Vitamin D(3) promotes the differentiation of colon carcinoma cells by the induction of E-cadherin and the inhibition of beta-catenin signaling
- PMID: 11470825
- PMCID: PMC2150773
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200102028
Vitamin D(3) promotes the differentiation of colon carcinoma cells by the induction of E-cadherin and the inhibition of beta-catenin signaling
Abstract
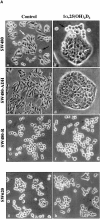
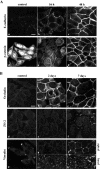
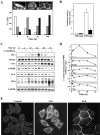
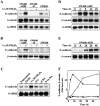
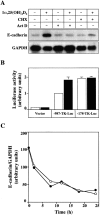
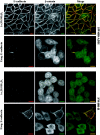
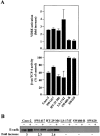
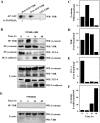
The beta-catenin signaling pathway is deregulated in nearly all colon cancers. Nonhypercalcemic vitamin D3 (1alpha,25-dehydroxyvitamin D(3)) analogues are candidate drugs to treat this neoplasia. We show that these compounds promote the differentiation of human colon carcinoma SW480 cells expressing vitamin D receptors (VDRs) (SW480-ADH) but not that of a malignant subline (SW480-R) or metastasic derivative (SW620) cells lacking VDR. 1alpha,25(OH)2D(3) induced the expression of E-cadherin and other adhesion proteins (occludin, Zonula occludens [ZO]-1, ZO-2, vinculin) and promoted the translocation of beta-catenin, plakoglobin, and ZO-1 from the nucleus to the plasma membrane. Ligand-activated VDR competed with T cell transcription factor (TCF)-4 for beta-catenin binding. Accordingly, 1alpha,25(OH)2D(3) repressed beta-catenin-TCF-4 transcriptional activity. Moreover, VDR activity was enhanced by ectopic beta-catenin and reduced by TCF-4. Also, 1alpha,25(OH)2D(3) inhibited expression of beta-catenin-TCF-4-responsive genes, c-myc, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta, Tcf-1, and CD44, whereas it induced expression of ZO-1. Our results show that 1alpha,25(OH)2D(3) induces E-cadherin and modulates beta-catenin-TCF-4 target genes in a manner opposite to that of beta-catenin, promoting the differentiation of colon carcinoma cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is abrogated by Snail1 in human colon cancer cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007 Mar;14(1):141-51. doi: 10.1677/ERC-06-0028. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17395983
-
1alpha,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 regulates the expression of Id1 and Id2 genes and the angiogenic phenotype of human colon carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2005 Sep 29;24(43):6533-44. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208801. Oncogene. 2005. PMID: 16007183
-
Nitric oxide-donating aspirin inhibits beta-catenin/T cell factor (TCF) signaling in SW480 colon cancer cells by disrupting the nuclear beta-catenin-TCF association.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Oct 28;100(22):12584-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2134840100. Epub 2003 Oct 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 14566053 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in colon cancer: role and regulation of DICKKOPF genes.Anticancer Res. 2008 Sep-Oct;28(5A):2613-23. Anticancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19035286 Review.
-
The effect of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 treatment on the mRNA levels of β catenin target genes in mice with colonic inactivation of both APC alleles.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;148:103-10. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Jan 15. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25597951 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin D3-dependent VDR signaling delays ron-mediated breast tumorigenesis through suppression of β-catenin activity.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 30;6(18):16304-20. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4059. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26008979 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D(3) and bladder cancer risk according to tumor stage and FGFR3 status: a mechanism-based epidemiological study.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012 Dec 19;104(24):1897-904. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djs444. Epub 2012 Oct 29. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012. PMID: 23108201 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of novel vitamin D receptor interacting proteins that modulate 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 signaling.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Oct;132(1-2):147-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.05.001. Epub 2012 May 14. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22626544 Free PMC article.
-
CYP24A1 and CYP27B1 Polymorphisms, Concentrations of Vitamin D Metabolites, and Odds of Colorectal Adenoma Recurrence.Nutr Cancer. 2015;67(7):1131-41. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2015.1068818. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Nutr Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26241700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of common gene variants in vitamin D modulating genes and colon cancer recurrence.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013 Sep;139(9):1457-64. doi: 10.1007/s00432-013-1461-x. Epub 2013 Jun 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23793229
References
-
- Akhter, J., X. Chen, P. Bowrey, E.J. Bolton, and D.L. Morris. 1997. Vitamin D3 analog, EB1089, inhibits growth of subcutaneous xenographs of the human colon cancer cell line, LoVo, in nude mouse model. Dis. Colon Rec. 40:317–321. - PubMed
-
- Batlle, E., E. Sancho, C. Francí, D. Domínguez, M. Monfar, J. Baulida, and A. García de Herreros. 2000. The transcription factor Snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumor cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2:84–89. - PubMed
-
- Behrens, J., J.P. von Kries, M. Külh, L. Bruhn, D. Wedlich, R. Grosschedl, and W. Birchmeier. 1996. Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcriptional factor LEF-1. Nature. 382:638–642. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

