Abstract
Plasmodium falciparum resistance to artemisinin derivatives in southeast Asia threatens malaria control and elimination activities worldwide. To monitor the spread of artemisinin resistance, a molecular marker is urgently needed. Here, using whole-genome sequencing of an artemisinin-resistant parasite line from Africa and clinical parasite isolates from Cambodia, we associate mutations in the PF3D7_1343700 kelch propeller domain (‘K13-propeller’) with artemisinin resistance in vitro and in vivo. Mutant K13-propeller alleles cluster in Cambodian provinces where resistance is prevalent, and the increasing frequency of a dominant mutant K13-propeller allele correlates with the recent spread of resistance in western Cambodia. Strong correlations between the presence of a mutant allele, in vitro parasite survival rates and in vivo parasite clearance rates indicate that K13-propeller mutations are important determinants of artemisinin resistance. K13-propeller polymorphism constitutes a useful molecular marker for large-scale surveillance efforts to contain artemisinin resistance in the Greater Mekong Subregion and prevent its global spread.
The emergence of Plasmodium falciparum resistance to artemisinin derivatives (ART) in Cambodia threatens the world’s malaria control and elimination efforts1,2. The risk of ART-resistant parasites spreading from western Cambodia to the Greater Mekong Subregion and to Africa, as happened previously with chloroquine- and sulphadoxine/pyrimethamine-resistant parasites3–5, is extremely worrisome. Clinical ART resistance is defined as a reduced parasite clearance rate1,6–10, expressed as an increased parasite clearance half-life11,12, or a persistence of microscopically detectable parasites on the third day of artemisininbased combination therapy (ACT)2. The half-life parameter correlates strongly with results from the in vitro ring-stage survival assay (RSA0–3 h) and results from the ex vivo RSA13, which measure the survival rate of young ring-stage parasites to a pharmacologically relevant exposure (700nM for 6h) to dihydroartemisinin (DHA)—the major metabolite of all ARTs. However, the present lack of a molecular marker hampers focused containment of ART-resistant parasites in areas where they have been documented and hinders rapid detection of these parasites elsewhere, where ACTs remain the most affordable, effective antimalarials. To detect and monitor the spread of ART resistance, a molecular marker for widespread use is needed.
Recent genome-wide analyses of P. falciparum isolates have provided evidence of recent positive selection in geographic areas of ART resistance9,14–16. Whereas parasite heritability of the clinical phenotype is above 50%, no reliable molecular marker has yet been identified. One possible explanation is that the parasite clearance half-life is not only determined by the intrinsic susceptibility of a parasite isolate to ART, but also by its developmental stage at the time of ART treatment and host-related parameters such as pharmacokinetics and immunity17. This issue was recently highlighted in patients presenting discordant data between parasite clearance half-life in vivo and RSA0–3 h survival rate in vitro13. Moreover, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are confounded by uncertainties about parasite population structure. Recent evidence for several highly differentiated subpopulations of ART-resistant parasites in western Cambodia15 suggests that distinct emergence events might be occurring. An alternative strategy to discover a molecular marker is to analyse mutations acquired specifically by laboratory-adapted parasite clones selected to survive high doses of ART in vitro, and use this information to guide analysis of polymorphism in clinical parasite isolates from areas where ART resistance is well documented at both temporal and geographical levels. Here we used this strategy to explore the molecular signatures of clinical ART resistance in Cambodia, where this phenotype was first reported1,8.
A candidate molecular marker of ART resistance
The ART-resistant F32-ART5 parasite line was selected by culturing the ART-sensitive F32-Tanzania clone under a dose-escalating, 125-cycle regimen of artemisinin for 5 years18. Whole-genome sequences were obtained for both F32-ART5 and F32-TEM (its sibling clone cultured without artemisinin) at 460× and 500× average nucleotide coverage, respectively. Compared to F32-TEM, no deleted genes were identified in F32-ART5. The exomes of F32-ART5 and F32-TEM were compared after excluding (1) genes from highly variable, multi-gene families (var, rifin and stevor), (2) positions with coverage lower than 25% of the mean coverage of the parasite line, (3) single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) found to be mixed in F32-ART5, given that acquired ART-resistance mutation(s) could be expected to be fixed in the sample after 5 years of continuous pressure, (4) SNPs shared between F32-ART5 and the ART-sensitive 3D7 parasite strain and (5) synonymous SNPs (Extended Data Fig. 1).
