Rac1 mediates STAT3 activation by autocrine IL-6
- PMID: 11470914
- PMCID: PMC55365
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.161281298
Rac1 mediates STAT3 activation by autocrine IL-6
Abstract
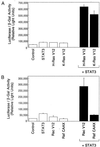
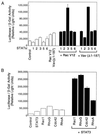
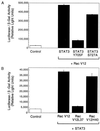
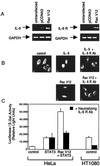
The activity of the small GTPase, Rac1, plays a role in various cellular processes including cytoskeletal rearrangement, gene transcription, and malignant transformation. In this report constitutively active Rac1 (Rac V12) is shown to stimulate the activation of STAT3, a member of the family of signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs). The activity of Rac1 leads to STAT3 translocation to the nucleus coincident with STAT3-dependent gene expression. The expression of Vav (Delta1-187), a constitutively active guanine nucleotide exchange factor for the Rho GTPases, or activated forms of Ras or Rho family members, leads to STAT3-specific activation. The activation of STAT3 requires tyrosine phosphorylation at residue 705, but is not dependent on phosphorylation of Ser-727. Our studies indicate that Rac1 induces STAT3 activation through an indirect mechanism that involves the autocrine production and action of IL-6, a known mediator of STAT3 response. Rac V12 expression results in the induction of the IL-6 and IL-6 receptor genes and neutralizing antibodies directed against the IL-6 receptor block Rac1-induced STAT3 activation. Furthermore, inhibition of the nuclear factor-kappaB activation or disruption of IL-6-mediated signaling through the expression of IkappaBalpha S32AS36A and suppressor of cytokine signaling 3, respectively, blocks Rac1-induced STAT3 activation. These findings elucidate a mechanism dependent on the induction of an autocrine IL-6 activation loop through which Rac1 mediates STAT3 activation establishing a link between oncogenic GTPase activity and Janus kinase/STAT signaling.
Figures
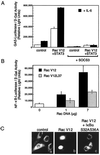
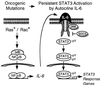
Similar articles
-
Rho family GTPases are required for activation of Jak/STAT signaling by G protein-coupled receptors.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(4):1316-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1316-1333.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12556491 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1 promotes chondrogenesis by regulating STAT3 signaling pathway.Cell Biol Int. 2016 Sep;40(9):976-83. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10635. Epub 2016 Jun 28. Cell Biol Int. 2016. PMID: 27306109
-
Activated Rac1 requires gp130 for Stat3 activation, cell proliferation and migration.Exp Cell Res. 2010 Mar 10;316(5):875-86. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.10.017. Epub 2009 Oct 21. Exp Cell Res. 2010. PMID: 19852956
-
Activation of STAT transcription factors by the Rho-family GTPases.Biochem Soc Trans. 2020 Oct 30;48(5):2213-2227. doi: 10.1042/BST20200468. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020. PMID: 32915198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The R(h)oads to Stat3: Stat3 activation by the Rho GTPases.Exp Cell Res. 2011 Aug 1;317(13):1787-95. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.05.008. Epub 2011 May 18. Exp Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21619876 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Hyper-IgE Syndromes: Lessons in Nature, From Bench to Bedside.World Allergy Organ J. 2012 Jul;5(7):79-87. doi: 10.1097/WOX.0b013e31825a73b2. World Allergy Organ J. 2012. PMID: 23283142 Free PMC article.
-
Rho family GTPases are required for activation of Jak/STAT signaling by G protein-coupled receptors.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;23(4):1316-33. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.4.1316-1333.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12556491 Free PMC article.
-
Autocrine STAT3 activation in HPV positive cervical cancer through a virus-driven Rac1-NFκB-IL-6 signalling axis.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jun 21;15(6):e1007835. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007835. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31226168 Free PMC article.
-
Differential implication of proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 in the development of cephalic versus extracephalic neuropathic pain in rats.J Neurosci. 2008 Aug 20;28(34):8489-501. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2552-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18716207 Free PMC article.
-
Active RAC1 Promotes Tumorigenic Phenotypes and Therapy Resistance in Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 11;12(6):1541. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061541. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Darnell J E., Jr Science. 1997;277:1630–1635. - PubMed
-
- Schindler C, Darnell J E., Jr Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:621–651. - PubMed
-
- Ihle J N. Nature (London) 1995;377:591–594. - PubMed
-
- Leonard W J, O'Shea J J. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:293–322. - PubMed
-
- Stark G R, Kerr I M, Williams B R, Silverman R H, Schreiber R D. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–264. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

