Potential therapeutic uses of interleukin 1 receptor antagonists in human diseases
- PMID: 12379516
- PMCID: PMC1753951
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.61.11.960
Potential therapeutic uses of interleukin 1 receptor antagonists in human diseases
Abstract
Objective: To review publications relating to the blocking of interleukin 1 (IL1) as a strategy for treating human disease, ranging from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) to Alzheimer's disease.
Methods: The National Library of Medicine's PubMed database was searched for articles about pharmaceutical agents that reduce the biological actions of IL1.
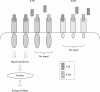
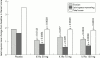
Results: Fish oils and corticosteroids were identified as non-selective pharmacological interventions that reduce the activity of IL1, whereas a recombinant human IL1 receptor antagonist (anakinra) and a soluble recombinant type I IL1 receptor act selectively. To date, anakinra is the only selective intervention that has been shown in controlled clinical trials to be effective and well tolerated in the treatment of a specific human disorder, RA. In controlled clinical trials, anakinra provided significant clinical improvement and slowed radiographic disease progression in patients with active RA. Moreover, addition of anakinra to existing methotrexate treatment significantly reduced signs and symptoms of active disease.
Conclusions: The clinical use of anakinra has been demonstrated in the management of RA, but blocking of IL1 in other human disorders, as well as the safety of the use of these blocking agents in chronic diseases, still needs to be defined by controlled clinical investigations.
Figures

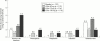
Similar articles
-
Anakinra treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Pharmacother. 2002 Jul-Aug;36(7-8):1204-9. doi: 10.1345/aph.1A396. Ann Pharmacother. 2002. PMID: 12086555 Review.
-
Anakinra shows promise for treating patients with rheumatoid arthritis.J Am Pharm Assoc (Wash). 2002 Jul-Aug;42(4):660-2. doi: 10.1331/108658002763029661. J Am Pharm Assoc (Wash). 2002. PMID: 12150367 No abstract available.
-
Anakinra: review of recombinant human interleukin-I receptor antagonist in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Ther. 2004 Dec;26(12):1960-75. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2004.12.019. Clin Ther. 2004. PMID: 15823761 Review.
-
Clinical and radiological effects of anakinra in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003 May;42 Suppl 2:ii22-8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keg329. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2003. PMID: 12817092 Review.
-
Anakinra (interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) has positive effects on function and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Adv Ther. 2006 Mar-Apr;23(2):208-17. doi: 10.1007/BF02850127. Adv Ther. 2006. PMID: 16751154 Review.
Cited by
-
Muscle IL1β Drives Ischemic Myalgia via ASIC3-Mediated Sensory Neuron Sensitization.J Neurosci. 2016 Jun 29;36(26):6857-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4582-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27358445 Free PMC article.
-
Probing Anti-inflammatory Properties Independent of NF-κB Through Conformational Constraint of Peptide-Based Interleukin-1 Receptor Biased Ligands.Front Chem. 2019 Feb 13;7:23. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00023. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 30815434 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of anakinra and canakinumab in PSTPIP1-associated inflammatory diseases: a comprehensive scoping review.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1339337. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1339337. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38259483 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic mimicry: phosphatidylserine liposomes reduce inflammation through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;151(6):844-50. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707302. Epub 2007 May 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17533418 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of interleukin 1 in type 1 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010 Mar;6(3):158-66. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2009.271. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20173777 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
