Bone morphogenetic proteins regulate the developmental program of human hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 10190905
- PMCID: PMC2193014
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1139
Bone morphogenetic proteins regulate the developmental program of human hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
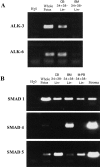
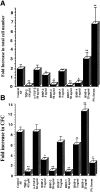
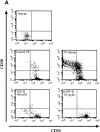
The identification of molecules that regulate human hematopoietic stem cells has focused mainly on cytokines, of which very few are known to act directly on stem cells. Recent studies in lower organisms and the mouse have suggested that bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) may play a critical role in the specification of hematopoietic tissue from the mesodermal germ layer. Here we report that BMPs regulate the proliferation and differentiation of highly purified primitive human hematopoietic cells from adult and neonatal sources. Populations of rare CD34(+)CD38(-)Lin- stem cells were isolated from human hematopoietic tissue and were found to express the BMP type I receptors activin-like kinase (ALK)-3 and ALK-6, and their downstream transducers SMAD-1, -4, and -5. Treatment of isolated stem cell populations with soluble BMP-2, -4, and -7 induced dose-dependent changes in proliferation, clonogenicity, cell surface phenotype, and multilineage repopulation capacity after transplantation in nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient (NOD/SCID) mice. Similar to transforming growth factor beta, treatment of purified cells with BMP-2 or -7 at high concentrations inhibited proliferation yet maintained the primitive CD34(+)CD38(-) phenotype and repopulation capacity. In contrast, low concentrations of BMP-4 induced proliferation and differentiation of CD34(+) CD38(-)Lin- cells, whereas at higher concentrations BMP-4 extended the length of time that repopulation capacity could be maintained in ex vivo culture, indicating a direct effect on stem cell survival. The discovery that BMPs are capable of regulating repopulating cells provides a new pathway for controlling human stem cell development and a powerful model system for studying the biological mechanism of BMP action using primary human cells.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
-
BMP-7 improved proliferation and hematopoietic reconstitution potential of ex vivo expanded cord blood-derived CD34(+) cells.Hum Cell. 2015 Jan;28(1):14-21. doi: 10.1007/s13577-014-0098-7. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Hum Cell. 2015. PMID: 25192984
-
Functional characterization of highly purified human hematopoietic repopulating cells isolated according to aldehyde dehydrogenase activity.Blood. 2004 Sep 15;104(6):1648-55. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-02-0448. Epub 2004 Jun 3. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15178579
-
Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-7 but not BMP-2 and BMP-4 improves maintenance of primitive peripheral blood-derived hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPC) cultured in serum-free medium supplemented with early acting cytokines.Cytokine. 2007 Dec;40(3):165-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2007.09.004. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Cytokine. 2007. PMID: 18029192
-
Characterization of human hematopoietic cells with short-lived in vivo repopulating activity.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001 Jun;938:63-70; discussion 70-1. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2001.tb03575.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001. PMID: 11458527 Review.
Cited by
-
Hyaluronan is required for generation of hematopoietic cells during differentiation of human embryonic stem cells.J Stem Cells. 2010;5(1):9-21. J Stem Cells. 2010. PMID: 20861924 Free PMC article.
-
BMP-6 inhibits growth of mature human B cells; induction of Smad phosphorylation and upregulation of Id1.BMC Immunol. 2005 May 9;6:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-6-9. BMC Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15877825 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons from the Niche for Generation and Expansion of Hematopoietic Stem Cells.Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2009 Winter;6(4):135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.ddstr.2009.06.003. Drug Discov Today Ther Strateg. 2009. PMID: 21212834 Free PMC article.
-
Tailbud-derived Bmp4 drives proliferation and inhibits maturation of zebrafish chordamesoderm.Development. 2008 Dec;135(23):3891-901. doi: 10.1242/dev.029264. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Development. 2008. PMID: 18948415 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative population genomic analysis uncovers novel genomic footprints and genes associated with small body size in Chinese pony.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jul 20;21(1):496. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-06887-2. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32689947 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Metcalf D. Hematopoietic regulators: redundancy or subtlety? . Blood. 1993;82:3515–3523. - PubMed
-
- Metcalf D. Lineage commitment and maturation in hematopoietic cells: the case for extrinsic regulation. Blood. 1998;92:345–347. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa M. Differentiation and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1993;81:2844–2853. - PubMed
-
- Huber TL, Zon LI. Transcriptional regulation of blood formation during Xenopusdevelopment. Semin Immunol. 1998;10:103–109. - PubMed
-
- Choi K, Kennedy M, Kazarov A, Papadimitriou JC, Keller G. A common precursor for hematopoietic and endothelial cells. Development (Camb) 1998;125:725–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

