Major histocompatibility complex class I-recognizing receptors are disease risk genes in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 11369787
- PMCID: PMC2193323
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.10.1159
Major histocompatibility complex class I-recognizing receptors are disease risk genes in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
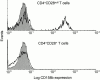
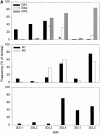
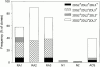
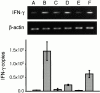
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a heterogeneous syndrome of which a subset of patients develops vascular inflammation. The genetic determinants that confer risk for rheumatoid vasculitis are not known, but patients with vascular complications are known to have an expansion of CD4(+)CD28(null) T cells, a cell population potentially involved in endothelial damage. CD4(+)CD28(null) T cell clones isolated from RA patients with vasculitis were found to express killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) with the stimulatory KIR2DS2 often present in the absence of opposing inhibitory receptors with related specificities. To test the hypothesis that the KIR2DS2 gene is involved in the development of vasculitis, association studies were performed. The KIR2DS2 gene was significantly enriched among patients with rheumatoid vasculitis compared with normal individuals (odds ratio 5.56, P = 0.001) and patients with RA but no vasculitis (odds ratio 7.96, P = 0.001). Also, the distribution of human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA)-C, the putative ligand for KIRs, was significantly different in patients with rheumatoid vasculitis in comparison with the control populations. These data suggest that HLA class I-recognizing receptors and HLA class I genes are genetic risk determinants that modulate the pattern of RA expression. Specifically, KIR2DS2 in conjunction with the appropriate HLA-C ligand may have a role in vascular damage by regulating CD4(+)CD28(null) T cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interleukin-15-induced maturation of human natural killer cells from early thymic precursors: selective expression of CD94/NKG2-A as the only HLA class I-specific inhibitory receptor.Eur J Immunol. 1997 Jun;27(6):1374-80. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830270612. Eur J Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9209487
-
Killer cell activating receptors function as costimulatory molecules on CD4+CD28null T cells clonally expanded in rheumatoid arthritis.J Immunol. 2000 Jul 15;165(2):1138-45. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.2.1138. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10878393
-
Regulation of the natural killer cell receptor repertoire.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:291-330. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.19.1.291. Annu Rev Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11244039 Review.
-
Natural killer cell recognition of HLA class I molecules.Rev Immunogenet. 2000;2(3):433-48. Rev Immunogenet. 2000. PMID: 11256749 Review.
-
Direct binding of purified HLA class I antigens by soluble NKG2/CD94 C-type lectins from natural killer cells.Scand J Immunol. 1999 May;49(5):459-65. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.1999.00566.x. Scand J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10320637
Cited by
-
Exploiting Gene-Expression Deconvolution to Probe the Genetics of the Immune System.PLoS Comput Biol. 2016 Apr 1;12(4):e1004856. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004856. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2016. PMID: 27035464 Free PMC article.
-
The story of CD4+ CD28- T cells revisited: solved or still ongoing?J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:348746. doi: 10.1155/2015/348746. Epub 2015 Mar 5. J Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25834833 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic (KIR, HLA-C) and Some Clinical Parameters Influencing the Level of Liver Enzymes and Early Virologic Response in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016 Feb;64(1):65-73. doi: 10.1007/s00005-015-0350-1. Epub 2015 Jul 24. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016. PMID: 26206121 Free PMC article.
-
Association of NKG2D gene variants with susceptibility and severity of rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Exp Immunol. 2017 Mar;187(3):369-375. doi: 10.1111/cei.12891. Epub 2016 Dec 18. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27783394 Free PMC article.
-
Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptors and Their HLA Ligands are Related with the Immunopathology of Chagas Disease.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015 May 15;9(5):e0003753. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003753. eCollection 2015 May. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2015. PMID: 25978047 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ollier W., Winchester R. The Germline and somatic genetic basis for rheumatoid arthritis. In: Theofilopoulos A.N., editor. Current Directions in Autoimmunity. S. Karger AG; Basel, Switzerland: 1999. pp. 166–193. - PubMed
-
- Seldin M.F., Amos C.I., Ward R., Gregersen P.K. The genetics revolution and the assault on rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1071–1079. - PubMed
-
- Weyand C.M., Goronzy J.J. Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1997;81:29–55. - PubMed
-
- Nepom G.T. Major histocompatibility complex-directed susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Adv. Immunol. 1998;68:315–332. - PubMed
-
- Weyand C.M., Klimiuk P.A., Goronzy J.J. Heterogeneity of rheumatoid arthritisfrom phenotypes to genotypes. Springer Semin. Immunopathol. 1998;20:5–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

