Molecular mechanism of insulin-induced degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
- PMID: 11809794
- PMCID: PMC134643
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.22.4.1016-1026.2002
Molecular mechanism of insulin-induced degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
Abstract
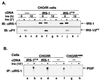
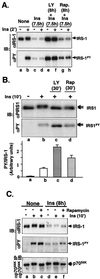
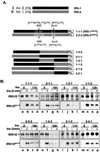
Insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) plays an important role in the insulin signaling cascade. In vitro and in vivo studies from many investigators have suggested that lowering of IRS-1 cellular levels may be a mechanism of disordered insulin action (so-called insulin resistance). We previously reported that the protein levels of IRS-1 were selectively regulated by a proteasome degradation pathway in CHO/IR/IRS-1 cells and 3T3-L1 adipocytes during prolonged insulin exposure, whereas IRS-2 was unaffected. We have now studied the signaling events that are involved in activation of the IRS-1 proteasome degradation pathway. Additionally, we have addressed structural elements in IRS-1 versus IRS-2 that are required for its specific proteasome degradation. Using ts20 cells, which express a temperature-sensitive mutant of ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1, ubiquitination of IRS-1 was shown to be a prerequisite for insulin-induced IRS-1 proteasome degradation. Using IRS-1/IRS-2 chimeric proteins, the N-terminal region of IRS-1 including the PH and PTB domains was identified as essential for targeting IRS-1 to the ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is necessary but not sufficient for activating and sustaining the IRS-1 ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway. In contrast, activation of mTOR is not required for IRS-1 degradation in CHO/IR cells. Thus, our data provide insight into the molecular mechanism of insulin-induced activation of the IRS-1 ubiquitin-proteasome degradation pathway.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A rapamycin-sensitive pathway down-regulates insulin signaling via phosphorylation and proteasomal degradation of insulin receptor substrate-1.Mol Endocrinol. 2000 Jun;14(6):783-94. doi: 10.1210/mend.14.6.0446. Mol Endocrinol. 2000. PMID: 10847581
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway regulates insulin signaling via subcellular redistribution of insulin receptor substrate 1 and integrates nutritional signals and metabolic signals of insulin.Mol Cell Biol. 2001 Aug;21(15):5050-62. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.15.5050-5062.2001. Mol Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11438661 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling by proteasome-mediated degradation of insulin receptor substrate-2.J Biol Chem. 2001 Oct 26;276(43):40362-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105332200. Epub 2001 Aug 23. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11546773
-
IRS-1 regulation in health and disease.IUBMB Life. 2003 Jul;55(7):367-74. doi: 10.1080/1521654031000138569. IUBMB Life. 2003. PMID: 14584587 Review.
-
Current Studies on Molecular Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance.J Diabetes Res. 2022 Dec 23;2022:1863429. doi: 10.1155/2022/1863429. eCollection 2022. J Diabetes Res. 2022. PMID: 36589630 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mTOR in the Development of Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk Factors.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 14;25(20):11023. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011023. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Obesity-Related Lipotoxicity and Clinical Perspective.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:131-166. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287851 Review.
-
Genetic Underpinnings of Fasting and Oral Glucose-stimulated Based Insulin Sensitivity Indices.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Oct 15;109(11):2754-2763. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae275. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38635292 Free PMC article.
-
Human cytomegalovirus attenuates AKT activity by destabilizing insulin receptor substrate proteins.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Apr 17:2023.04.17.537203. doi: 10.1101/2023.04.17.537203. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Virol. 2023 Oct 31;97(10):e0056323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00563-23. PMID: 37131605 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics Reveal the Mechanism of GuaLouQuMaiWan in Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Its Active Small Molecular Compound.J Diabetes Res. 2022 Oct 6;2022:2736504. doi: 10.1155/2022/2736504. eCollection 2022. J Diabetes Res. 2022. PMID: 36248223 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anai, M., M. Funaki, T. Ogihara, J. Terasaki, K. Inukai, H. Katagiri, Y. Fukushima, Y. Yazaki, M. Kikuchi, Y. Oka, and T. Asano. 1998. Altered expression levels and impaired steps in the pathway to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation via insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 in Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes 47:13-23. - PubMed
-
- Araki, E., M. A. Lipes, M. E. Patti, J. C. Bruning, B. Haag, 3rd, R. S. Johnson, and C. R. Kahn. 1994. Alternative pathway of insulin signalling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature 372:186-190. - PubMed
-
- Backer, J. M., M. G. Myers, Jr., X. J. Sun, D. J. Chin, S. E. Shoelson, M. Miralpeix, and M. F. White. 1993. Association of IRS-1 with the insulin receptor and the phosphatidylinositol 3"-kinase. Formation of binary and ternary signaling complexes in intact cells. J. Biol. Chem. 268:8204-8212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
