Enhanced antitumor immunity in mice deficient in CD69
- PMID: 12732655
- PMCID: PMC2193974
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20021337
Enhanced antitumor immunity in mice deficient in CD69
Abstract
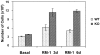
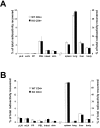
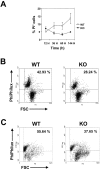
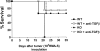
We investigated the in vivo role of CD69 by analyzing the susceptibility of CD69-/- mice to tumors. CD69-/- mice challenged with MHC class I- tumors (RMA-S and RM-1) showed greatly reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival compared with wild-type (WT) mice. The enhanced anti-tumor response was NK cell and T lymphocyte-mediated, and was due, at least in part, to an increase in local lymphocytes. Resistance of CD69-/- mice to MHC class I- tumor growth was also associated with increased production of the chemokine MCP-1, diminished TGF-beta production, and decreased lymphocyte apoptosis. Moreover, the in vivo blockade of TGF-beta in WT mice resulted in enhanced anti-tumor response. In addition, CD69 engagement induced NK and T cell production of TGF-beta, directly linking CD69 signaling to TGF-beta regulation. Furthermore, anti-CD69 antibody treatment in WT mice induced a specific down-regulation in CD69 expression that resulted in augmented anti-tumor response. These data unmask a novel role for CD69 as a negative regulator of anti-tumor responses and show the possibility of a novel approach for the therapy of tumors.
Figures






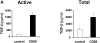
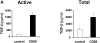
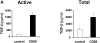
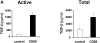
Similar articles
-
Induction of tumor NK-cell immunity by anti-CD69 antibody therapy.Blood. 2005 Jun 1;105(11):4399-406. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-3854. Epub 2005 Feb 3. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15692061
-
CD69 regulates type I IFN-induced tolerogenic signals to mucosal CD4 T cells that attenuate their colitogenic potential.J Immunol. 2012 Feb 15;188(4):2001-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100765. Epub 2012 Jan 16. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22250092
-
Role of CD69 in acute lung injury.Life Sci. 2012 May 15;90(17-18):657-65. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2012.03.018. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22483694
-
The activation antigen CD69.Stem Cells. 1994 Sep;12(5):456-65. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530120502. Stem Cells. 1994. PMID: 7804122 Review.
-
A new therapeutic target: the CD69-Myl9 system in immune responses.Semin Immunopathol. 2019 May;41(3):349-358. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00734-7. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Semin Immunopathol. 2019. PMID: 30953160 Review.
Cited by
-
CD69 gene is differentially regulated in T and B cells by evolutionarily conserved promoter-distal elements.J Immunol. 2009 Nov 15;183(10):6513-21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900839. Epub 2009 Oct 19. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19841192 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor cell lysate induces the immunosuppression and apoptosis of mouse immunocytes.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Dec;10(6):2827-34. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2606. Epub 2014 Oct 2. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 25310154 Free PMC article.
-
The early activation marker CD69 regulates the expression of chemokines and CD4 T cell accumulation in intestine.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 12;8(6):e65413. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065413. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23776480 Free PMC article.
-
MSI-H colorectal cancers preferentially retain and expand intraepithelial lymphocytes rather than peripherally derived CD8+ T cells.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009 Jan;58(1):135-44. doi: 10.1007/s00262-008-0534-1. Epub 2008 May 17. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2009. PMID: 18488217 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-CD69 monoclonal antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation in a mouse model of asthma.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015 Jul;16(7):622-31. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1400285. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2015. PMID: 26160720 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez-Mateos, P., and F. Sanchez-Madrid. 1991. Structure-function relationship and immunochemical mapping of external and intracellular antigenic sites on the lymphocyte activation inducer molecule, AIM/CD69. Eur. J. Immunol. 21:2317–2325. - PubMed
-
- Sant'Angelo, D.B., B. Lucas, P.G. Waterbury, B. Cohen, T. Brabb, J. Goverman, R.N. Germain, and C.A. Janeway, Jr. 1998. A molecular map of T cell development. Immunity. 9:179–186. - PubMed
-
- Testi, R., D. D'Ambrosio, R. De Maria, and A. Santoni. 1994. The CD69 receptor: a multipurpose cell-surface trigger for hematopoietic cells. Immunol. Today. 15:479–483. - PubMed
-
- Lauzurica, P., D. Sancho, M. Torres, B. Albella, M. Marazuela, T. Merino, J.A. Bueren, A.C. Martinez, and F. Sanchez-Madrid. 2000. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of hematopoietic cell lineages in CD69-deficient mice. Blood. 95:2312–2320. - PubMed
-
- Testi, R., J.H. Phillips, and L.L. Lanier. 1989. T cell activation via Leu-23 (CD69). J. Immunol. 143:1123–1128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