This analysis identified eight mutations in seven genes that were subsequently confirmed by Sanger sequencing of PCR products (Extended Data Table 1). Each gene harbours one mutant codon in F32-ART5 compared to F32-TEM, F32-Tanzania or 3D7 (Extended Data Table 2). Information on the expression of the genes and the biological function of the proteins are listed in Extended Data Table 3. Only one of these genes, cysteine protease falcipain 2a (PF3D7_1115700), has previously been associated with in vitro responses to ART19. To determine when each mutation arose in the F32-ART5 lineage, we analysed the whole-genome sequences of parasites at various drug-pressure cycles (Fig. 1). This analysis showed that the PF3D7_0110400 D56V and PF3D7_1343700 M476I mutations were acquired first, during the steep increase of ART resistance, and remained stable thereafter. Importantly, the appearance of these two mutations is associated with an increase in the RSA0–3 h survival rate, from less than 0.01% to 12.8%. Subsequent PCR analysis of the PF3D7_1343700 locus detected the M476I mutation after 30 drug-pressure cycles, consistent with the sharp increase in RSA0–3 h survival rate observed thereafter. The other SNPs appeared stepwise at later stages of selection: PF3D7_0213400 (68 cycles); PF3D7_1115700 (98 cycles); PF3D7_1302100, PF3D7_1459600 and PF3D7_1464500 (120 cycles) (Extended Data Table 2). These data indicate that the PF3D7_1343700 M476I mutation increased the resistance of F32-Tanzania to DHA in the RSA0–3h.
Figure 1. Temporal acquisition of mutations in F32-ART5.
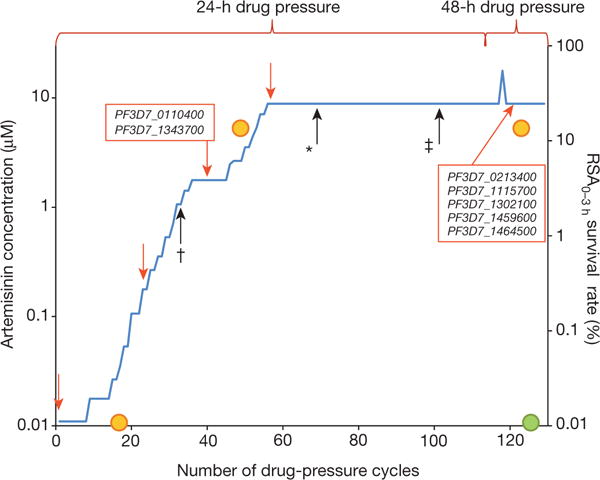
F32-Tanzania parasites exposed to increasing artemisinin concentrations for 120 consecutive cycles18 were analysed by whole-genome sequencing at five time-points (red arrows). Loci mutated after a given number of drug-pressure cycles are shown (red boxes). The earliest time-points where three mutations were detected by PCR (black arrows) are indicated by † for PF3D7_1343700, * for PF3D7_0213400 and ‡ for PF3D7_1115700. Orange and green circles indicate RSA0–3 h survival rates for F32-ART5 and F32-TEM parasites, respectively (mean of 3 experiments each).
To explore whether these mutations are associated with ART resistance in Cambodia, we investigated sequence polymorphismin all seven genes by mining whole-genome or Sanger sequences for 49 culture-adapted parasite isolates collected in 2010–2011 (see Methods). We chose these isolates based on their differential RSA0–3 h survival rates (Supplementary Table 1) and their sequences were compared to those of control parasites lines 3D7, 89F520 and K1992 (see Methods). Three genes (PF3D7_0110400, PF3D7_0213400 and PF3D7_1302100) encode a wild-type sequence for all parasite isolates. The other four genes show intra-population diversity, with previously reported or novel SNPs (Supplementary Table 1). PF3D7_1115700 has 11 SNPs that are not associated with RSA0–3h survival rates (P = 0.06, Kruskal–Wallis test). PF3D7_1459600 has 6 SNPs that are not associated with survival rates (P = 0.65). PF3D7_1464500 has 12 SNPs previously reported in older isolates from southeast Asia, including the ART-susceptible Dd2 line21, probably reflecting a geographic signature. These SNPs also show no significant association with survival rates (P = 0.42). Therefore, these six genes were not studied further.
In contrast, PF3D7_1343700 polymorphism shows a significant association with RSA0–3 h survival rates (Fig. 2). Indeed, RSA0–3 h survival rates differ substantially between parasite isolates with wild-type (median 0.17%, range 0.06–0.51%, n = 16) or mutant (18.8%, 3.8–58%, n = 33) K13-propeller alleles (P < 10−4, Mann–Whitney U test) (Supplementary Table 1). Four mutant alleles are observed, each harbouring a single non-synonymous SNP within a kelch repeat of the C-terminal K13-propeller domain, namely Y493H, R539T, I543T and C580Y located within repeats no. 2, 3, 3 and 4, respectively. Both the K1992 and the ART-susceptible 89F5 lines carry a wild-type K13-propeller. There are no associations between polymorphisms in the K13-propeller and those in the other candidate genes (Supplementary Table 1). Based on these observations and the acquisition of M476I in kelch repeat no. 2 by F32-ART5, we investigated whether K13-propeller polymorphism is a molecular signature of ART resistance in Cambodia.
