Mechanism by which high-dose aspirin improves glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 12021247
- PMCID: PMC150979
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI14955
Mechanism by which high-dose aspirin improves glucose metabolism in type 2 diabetes
Abstract
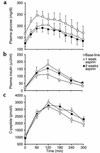
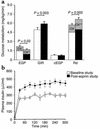
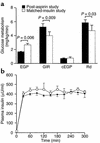
Recent studies have implicated fatty acid-dependent activation of the serine kinase IKKbeta, which plays a key role in tissue inflammation, in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. High doses of salicylates have recently been shown to inhibit IKKbeta activity and might therefore ameliorate insulin resistance and improve glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes. To test this hypothesis, we studied nine type 2 diabetic subjects before and after 2 weeks of treatment with aspirin ( approximately 7 g/d). Subjects underwent mixed-meal tolerance tests and hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamps with [6,6-(2)H2]glucose to assess glucose turnover before and after treatment. High-dose aspirin treatment resulted in a approximately 25% reduction in fasting plasma glucose, associated with a approximately 15% reduction in total cholesterol and C-reactive protein, a approximately 50% reduction in triglycerides, and a approximately 30% reduction in insulin clearance, despite no change in body weight. During a mixed-meal tolerance test, the areas under the curve for plasma glucose and fatty acid levels decreased by approximately 20% and approximately 50%, respectively. Aspirin treatment also resulted in a approximately 20% reduction in basal rates of hepatic glucose production and a approximately 20% improvement in insulin-stimulated peripheral glucose uptake under matched plasma insulin concentrations during the clamp. In conclusion, these data support the hypothesis that IKKbeta represents a new target for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanism of metformin action in obese and lean noninsulin-dependent diabetic subjects.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Dec;73(6):1294-301. doi: 10.1210/jcem-73-6-1294. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991. PMID: 1955512
-
Effect of rosiglitazone on glucose and non-esterified fatty acid metabolism in Type II diabetic patients.Diabetologia. 2001 Dec;44(12):2210-9. doi: 10.1007/s001250100031. Diabetologia. 2001. PMID: 11793023 Clinical Trial.
-
Association of insulin resistance with hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-diabetic pigs: effects of metformin at isoenergetic feeding in a type 2-like diabetic pig model.Metabolism. 2006 Jul;55(7):960-71. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2006.03.004. Metabolism. 2006. PMID: 16784971
-
Dissociation between fat-induced in vivo insulin resistance and proximal insulin signaling in skeletal muscle in men at risk for type 2 diabetes.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004 Mar;89(3):1301-11. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031243. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004. PMID: 15001626 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of pioglitazone on abdominal fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002 Jun;87(6):2784-91. doi: 10.1210/jcem.87.6.8567. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002. PMID: 12050251
Cited by
-
Innate immune activation in obesity.Mol Aspects Med. 2013 Feb;34(1):12-29. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2012.10.002. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Mol Aspects Med. 2013. PMID: 23068074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bone marrow-CNS connections: implications in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012 Sep;31(5):481-94. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.04.005. Epub 2012 May 15. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22609081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lumazine peptides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus.Mar Drugs. 2015 Mar 12;13(3):1290-303. doi: 10.3390/md13031290. Mar Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25775424 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin, a Potential GLUT1 Inhibitor in a Vascular Endothelial Cell Line.Open Med (Wars). 2019 Sep 12;14:552-560. doi: 10.1515/med-2019-0062. eCollection 2019. Open Med (Wars). 2019. PMID: 31565672 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction and type 2 diabetes.Curr Diab Rep. 2005 Jun;5(3):177-83. doi: 10.1007/s11892-005-0006-3. Curr Diab Rep. 2005. PMID: 15929863 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- De Fea K, Roth RA. Protein kinase C modulation of insulin receptor substrate-1 tyrosine phosphorylation requires serine 612. Biochemistry. 1997;36:12939–12947. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz-Peiffer C, et al. Alterations in the expression and cellular localization of protein kinase C isozymes epsilon and theta are associated with insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of the high fat fed rat. Diabetes. 1997;46:169–178. - PubMed
-
- Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS, Spiegelman BM. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science. 1993;259:87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

