Pharmacological chaperones rescue cell-surface expression and function of misfolded V2 vasopressin receptor mutants
- PMID: 10749568
- PMCID: PMC377482
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI8688
Pharmacological chaperones rescue cell-surface expression and function of misfolded V2 vasopressin receptor mutants
Abstract
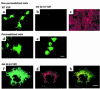
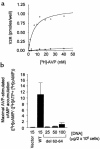
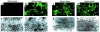
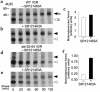
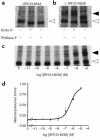
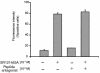
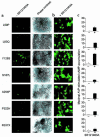
Over 150 mutations within the coding sequence of the V2 vasopressin receptor (V2R) gene are known to cause nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI). A large number of these mutant receptors fail to fold properly and therefore are not routed to the cell surface. Here we show that selective, nonpeptidic V2R antagonists dramatically increase cell-surface expression and rescue the function of 8 mutant NDI-V2Rs by promoting their proper folding and maturation. A cell-impermeant V2R antagonist could not mimic these effects and was unable to block the rescue mediated by a permeant agent, indicating that the nonpeptidic antagonists act intracellularly, presumably by binding to and stabilizing partially folded mutants. In addition to opening new therapeutic avenues for NDI patients, these data demonstrate that by binding to newly synthesized mutant receptors, small ligands can act as pharmacological chaperones, promoting the proper folding and maturation of receptors and their targeting to the cell surface.
Figures
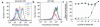

Comment in
-
Antagonists to the rescue.J Clin Invest. 2000 Apr;105(7):853-4. doi: 10.1172/JCI9158. J Clin Invest. 2000. PMID: 10749562 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Functional rescue of vasopressin V2 receptor mutants in MDCK cells by pharmacochaperones: relevance to therapy of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):F253-60. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00247.2006. Epub 2006 Aug 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007. PMID: 16926443
-
Molecular genetic study of congenital nephrogenic diabetes insipidus and rescue of mutant vasopressin V2 receptor by chemical chaperones.Nephrology (Carlton). 2007 Apr;12(2):113-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2006.00759.x. Nephrology (Carlton). 2007. PMID: 17371330
-
Characterization of vasopressin V2 receptor mutants in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in a polarized cell model.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005 Aug;289(2):F265-72. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00404.2004. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005. PMID: 16006591
-
Potential of nonpeptide (ant)agonists to rescue vasopressin V2 receptor mutants for the treatment of X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus.J Neuroendocrinol. 2010 May;22(5):393-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2010.01983.x. Epub 2010 Feb 12. J Neuroendocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20163515 Review.
-
Pharmacological chaperones in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: possibilities for clinical application.BioDrugs. 2007;21(3):157-66. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200721030-00003. BioDrugs. 2007. PMID: 17516711 Review.
Cited by
-
Laminin β2 gene missense mutation produces endoplasmic reticulum stress in podocytes.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013 Jul;24(8):1223-33. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2012121149. Epub 2013 May 30. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23723427 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological folding chaperones act as allosteric ligands of Frizzled4.Nat Chem Biol. 2015 Apr;11(4):280-6. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1770. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Nat Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25751279
-
Ligands for Melanocortin Receptors: Beyond Melanocyte-Stimulating Hormones and Adrenocorticotropin.Biomolecules. 2022 Oct 1;12(10):1407. doi: 10.3390/biom12101407. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Potential Pharmacoperones Capable of Rescuing the Functionality of Misfolded Vasopressin 2 Receptor Involved in Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus.J Biomol Screen. 2016 Sep;21(8):824-31. doi: 10.1177/1087057116653925. Epub 2016 Jun 8. J Biomol Screen. 2016. PMID: 27280550 Free PMC article.
-
Assay strategies for identification of therapeutic leads that target protein trafficking.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015 Aug;36(8):498-505. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 Jun 8. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26067100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Knoers NV, Monnens LL. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Semin Nephrol. 1999;19:344–352. - PubMed
-
- Bichet, D.G., and Fujiwara, T.M. 2000. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. In The metabolic and molecular basis of inherited disease. 8th edition. C.R. Scriver et al., editors. McGraw-Hill. New York, NY. In press.
-
- Schülein R, Rutz C, Rosenthal W. Membrane targeting and determination of transmembrane topology of the human vasopressin V2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28844–28852. - PubMed
-
- Wenkert D, et al. Functional characterization of five V2 vasopressin receptor gene mutations. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1996;124:43–50. - PubMed
-
- Sadeghi HM, Innamorati G, Birnbaumer M. An X-linked NDI mutation reveals a requirement for cell surface V2R expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:706–713. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