Figure 2. Survival rates of Cambodian parasite isolates in the RSA0–3 h, stratified by K13-propeller allele.
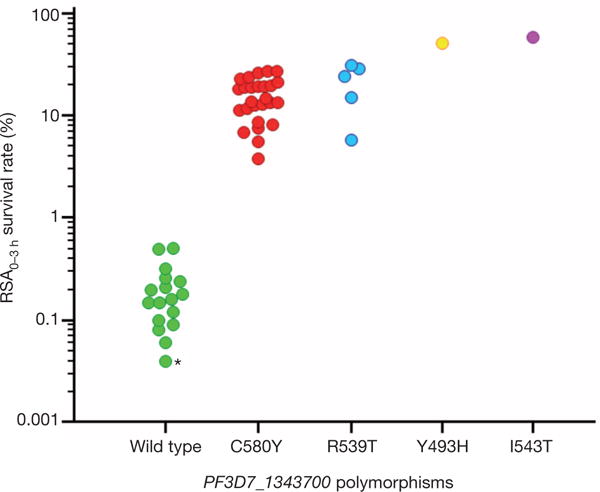
Genotypes were obtained by mining whole-genome sequence data (n = 21) or sequencing PCR products (n = 28). Mutant parasites have significantly higher RSA0–3 h survival rates than wild-type parasites: wild type (n = 17, median 0.16%, IQR 0.09–0.24, range 0.04–0.51); C580Y (n = 26, median 14.1%, IQR 11.3–19.6, range 3.8–27.3, P < 10−6 for wild type versus C580Y, Mann–Whitney U test); R539T (n = 5, median 24.2%, IQR 12.6–29.5, range 5.8–31.3, P < 10−3 for wild type versus R539T); Y493H (51.4%); and I543T (58.0%). The RSA0–3 h survival rate (0.04%) of control 3D7 parasites is indicated by an asterisk.
Emergence and spread of K13-propeller mutants in Cambodia
Over the last decade, the prevalence of ART resistance has steadily increased in the western provinces of Cambodia, but not elsewhere in the country2. To test whether the spatiotemporal distribution of K13-propeller mutations correlates with that of ART resistance, we sequenced the K13-propeller of archived parasite isolates from Cambodian patients with malaria in 2001–2012 (Extended Data Table 4). Data from six provinces were compared (n = 886): Pailin, Battambang and Pursat in the west where ART resistance is established1,6,8,22, Kratie in the southeast where ART resistance has increased in recent years2, and Preah Vihear in the north and Ratanakiri in the northeast where there was virtually no evidence of ART resistance during this time period2. This analysis reveals overall 17 mutant alleles, including three high-frequency (> 5%) alleles (C580Y, R539T and Y493H). The frequency of wild-type sequence decreased significantly over time in all three western provinces, but not in Preah Vihear or Ratanakiri. The frequency of the C580Y allele increased significantly from 2001–2002 to 2011–2012 in Pailin and Battambang, indicating its rapid invasion of the population and near fixation in these areas (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. Frequency of K13-propeller alleles in 886 parasite isolates in six Cambodian provinces in 2001–2012.
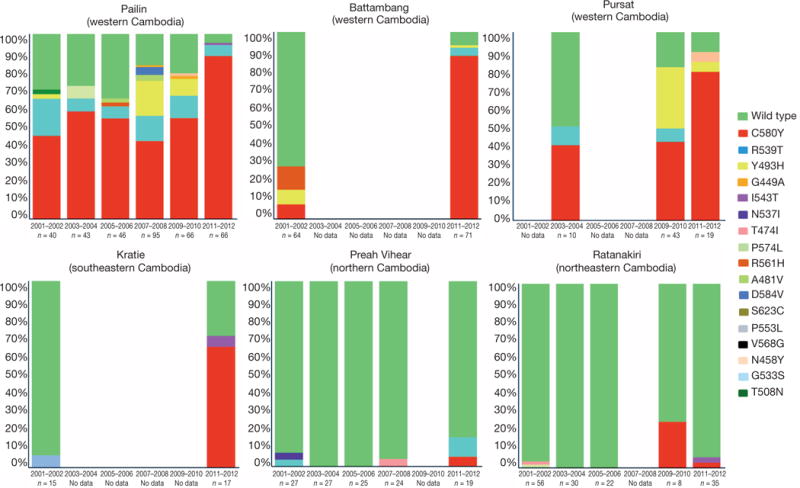
Genotypes were obtained by sequencing PCR products from archived blood samples. All mutant alleles carry a single non-synonymous SNP (colour-coded, same colour codes as in Fig. 2 for wild type, C580Y, R539T, Y493H and I543T). Significant reductions (Fisher’s exact test) in wild-type allele frequencies were observed in Pailin, Battambang, Pursat and Kratie over time (see Methods).
