Comparative sequence analysis of the X-inactivation center region in mouse, human, and bovine
- PMID: 12045143
- PMCID: PMC1383731
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.152902
Comparative sequence analysis of the X-inactivation center region in mouse, human, and bovine
Abstract
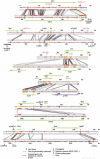
We have sequenced to high levels of accuracy 714-kb and 233-kb regions of the mouse and bovine X-inactivation centers (Xic), respectively, centered on the Xist gene. This has provided the basis for a fully annotated comparative analysis of the mouse Xic with the 2.3-Mb orthologous region in human and has allowed a three-way species comparison of the core central region, including the Xist gene. These comparisons have revealed conserved genes, both coding and noncoding, conserved CpG islands and, more surprisingly, conserved pseudogenes. The distribution of repeated elements, especially LINE repeats, in the mouse Xic region when compared to the rest of the genome does not support the hypothesis of a role for these repeat elements in the spreading of X inactivation. Interestingly, an asymmetric distribution of LINE elements on the two DNA strands was observed in the three species, not only within introns but also in intergenic regions. This feature is suggestive of important transcriptional activity within these intergenic regions. In silico prediction followed by experimental analysis has allowed four new genes, Cnbp2, Ftx, Jpx, and Ppnx, to be identified and novel, widespread, complex, and apparently noncoding transcriptional activity to be characterized in a region 5' of Xist that was recently shown to attract histone modification early after the onset of X inactivation.
Figures
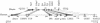
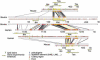

Similar articles
-
Comparative sequence and x-inactivation analyses of a domain of escape in human xp11.2 and the conserved segment in mouse.Genome Res. 2004 Jul;14(7):1275-84. doi: 10.1101/gr.2575904. Epub 2004 Jun 14. Genome Res. 2004. PMID: 15197169 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparative organization and the origin of noncoding regulatory RNA genes from X-chromosome inactivation center of human and mouse].Genetika. 2010 Oct;46(10):1386-91. Genetika. 2010. PMID: 21254562 Russian.
-
Dosage compensation of X-chromosome inactivation center-linked genes in porcine preimplantation embryos: Non-chromosome-wide initiation of X-chromosome inactivation in blastocysts.Mech Dev. 2015 Nov;138 Pt 3:246-55. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2015.10.005. Epub 2015 Oct 24. Mech Dev. 2015. PMID: 26598280
-
Origin and evolution of the long non-coding genes in the X-inactivation center.Biochimie. 2011 Nov;93(11):1935-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 27. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 21820484 Review.
-
Gene-containing regions of wheat and the other grass genomes.Plant Physiol. 2002 Mar;128(3):803-11. doi: 10.1104/pp.010745. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11891237 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
X-chromosome inactivation in rett syndrome human induced pluripotent stem cells.Front Psychiatry. 2012 Mar 23;3:24. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00024. eCollection 2012. Front Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22470355 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-Strain Epigenomic Profiling Reveals a Candidate IAP Master Copy in C3H Mice.Viruses. 2020 Jul 21;12(7):783. doi: 10.3390/v12070783. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32708087 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitinated proteins including uH2A on the human and mouse inactive X chromosome: enrichment in gene rich bands.Chromosoma. 2004 Dec;113(6):324-35. doi: 10.1007/s00412-004-0325-1. Epub 2004 Nov 20. Chromosoma. 2004. PMID: 15616869
-
Α de novo 3.8-Mb inversion affecting the EDA and XIST genes in a heterozygous female calf with generalized hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia.BMC Genomics. 2019 Sep 18;20(1):715. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6087-1. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31533624 Free PMC article.
-
A novel RNA transcript with antiapoptotic function is silenced in fragile X syndrome.PLoS One. 2008 Jan 23;3(1):e1486. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001486. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18213394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ansari-Lari MA, Oeltjen JC, Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Muzny DM, Lu J, Gorrell JH, Chinault AC, Belmont JW, Miller W, et al. Comparative sequence analysis of a gene-rich cluster at human chromosome 12p13 and its syntenic region in mouse chromosome 6. Genome Res. 1998;8:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Avner P, Heard E. X-chromosome inactivation: Counting, choice and initiation. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:59–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
