Structure and coding content of CST (BART) family RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus
- PMID: 10708423
- PMCID: PMC111807
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.74.7.3082-3092.2000
Structure and coding content of CST (BART) family RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus
Abstract
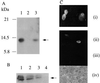
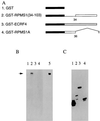
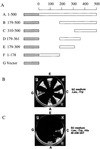
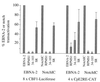
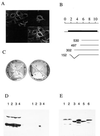
CST (BART BARF0) family viral RNAs are expressed in several types of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection, including EBV-associated cancers. Many different spliced forms of these RNAs have been described; here we have clarified the structures of some of the more abundant splicing patterns. We report the first cDNAs representing a full-length CST mRNA from a clone library and further characterize the transcription start. The relative abundance of splicing patterns and genomic analysis of the open reading frames (ORFs) suggest that, in addition to the much studied BARF0 ORF, there may be important products made from some of the upstream ORFs in the CST RNAs. Potential biological functions are identified for two of these. The product of the RPMS1 ORF is shown to be a nuclear protein that can bind to the CBF1 component of Notch signal transduction. RPMS1 can inhibit the transcription activation induced through CBF1 by NotchIC or EBNA-2. The protein product of another CST ORF, A73, is shown to be a cytoplasmic protein which can interact with the cell RACK1 protein. Since RACK1 modulates signaling from protein kinase C and Src tyrosine kinases, the results suggest a possible role for CST products in growth control, perhaps consistent with the abundant transcription of CST RNAs in cancers such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Figures

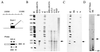


Similar articles
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Qualitative evidence synthesis informing our understanding of people's perceptions and experiences of targeted digital communication.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Oct 23;10(10):ED000141. doi: 10.1002/14651858.ED000141. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31643081 Free PMC article.
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
"It Is a Big Spider Web of Things": Sensory Experiences of Autistic Adults in Public Spaces.Autism Adulthood. 2023 Dec 1;5(4):411-422. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0024. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Autism Adulthood. 2023. PMID: 38116051 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Surgical and Nonsurgical Aesthetic Procedures: A 14-Year Analysis of the International Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery-ISAPS.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Oct;48(20):4217-4227. doi: 10.1007/s00266-024-04260-2. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 39103642 Review.
Cited by
-
Epstein-Barr virus microRNAs are evolutionarily conserved and differentially expressed.PLoS Pathog. 2006 Mar;2(3):e23. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0020023. Epub 2006 Mar 24. PLoS Pathog. 2006. PMID: 16557291 Free PMC article.
-
Aid or Antagonize: Nuclear Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate Host Responses and Outcomes of Viral Infections.Cells. 2023 Mar 23;12(7):987. doi: 10.3390/cells12070987. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EBV and Apoptosis: The Viral Master Regulator of Cell Fate?Viruses. 2017 Nov 13;9(11):339. doi: 10.3390/v9110339. Viruses. 2017. PMID: 29137176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression of BamHI-A Rightward Transcripts in Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancers.Cancer Res Treat. 2011 Dec;43(4):250-4. doi: 10.4143/crt.2011.43.4.250. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Cancer Res Treat. 2011. PMID: 22247711 Free PMC article.
-
Clustered microRNAs of the Epstein-Barr virus cooperatively downregulate an epithelial cell-specific metastasis suppressor.J Virol. 2015 Mar;89(5):2684-97. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03189-14. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25520514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baer R, Bankier A T, Biggin M D, Deininger P L, Farrell P J, Gibson T J, Hatfull G, Hudson G S, Satchwell S C, Seguin C, Tuffnell P, Barrell B. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984;310:207–211. - PubMed
-
- Breeden L, Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. - PubMed
-
- Chen H, Smith P, Ambinder R F, Hayward S D. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus BamHI-A rightward transcripts in latently infected B cells from peripheral blood. Blood. 1999;93:3026–3032. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