To further investigate the geographic diversity of K13-propeller polymorphism in Cambodia, we extended our sequence analysis to include data from four additional provinces (n = 55, Kampong Som, Kampot, Mondulkiri and Oddar Meanchey) in 2011–2012 (Extended Data Table 4). Although a large number of mutations are observed (Supplementary Fig. 1 and Extended Data Table 5), the C580Y allele accounts for 85% (189/222) of all mutant alleles observed in 2011–2012 (Extended Data Fig. 2). This mapping outlines the elevated frequency (74%, 222/300) of parasites harbouring a single non-synonymous mutation in the K13-propeller and the geographic disparity of their distribution. Importantly, the frequency distribution of mutant alleles over the various provinces matches that of day 3 positivity in patients treated for malaria with an ACT (Spearman’s r = 0.99, 95% confidence interval 0.96–0.99, P < 0.0001), considered a suggestive sign of clinical ART resistance (Extended Data Fig. 3).
K13-propeller polymorphisms and clinical ART resistance
To confirm that K13-propeller polymorphism is a molecular marker of clinical ART resistance, we first identified 163 patients from Pursat and Ratanakiri in whom we measured parasite clearance half-lives (range 1.58–11.53 h)6 in 2009–2010 and for which parasites were previously assigned to a KH subpopulation (KH1, KH2, KH3, KH4 or KHA) on the basis of ancestry analysis of whole-genome sequence data15. Thirteen patients with mixed genotypes (a wild-type and one or more mutant K13-propeller alleles) were excluded. Of the remaining 150 patients, 72 carried parasites with a wild-type allele and the others carried parasites with only a single non-synonymous SNP in the K13-propeller: C580Y (n = 51), R539T (n = 6) and Y493H (n = 21) (Extended Data Table 6). The parasite clearance half-life in patients with wild-type parasites is significantly shorter (median 3.30 h, interquartile range (IQR) 2.59–3.95) than those with C580Y (7.19h, 6.47–8.31, P < 10−6, Mann–Whitney U test), R539T (6.64h, 6.00–6.72, P < 10−4)or Y493H (6.28 h, 5.37–7.14, P < 10−6) parasites (Fig. 4a). Also, the parasite clearance half-life in patients carrying C580Y parasites is significantly longer than those with Y493H parasites (P = 0.007, Mann–Whitney U test). These data indicate that C580Y, R539T and Y493H identify slow-clearing parasites in malaria patients treated with ART.
Figure 4. Parasite clearance half-lives.
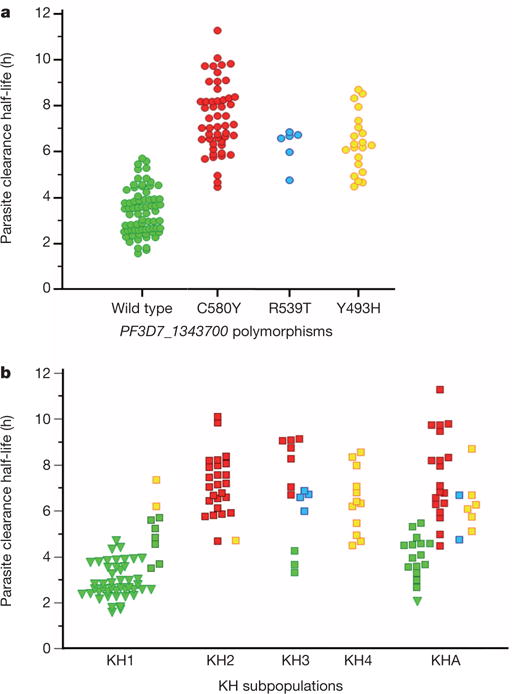
a, Correlation of parasite clearance half-lives and K13-propeller alleles for parasite isolates in Pursat and Ratanakiri in 2009–2010. Wild-type parasites have shorter half-lives (median 3.30 h, IQR 2.59–3.95, n = 72) than C580Y (7.19 h, 6.47–8.31, n = 51, P < 10−6, Mann– Whitney U test), R539T (6.64 h, 6.00–6.72, n = 6, P < 10−6) or Y493H (6.28 h, 5.37–7.14, n = 21, P < 10−6) parasites. The half-life of C580Y parasites is significantly longer than that of Y493H parasites (P = 0.007). b, Correlation of parasite clearance half-lives, KH subpopulations15 and K13-propeller alleles for the same 150 parasite isolates. Half-lives are shown for Pursat (squares) and Ratanakiri (triangles) parasites, stratified by KH group and K13-propeller allele (colour-coded as in a). Median half-lives stratified by K13-propeller allele are KH1: wild type (2.88) and Y493H (6.77); KH2: C580Y (7.13) and Y493H (4.71); KH3: wild type (3.65), C580Y (8.73) and R539T (6.65); KH4: Y493H (6.37); and KHA: wild type (4.01), C580Y (7.09), Y493H (6.18) and R539T (5.73).
