A viral protein that selectively downregulates ICAM-1 and B7-2 and modulates T cell costimulation
- PMID: 11413168
- PMCID: PMC200195
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI12432
A viral protein that selectively downregulates ICAM-1 and B7-2 and modulates T cell costimulation
Abstract
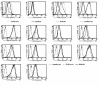
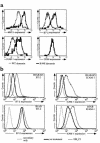
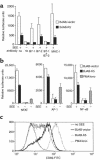
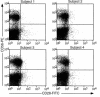
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated (KS-associated) herpesvirus (KSHV) is a B-lymphotropic agent linked to AIDS-related lymphoproliferative disorders and KS. We and others have earlier identified two viral genes, K3 and K5, that encode endoplasmic reticulum proteins that downregulate surface MHC-I chains by enhancing their endocytosis. Here we have examined the ability of these proteins to influence the disposition of other host surface proteins implicated in immune recognition and activation. We report that K5, but not K3, expression in BJAB cells dramatically reduces ICAM-1 and B7-2 surface expression; B7-1 expression is unaffected. This K5-induced reduction can be reversed by coexpression of a dominant negative mutant of dynamin, indicating that the loss of ICAM and B7-2 surface expression is due to their enhanced endocytosis. This downregulation is functionally significant, because K5-transfected B cells show substantial impairment in their ability to induce T cell activation. K5 is thus the first example of a viral modulator of immunological synapse formation and T cell costimulation. We propose that its expression reduces T cell responses to KSHV-infected B cells early in infection, thereby diminishing antiviral cytokine release and the production of stimulatory signals for CTL generation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K5 protein.Immunity. 2000 Sep;13(3):365-74. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)00036-4. Immunity. 2000. PMID: 11021534
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 proteins block distinct steps in transendothelial migration of effector memory CD4+ T cells by targeting different endothelial proteins.J Immunol. 2010 May 1;184(9):5186-92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0902938. Epub 2010 Mar 31. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20357254 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 ubiquitin E3 ligases have stage-specific immune evasion roles during lytic replication.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9335-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00873-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899205 Free PMC article.
-
T Cell Activation Pathways: B7, LFA-3, and ICAM-1 Shape Unique T Cell Profiles.Crit Rev Immunol. 2017;37(2-6):463-481. doi: 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.v37.i2-6.130. Crit Rev Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29773030 Review.
-
The expression of LFA-1, ICAM-1, CD80 and CD86 molecules in lupus patients: implication for immunotherapy.Intern Med. 1999 Feb;38(2):175-7. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.38.175. Intern Med. 1999. PMID: 10225679 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Lytic KSHV Infection in Human Endothelial Cells Reveals Targets of Viral Immune Modulation.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108249. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108249. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33053346 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Immune System by Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus: Lessons from Viral Evasion Strategies.Front Microbiol. 2012 Mar 5;3:44. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00044. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22403573 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 proteins down regulate both DC-SIGN and DC-SIGNR.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e58056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058056. Epub 2013 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23460925 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus K5 removes CD31/PECAM from endothelial cells.Blood. 2006 Sep 15;108(6):1932-40. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-11-4404. Epub 2006 Apr 6. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16601245 Free PMC article.
-
[Humanes herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) and Kaposi sarcoma].Hautarzt. 2008 Jan;59(1):18-25. doi: 10.1007/s00105-007-1445-3. Hautarzt. 2008. PMID: 18209996 Review. German.
References
-
- Unanue ER. Antigen-presenting function of the macrophage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:395–428. - PubMed
-
- Iezzi G, Karjalainen K, Lanzavecchia A. The duration of antigenic stimulation determines the fate of naive and effector T cells. Immunity. 1998;8:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Demotz S, Grey HM, Sette A. The minimal number of class II MHC-antigen complexes needed for T cell activation. Science. 1990;249:1028–1030. - PubMed
-
- Harding CV, Unanue ER. Quantitation of antigen-presenting cell MHC class II/peptide complexes necessary for T-cell stimulation. Nature. 1990;346:574–576. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

