Downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 proteins
- PMID: 10799607
- PMCID: PMC110885
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.11.5300-5309.2000
Downregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 proteins
Abstract
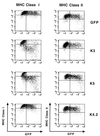
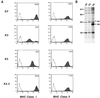
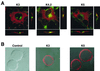
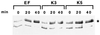
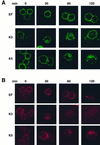
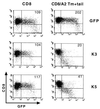
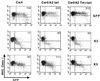
The T-cell-mediated immune response plays a central role in the defense against intracellular pathogens. To avoid this immune response, viruses have evolved elaborate mechanisms that target and modulate many different aspects of the host's immune system. A target common to many of these viruses is the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) encodes K3 and K5 zinc finger membrane proteins which remove MHC class I molecules from the cell surface. K3 and K5 exhibit 40% amino acid identity to each other and localize primarily near the plasma membrane. While K3 and K5 dramatically downregulated class I molecules, they displayed different specificities in downregulation of HLA allotypes. K5 significantly downregulated HLA-A and -B and downregulated HLA-C only weakly, but not HLA-E, whereas K3 downregulated all four HLA allotypes. This selective downregulation of HLA allotypes by K5 was partly due to differences in amino acid sequences in their transmembrane regions. Biochemical analyses demonstrated that while K3 and K5 did not affect expression and intracellular transport of class I molecules, their expression induced rapid endocytosis of the molecules. These results demonstrate that KSHV has evolved a novel immune evasion mechanism by harboring similar but distinct genes, K3 and K5, which target MHC class I molecules in different ways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K3 and K5 ubiquitin E3 ligases have stage-specific immune evasion roles during lytic replication.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):9335-49. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00873-14. Epub 2014 Jun 4. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24899205 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ubiquitin ligases downregulate cell surface expression of l-selectin.J Gen Virol. 2021 Nov;102(11). doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001678. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 34726593
-
Immune evasion by a novel family of viral PHD/LAP-finger proteins of gamma-2 herpesviruses and poxviruses.Virus Res. 2002 Sep;88(1-2):55-69. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(02)00120-x. Virus Res. 2002. PMID: 12297327 Review.
-
Major histocompatibility complex class I molecules are down-regulated at the cell surface by the K5 protein encoded by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus-8.J Gen Virol. 2001 May;82(Pt 5):1175-1180. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-82-5-1175. J Gen Virol. 2001. PMID: 11297692
-
[The HIV nef and the Kaposi-sarcoma-associated virus K3/K5 proteins: "parasites"of the endocytosis pathway].Med Sci (Paris). 2003 Jan;19(1):100-6. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2003191100. Med Sci (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12836198 Review. French.
Cited by
-
EBV BILF1 evolved to downregulate cell surface display of a wide range of HLA class I molecules through their cytoplasmic tail.J Immunol. 2013 Feb 15;190(4):1672-84. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102462. Epub 2013 Jan 11. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23315076 Free PMC article.
-
AKTivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by KSHV.Front Immunol. 2013 Jan 7;3:401. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00401. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23316192 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded viral IRF3 modulates major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) antigen presentation through MHC-II transactivator-dependent and -independent mechanisms: implications for oncogenesis.J Virol. 2013 May;87(10):5340-50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00250-13. Epub 2013 Feb 28. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23449805 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1 mediates functional exhaustion of activated NK cells in patients with Kaposi sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 8;7(45):72961-72977. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12150. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27662664 Free PMC article.
-
Newly discovered viral E3 ligase pK3 induces endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation of class I major histocompatibility proteins and their membrane-bound chaperones.J Biol Chem. 2012 Apr 27;287(18):14467-79. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.325340. Epub 2012 Mar 8. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22403403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahn K, Gruhler A, Galocha B, Jones T R, Wiertz E J, Ploegh H L, Peterson P A, Yang Y, Fruh K. The ER-luminal domain of the HCMV glycoprotein US6 inhibits peptide translocation by TAP. Immunity. 1997;6:613–621. - PubMed
-
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore P S, Said J W, Knowles D M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin M S, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles D M, Moore P S. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–1869. - PubMed
-
- Cohen G B, Gandhi R T, Davis D M, Mandelboim O, Chen B K, Strominger J L, Baltimore D. The selective downregulation of class I major histocompatibility complex proteins by HIV-1 protects HIV-infected cells from NK cells. Immunity. 1999;10:661–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