Because KH2, KH3, KH4 and KHA parasites have longer half-lives than KH1 parasites15, we proposed that allelic variation in the K13-propeller accounts for these differences. Among 150 parasites, 55, 26, 14, 12 and 43 are classified as KH1, KH2, KH3, KH4 and KHA, respectively. Three K13-propeller alleles strongly associate with KH groups: 96% (53/55) of KH1, 96% (25/26) of KH2 and 100% (12/12) of KH4 parasites carry the wild-type, C580Y and Y493H alleles, respectively (Extended Data Table 6). Whereas KH3 parasites (n = 14) carry the wild-type, C580Y and R539T alleles, R539T is not observed in KH1, KH2 or KH4 parasites. As expected, KHA parasites have a mixed allele composition. Importantly, K13-propeller mutations more accurately identify slow-clearing parasites than KH group (Fig. 4b), demonstrating that the association of K13-propeller polymorphism with clinical ART resistance in Cambodia is partially independent of the genetic background of KH subpopulations. Within the KH1 group (n = 55), the parasite clearance half-life in patients with wild-type parasites is significantly shorter (n = 53, median 2.88h, IQR 2.52–3.79) than those with Y493H parasites (n = 2, median 6.77 h, P = 0.02, Mann–Whitney U test). Within the KH3 subpopulation (n = 14), the half-life in patients with wild-type parasites is shorter (n = 3, median 3.65 h) than those with C580Y (n = 7, median 8.73h, IQR 7.35–9.06, P = 0.02) or R539T (n = 4, 6.65 h, 6.29–6.80, P = 0.03) parasites.
Discussion
The F32-ART5 lineage acquired a K13-propeller mutation as it developed ART resistance, as indicated by its ability to survive a pharmacologically relevant exposure to DHA in the RSA0–3 h. Genes putatively associated with ART resistance (Pfcrt23,24, Pftctp25,26, Pfmdr18,27,28, Pfmrp127–29 and ABC transporters30) or encoding putative targets of ART (PfATPase631,32 and Pfubcth—the orthologue of Plasmodium chabaudi ubp133,34) were not mutated during the 5-year selection of F32-ART5, and Pfmdr1 amplification was not observed35–40. In addition, all candidate ART resistance genes recently identified using population genetics approaches14,40,41 remained unaltered in F32-ART5, except for PF3D7_1343700 and PF3D7_1459600 located in the linkage-disequilibrium windows identified in ref. 16. These findings led us to identify another 17 single K13-propeller mutations in naturally circulating parasites in Cambodia. Several of these mutations associate strongly with the spatiotemporal distribution of ART resistance in Cambodia, increased parasite survival rates in response to DHA in vitro, and long parasite clearance half-lives in response to ART treatment in vivo. None of the six other genes mutated in F32-ART5 associate with RSA0–3h survival rates in parasite isolates from Cambodia.
K13-propeller polymorphism fulfils the definition of a molecular marker of ART resistance for several reasons: (1) there has been a progressive loss of wild-type parasites in western Cambodia during the decade of emerging ART resistance in this region; (2) mutant parasites cluster in Cambodian provinces where ART resistance is well established and are less prevalent where ART resistance is uncommon; (3) PF3D7_1343700 is located 5.9 kilobases upstream of the 35-kb locus identified in ref. 14 as being under recent positive selection, and within the region of top-ranked signatures of selection outlined in ref. 16; (4) multiple mutations, all non-synonymous, are present in the K13-propeller, reflecting positive selection rather than a hitchhiking effect or genetic drift; (5) mutations occur in a domain that is highly conserved in P. falciparum, with only one non-synonymous SNP being documented in a single parasite isolate from Africa42; (6) all polymorphisms we observe in Cambodia are novel and all but one (V568G) occur at positions strictly conserved between Plasmodium species (Supplementary Fig. 1 and Supplementary Fig. 2), suggesting strong structural and functional constraints on the protein; (7) the three most-prevalent K13-propeller mutations correlate strongly with RSA0–3 h survival rates in vitro and parasite clearance half-lives in vivo at the level of individual parasite isolates and malaria patients, respectively; and (8) the frequency of mutant alleles correlates strongly with the prevalence of day 3 positivity after ACT treatment at the level of human populations in Cambodia.
