Autostimulation of the Epstein-Barr virus BRLF1 promoter is mediated through consensus Sp1 and Sp3 binding sites
- PMID: 11333906
- PMCID: PMC114930
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.11.5240-5251.2001
Autostimulation of the Epstein-Barr virus BRLF1 promoter is mediated through consensus Sp1 and Sp3 binding sites
Abstract
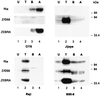
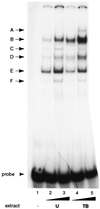
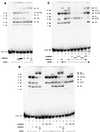
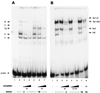
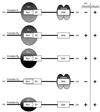
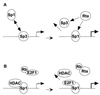
As an essential step in the lytic cascade, the Rta homologues of gammaherpesviruses all activate their own expression. Consistent with this biologic function, the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) Rta protein powerfully stimulates the promoter of its own gene, Rp, in EBV-positive B cells in transient-transfection reporter-based assays. We analyzed the activity of RpCAT in response to Rta by deletional and site-directed mutagenesis. Two cognate Sp1 binding sites located at -279 and -45 relative to the transcriptional start site proved crucial for Rta-mediated activation. Previously described binding sites for the cellular transcription factor Zif268 and the viral transactivator ZEBRA were found to be dispensable for activation of RpCAT by Rta. Gel shift analysis, using extracts of B cells in latency or induced into the lytic cycle, identified Sp1 and Sp3 as the predominant cellular proteins bound to Rp near -45. During the lytic cycle, ZEBRA bound Rp near the Sp1/Sp3 site. The binding of Sp1 and Sp3 to Rp correlated with the reporter activities in the mutagenesis study, establishing a direct link between transcriptional activation of Rp by Rta and DNA binding by Sp1 and/or Sp3. The relative abundance or functional state of the cellular Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors may be altered in response to stimuli that induce the BRLF1 promoter and thereby contribute to the activation of the viral lytic cycle.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synergistic autoactivation of the Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early BRLF1 promoter by Rta and Zta.Virology. 2003 Jun 5;310(2):199-206. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(03)00145-4. Virology. 2003. PMID: 12781707
-
Transcriptional activation of Epstein-Barr virus BRLF1 by USF1 and Rta.J Gen Virol. 2015 Sep;96(9):2855-2866. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.000230. Epub 2015 Jun 30. J Gen Virol. 2015. PMID: 26297580
-
Binding of the ubiquitous cellular transcription factors Sp1 and Sp3 to the ZI domains in the Epstein-Barr virus lytic switch BZLF1 gene promoter.Virology. 1997 Feb 3;228(1):11-8. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.8371. Virology. 1997. PMID: 9024805
-
The Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early promoter BRLF1 can be activated by the cellular Sp1 transcription factor.J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7282-92. doi: 10.1128/JVI.66.12.7282-7292.1992. J Virol. 1992. PMID: 1331521 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Properties of the EBV ZEBRA Protein.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 5;12(6):1479. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061479. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32517128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Sp1 response element in the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus open reading frame 50 promoter mediates lytic cycle induction by butyrate.J Virol. 2005 Feb;79(3):1397-408. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.3.1397-1408.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15650166 Free PMC article.
-
Meta-analysis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma microarray data explores mechanism of EBV-regulated neoplastic transformation.BMC Genomics. 2008 Jul 7;9:322. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-322. BMC Genomics. 2008. PMID: 18605998 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation-Dependent LMP1 Expression Is Required for Efficient Lytic Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation in Epithelial Cells.J Virol. 2017 Mar 29;91(8):e02438-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02438-16. Print 2017 Apr 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28179525 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the TSG101 gene in Epstein-Barr virus late gene transcription.J Virol. 2007 Mar;81(5):2459-71. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02289-06. Epub 2006 Dec 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17182691 Free PMC article.
-
EBV and Apoptosis: The Viral Master Regulator of Cell Fate?Viruses. 2017 Nov 13;9(11):339. doi: 10.3390/v9110339. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29137176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apt D, Watts R M, Suske G, Bernard H U. High Sp1/Sp3 ratios in epithelial cells during epithelial differentiation and cellular transformation correlate with the activation of the HPV-16 promoter. Virology. 1996;224:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong S A, Barry D A, Leggett R W, Mueller C R. Casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of the C terminus of Sp1 decreases its DNA binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:13489–13495. - PubMed
-
- Babcock G J, Decker L L, Volk M, Thorley-Lawson D A. EBV persistence in memory B cells in vivo. Immunity. 1998;9:395–404. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

