic transposable element detection.Brief Bioinform. 2017 Nov 1;18(6):908-918. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw072. Brief Bioinform. 2017. PMID: 27524380 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting retrotransposons: a review.Mob DNA. 2016 Aug 11;7:16. doi: 10.1186/s13100-016-0070-z. eCollection 2016. Mob DNA. 2016. PMID: 27525044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polymorphic SVA retrotransposons at four loci and their association with classical HLA class I alleles in Japanese, Caucasians and African Americans.Immunogenetics. 2010 Apr;62(4):211-30. doi: 10.1007/s00251-010-0427-2. Epub 2010 Feb 20. Immunogenetics. 2010. PMID: 20174920
-
Transposable elements and the dynamic somatic genome.Genome Biol. 2007;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S5. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-s1-s5. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 18047697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of retrotransposons on human genome evolution.Nat Rev Genet. 2009 Oct;10(10):691-703. doi: 10.1038/nrg2640. Nat Rev Genet. 2009. PMID: 19763152 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for contigs AC037439 and AC068352 and BAC clone RP11-166N6 [contig AC016142])
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