On the basis of homology with other kelch propeller domains, we anticipate that the observed K13-propeller mutations destabilize the domain scaffold and alter its function. The carboxy-terminal portion of PF3D7_1343700 encodes six kelch motifs, which are found in a large number of proteins with diverse cellular functions43,44. Given that the toxicity of ART derivatives depends principally on their pro-oxidant activity, the reported role of some kelch-containing proteins in regulating cytoprotective and protein degradation responses to external stress is particularly intriguing. The K13-propeller shows homology with human KLHL12 and KLHL2, involved in ubiquitin-based protein degradation, and KEAP1, involved in cell adaptation to oxidative stress (Extended Data Fig. 4). More work is needed to delineate the normal function of K13 and the effect of various mutations. Allele exchange studies in mutant and wild-type parasites may help to define the contribution of K13-propeller polymorphisms on different genetic backgrounds to the RSA0–3h survival rate. Indeed, it is particularly worrying that as few as two mutations, that is, the K13-propeller M476I and PF3D7_0110400 D56V, were sufficient to confer ART resistance to F32-Tanzania, which has a typical African genetic background. Cambodian parasites with mutant K13-propellers display a wide range of RSA0–3 h survival rates (3.8–58%) and parasite clearance half-lives (4.5–11.5 h). Further studies are therefore required to identify additional genetic determinants of ART resistance, which may reside in the strongly selected regions recently identified14,16. In this context, analysing the RSA0–3h survival rates as a quantitative trait among parasites harbouring the same K13-propeller mutation could help to identify additional genetic loci involved in ART resistance.
In summary, K13-propeller polymorphism seems to be a useful molecular marker for tracking the emergence and spread of ART-resistant P. falciparum.
METHODS SUMMARY
The ART-resistant F32-ART5 parasite line was selected by culturing the ART-sensitive F32-Tanzania clone under a dose-escalating regimen of artemisinin for 5 years. The F32-TEM line was obtained by culturing F32-Tanzania in parallel without artemisinin exposure. Reference DNA was extracted from P. falciparum lines 3D7, 89F5 Palo Alto Uganda and K1992. The ring-stage survival assay (RSA0–3 h) was performed as described previously13. Whole-genome sequencing was performed on F32-Tanzania, F32-TEM, F32-ART5 (4 time points), three reference strains (3D7, 89F5 and K1992) and 21 Cambodian parasite isolates, using an Illumina paired-reads sequencing technology. A set of 1091 clinical P. falciparum isolates was collected from patients participating in ACT efficacy studies in 2001–2012. The K13-propeller was amplified using nested PCR. Double-strand sequencing of PCR products was performed by Macrogen. Sequences were analysed with MEGA 5 software version 5.10 to identify specific SNP combinations. Data were analysed with Microsoft Excel and MedCalc version 12. Differences were considered statistically significant when P values were less than 0.05. Ethical clearances for parasite isolate collections were obtained from the Cambodian National Ethics Committee for Health Research, the Institutional Review Board of the Naval Medical Research Center, the Technical Review Group of the WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific, and the Institutional Review Board of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
METHODS
Artemisinin- and mock-pressured P. falciparum F32 lineages
Mycoplasma-free F32-Tanzania parasites were maintained in human type O red blood cells (RBCs) (Etablisssement Français du Sang) diluted to 2.5% haematocrit in RPMI-1640 medium (Invitrogen, San Diego, CA) supplemented with 5% human serum. Parasite cultures were maintained at 37 °C in an atmosphere of 5% CO2. Parasitaemia was checked daily and maintained below 10%. For the selection of ART-resistant parasites, asynchronous cultures were adjusted to 5–7% parasitaemia and grown in the presence of escalating doses of artemisinin (from 10 nM to 9 μM) for 24 h for the first 3 years of drug pressure18. In the subsequent 2 years, each drug-pressure cycle was done for 48 h with doses ranging from 9 μM to 18 μM. After drug exposure, the medium was discarded and replaced by human-serum-supplemented (20%) drug-free medium. Parasitaemia was monitored daily until it reached 5%. At that time, drug pressure was reapplied. The parasite line obtained after an effective 5 years of discontinuous ART pressure was named F32-ART5. In parallel, the parental F32-Tanzania line was kept as a control in continuous culture for the same time under the same conditions (that is, RBCs, serum and media) but without artemisinin exposure. The resulting control line was called F32-TEM.
