Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain
- PMID: 14581618
- PMCID: PMC263865
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2234031100
Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain
Abstract
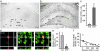
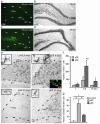
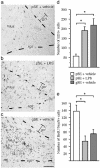
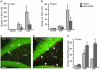
New hippocampal neurons are continuously generated in the adult brain. Here, we demonstrate that lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation, which gives rise to microglia activation in the area where the new neurons are born, strongly impairs basal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. The increased neurogenesis triggered by a brain insult is also attenuated if it is associated with microglia activation caused by tissue damage or lipopolysaccharide infusion. The impaired neurogenesis in inflammation is restored by systemic administration of minocycline, which inhibits microglia activation. Our data raise the possibility that suppression of hippocampal neurogenesis by activated microglia contributes to cognitive dysfunction in aging, dementia, epilepsy, and other conditions leading to brain inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intrathecal minocycline attenuates peripheral inflammation-induced hyperalgesia by inhibiting p38 MAPK in spinal microglia.Eur J Neurosci. 2005 Nov;22(10):2431-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04451.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16307586
-
Prenatal inflammation impairs adult neurogenesis and memory related behavior through persistent hippocampal TGFβ1 downregulation.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 Nov;24(8):1301-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2010.06.005. Epub 2010 Jun 20. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 20600816
-
Roles of astrocytes and microglia in seizure-induced aberrant neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult rats.J Neurosci Res. 2010 Feb 15;88(3):519-29. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22224. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 19774666
-
Research update: neurogenesis in adult brain and neuropsychiatric disorders.Mt Sinai J Med. 2006 Nov;73(7):931-40. Mt Sinai J Med. 2006. PMID: 17195878 Review.
-
Brain inflammation and adult neurogenesis: the dual role of microglia.Neuroscience. 2009 Feb 6;158(3):1021-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.052. Epub 2008 Jul 3. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 18662748 Review.
Cited by
-
A longitudinal study of cognition, proton MR spectroscopy and synaptic and neuronal pathology in aging wild-type and AβPPswe-PS1dE9 mice.PLoS One. 2013 May 22;8(5):e63643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063643. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23717459 Free PMC article.
-
Minocycline- and tetracycline-class antibiotics are protective against partial seizures in vivo.Epilepsy Behav. 2012 Jul;24(3):314-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2012.03.035. Epub 2012 May 11. Epilepsy Behav. 2012. PMID: 22579030 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic B-cell depletion reverses progression of Alzheimer's disease.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 12;12(1):2185. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22479-4. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33846335 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of microglia- and astrocyte-derived factors on neurogenesis in health and disease.Eur J Neurosci. 2021 Sep;54(5):5880-5901. doi: 10.1111/ejn.14969. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 32920880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of microfold cells ameliorates early pathological phenotypes by modulating microglial functions in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Nov 27;20(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02966-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 38012646 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cameron, H. A. & McKay, R. D. (2001) J. Comp. Neurol. 435, 406-417. - PubMed
-
- Shors, T. J., Miesegaes, G., Beylin, A., Zhao, M., Rydel, T. & Gould, E. (2001) Nature 410, 372-376. - PubMed
-
- Santarelli, L., Saxe, M., Gross, C., Surget, A., Battaglia, F., Dulawa, S., Weisstaub, N., Lee, J., Duman, R., Arancio, O., Belzung, C. & Hen, R. (2003) Science 301, 805-809. - PubMed
-
- Zitnik, G. & Martin, G. M. (2002) J. Neurosci. Res. 70, 258-263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

