N-cadherin promotes motility in human breast cancer cells regardless of their E-cadherin expression
- PMID: 10545506
- PMCID: PMC2151177
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.147.3.631
N-cadherin promotes motility in human breast cancer cells regardless of their E-cadherin expression
Abstract
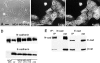
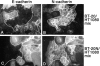
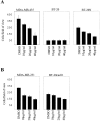
E-cadherin is a transmembrane glycoprotein that mediates calcium-dependent, homotypic cell-cell adhesion and plays a role in maintaining the normal phenotype of epithelial cells. Decreased expression of E-cadherin has been correlated with increased invasiveness of breast cancer. In other systems, inappropriate expression of a nonepithelial cadherin, such as N-cadherin, by an epithelial cell has been shown to downregulate E-cadherin expression and to contribute to a scattered phenotype. In this study, we explored the possibility that expression of nonepithelial cadherins may be correlated with increased motility and invasion in breast cancer cells. We show that N-cadherin promotes motility and invasion; that decreased expression of E-cadherin does not necessarily correlate with motility or invasion; that N-cadherin expression correlates both with invasion and motility, and likely plays a direct role in promoting motility; that forced expression of E-cadherin in invasive, N-cadherin-positive cells does not reduce their motility or invasive capacity; that forced expression of N-cadherin in noninvasive, E-cadherin-positive cells produces an invasive cell, even though these cells continue to express high levels of E-cadherin; that N-cadherin-dependent motility may be mediated by FGF receptor signaling; and that cadherin-11 promotes epithelial cell motility in a manner similar to N-cadherin.
Figures

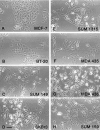
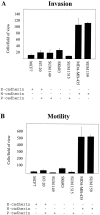
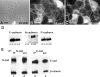
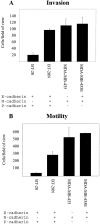

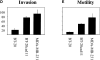
Similar articles
-
Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis.J Cell Biol. 2000 Feb 21;148(4):779-90. doi: 10.1083/jcb.148.4.779. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10684258 Free PMC article.
-
Alkyl-lysophospholipid 1-O-octadecyl-2-O-methyl- glycerophosphocholine induces invasion through episialin-mediated neutralization of E-cadherin in human mammary MCF-7 cells in vitro.Int J Cancer. 2001 May 15;92(4):527-36. doi: 10.1002/ijc.1216. Int J Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11304687
-
Expression of N-cadherin by human squamous carcinoma cells induces a scattered fibroblastic phenotype with disrupted cell-cell adhesion.J Cell Biol. 1996 Dec;135(6 Pt 1):1643-54. doi: 10.1083/jcb.135.6.1643. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8978829 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the E-cadherin/catenin complex in gastrointestinal cancer.Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1999 Oct-Dec;62(4):393-402. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 1999. PMID: 10692769 Review.
-
Downregulation in vivo of the invasion-suppressor molecule E-cadherin in experimental and clinical cancer.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994;24:63-80. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1994. PMID: 8983064 Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human lung cancer H460 cells via superoxide anion-dependent mechanism.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Jun 17;16:48. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0323-4. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 27330411 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Cadherins in Cancer-A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 15;21(20):7624. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207624. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33076339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-cadherin regulates mammary tumor cell migration through Akt3 suppression.Oncogene. 2013 Jan 24;32(4):422-30. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.65. Epub 2012 Mar 12. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 22410780 Free PMC article.
-
Lycopene Inhibits Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Promotes Apoptosis in Oral Cancer via PI3K/AKT/m-TOR Signal Pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Jun 24;14:2461-2471. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S251614. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32606612 Free PMC article.
-
N-cadherin and keratinocyte growth factor receptor mediate the functional interplay between Ki-RASG12V and p53V143A in promoting pancreatic cell migration, invasion, and tissue architecture disruption.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Jun;26(11):4185-200. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01055-05. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16705170 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aberle H., Butz S., Stappert J., Weissig H., Kemler R., Hoschuetzky H. Assembly of the cadherin–catenin complex in vitro with recombinant proteins. J. Cell Sci. 1994;107:3655–3663. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J., Weidner K.M., Frixen U.H., Schipper J.H., Sachs M., Arakaki N., Daikuhara Y., Birchmeier W. The role of E-cadherin and scatter factor in tumor invasion and cell motility. Exper. Suppl. 1991;59:109–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