Laboratory-adapted P. falciparum lines
Reference DNA was extracted from the laboratory-adapted P. falciparum lines 3D7 (MR4, Manassas, VA), 89F5 Palo Alto Uganda (a clone from the Palo Alto line, originating from Uganda in 1978, which displayed high susceptibility to artemether treatment in the Saimiri sciureus experimental host (O. Mercereau-Puijalon, H. Contamin and J.-C. Barale, unpublished data)) and K1992, an isolate collected in Pailin in 1992 before the mass deployment of ART in that area (provided by the French National Reference Center of Malaria). Parasite DNA was extracted from frozen blood aliquots (200 μl) using the Mini blood kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Culture-adapted P. falciparum isolates from Cambodia
Fifty clinical P. falciparum isolates from Cambodia (collected in 2010 and 2011) were adapted to in vitro culture as described in ref. 45. Their geographic origin is indicated in Supplementary Table 1. Parasite clearance rates were not determined for these patient isolates, as they were collected during field trials that did not include such measurements. Parasite DNA was extracted from frozen blood aliquots (200 μl) using the Mini blood kit (Qiagen).
Ring-stage survival assay
The ring-stage survival assay (RSA0–3 h) was carried out as described in ref. 13 using highly synchronous parasite cultures. In brief, 0–3 h post-invasion ring-stage parasites were exposed to 700 nM DHA (dihydroartemisinin, obtained from WWARN (http://www.wwarn.org/research/tools/qaqc)) or its solvent DMSO for 6 h, washed and then cultivated for the next 66 h without drug. Survival rates were assessed microscopically by counting in Giemsastained thin smears the proportion of viable parasites that developed into second-generation rings or trophozoites with normal morphology.
Ethical clearance
Ethical clearances for the collection of parasite isolates from patients were obtained from the Cambodian National Ethics Committee for Health Research, the Institutional Review Board of the Naval Medical Research Center, the Technical Review Group of the WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific, and the Institutional Review Board of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Work was conducted in compliance with all relevant ethical standards and regulations governing research involving human subjects. Written informed consent was obtained from all adult participants or the parents or guardians of children.
Temporal and geographical sample collection
A set of 941 clinical P. falciparum isolates was collected from patients participating in therapeutic efficacy studies of ACTs, conducted as part of the routine antimalarial drug efficacy monitoring of Cambodia’s National Malaria Control Program from 2001 to 2012, and from studies conducted by NAMRU-2 (Extended Data Table 4). Venous blood samples (5 ml) collected in EDTA or ACD were transported to Institut Pasteur du Cambodge in Phnom Penh within 48 h of collection at 4 °C and then kept at −20 °C until DNA extraction. Parasite DNA was extracted from frozen blood aliquots (200 μl) using the Mini blood kit (Qiagen).
Measurement of parasite clearance half-life
Patients with un complicated or severe P. falciparum malaria and initial parasite density ≥ 10,000 μl−1 were enrolled in Pursat and Ratanakiri provinces in 2009 and 2010 as described6,13. Patients were treated with an ART and their parasite density measured every 6 h from thick blood films until parasitaemia was undetectable. The parasite clearance half-life in 163 patients was derived from these parasite counts using WWARN’s on-line Parasite Clearance Estimator (http://www.wwarn.org/toolkit/data-management/parasite-clearance-estimator). The study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (number NCT00341003).
Whole-genome sequencing of parasite DNA
Whole-genome sequencing was performed on F32-Tanzania, F32-TEM, the F32-ART5 lineage (4 time-points), three reference strains (3D7, 89F5 and K1992) and 21 parasite isolates from Cambodia, using an Illumina paired-reads sequencing technology. Illumina library preparation and sequencing followed standard protocols developed by the supplier. Briefly, genomic DNA was sheared by nebulization, and sheared fragments were end-repaired and phosphorylated. Blunt-end fragments were A-tailed, and sequencing adapters were ligated to the fragments. Inserts were sized using Agencourt AMPure XP Beads (± 500 bp; Beckman Coulter Genomics) and enriched using 10 cycles of PCR before library quantification and validation. Hybridization of the library to the flow cell and bridge amplification was performed to generate clusters, and paired-end reads of 100 cycles were collected on a HiSeq 2000 instrument (Illumina). After sequencing was complete, image analysis, base calling and error estimation were performed using Illumina Analysis Pipeline version 1.7.
Raw sequence files were filtered using Fqquality tool, a read-quality filtering software developed by N. Joly, which enables the trimming of the first and last low-quality bases in reads. The trimmed reads from controlled Fastq files were mapped on a reference genome (P. falciparum 3D7) with the Burrows-Wheeler Alignment (BWA), generating a BAM file (a binary file of tab-delimited format SAM). Next, we used Samtools to prepare a pileup file, which was formatted using in-house software to implement the data into the Wholegenome Data Manager (WDM) database (Beghain et al., in preparation). WDM software is designed to compare and/or align partial or whole P. falciparum genomes.
Sequencing genes containing non-synonymous SNPs in F32-ART5
PCR amplification of selected genes was performed using the primers listed in Extended Data Table 1. Two μl of DNA was amplified with 1 μM of each primer, 0.2 mM dNTP (Solis Biodyne), 3 mM MgCl2 and 2 U Taq DNA polymerase (Solis Biodyne), using the following cycling program: 5 min at 94 °C, then 40 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 90 s at 60 °C, 90 s at 72 °C and final extension 10 min at 72 °C. PCR products were detected by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. Double-strand sequencing of PCR products was performed by Beckman Coulter Genomics. Sequences were analysed with MEGA 5 software version 5.10 in order to identify specific SNP combinations.
Sequencing the K13-propeller domain
The K13-propeller domain was amplified using the following primers: for the primary PCR (K13-1 5′-cggagtgaccaaatctggga-3′ and K13-4 5′-gggaatctggtggtaacagc-3′) and the nested PCR (K13-2 5′-gccaagctgccattcatttg-3′ and K13-3 5′-gccttgttgaaagaagcaga-3′). One μl of DNA was amplified with 1 μM of each primer, 0.2 mM dNTP (Solis Biodyne), 3 mM MgCl2 and 2 U Taq DNA polymerase (Solis Biodyne), using the following cycling program: 5 min at 94 °C, then 40 cycles of 30 s at 94 °C, 90 s at 60 °C, 90 s at 72 °C and final extension 10 min at 72 °C. For the nested PCR, 2 μl of primary PCR products were amplified under the same conditions, except for the MgCl2 concentration (2.5mM). PCR products were detected using 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. Double-strand sequencing of PCR products was performed by Macrogen. Sequences were analysed with MEGA 5 software version 5.10 to identify specific SNP combinations.
Deep-sequencing of clinical parasite isolates and population structure analysis
DNA extraction, Illumina sequencing and SNP genotyping of clinical parasite isolates obtained from malaria patients in Pursat and Ratanakiri provinces, Cambodia, have been previously described15. Population structure analysis of these parasites identified four subpopulations: KH1, KH2, KH3 and KH4. Parasites with <80% ancestry from any of these four groups were deemed admixed (KHA).
Temporal acquisition of mutations in the F32-ART5 lineage
The F32-ART5 lineage was explored by whole-genome sequencing using samples collected at time 0 (original F32-Tanzania clonal line), day 196 (0.2-μM pressure cycle no. 23), day 385 (1.8-μM pressure cycle no. 39), day 618 (9-μM pressure cycle no. 56) and day 2,250 (9-μM pressure cycle no. 120). The F32-TEM sample was collected on day 2,250. Additional samples collected at the time of the 30th, 33rd, 34th, 36th, 68th and 98th pressure cycles were studied by PCR. DNA from parasite cultures was extracted using the High Pure PCR Template Preparation Kit (Roche Diagnostics) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The F32-ART5 samples tested in the ring-stage survival assay (RSA0–3 h) were collected at the time of the 17th, 48th and 122nd pressure cycles (0.04, 2.7 and 9 μM ART), respectively. The F32-TEM sample was collected at the last mock pressure cycle. The RSA0–3 h survival rates were determined in triplicate experiments with different batches of red blood cells, and evaluated as above using Giemsa-stained thin smears read by two independent microscopists (B.W. and F.B.-V.). Survival rates were compared using Mann–Whitney U test. The RSA0–3 h survival rates of the F32-ART5 samples were as follows: at drug-pressure cycles: no. 17 (n = 3, median 0%, IQR 0–0.07), no. 48 (n = 3, median 11.7%, IQR 10.3–14.6; P = 0.04 for no. 17 versus no. 48, Mann–Whitney U test) and no. 122 (n = 3, median 12.8%, IQR 10.6–14.5, P = 0.04 and P = 0.82 for no. 17 versus no. 122 and no. 48 versus no. 122). The RSA0–3 h survival rate of the F32-TEM line was also determined in triplicate experiments (n = 3, median 0%, IQR 0–0.05, P = 0.81 for TEM versus no. 17, Mann–Whitney U test).
Prevalence of K13-propeller mutations in 886 clinical parasite isolates collected in six Cambodian provinces in 2001–2012
The K13-propeller was genotyped by sequencing PCR products amplified from 886 archived blood samples. The number of samples analysed from each province each year is indicated in Fig.3. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare the frequency of isolates harbouring a wild-type K13-propeller sequence in each province over time. A significant decrease of the frequency of the wild-type K13-propeller allele was observed in the western provinces during the decade. In Pailin, it decreased from 30.0% in 2001–2002 (12/40) to 4.8% in 2011–2012 (4/84), P = 0.0002, in Battambang from 71.9% in 2001–2002 (46/64) to 7.0% in 2011–2012 (5/71), P < 10−6, in Pursat from 50.0% in 2003–2004 (5/10) to 10.5% in 2011–2012 (2/19), P = 0.03; and in Kratie from 93.3% in 2001–2002 (14/15) to 29.4% in 2011–2012 (5/17), P = 0.0003. Significant decreases in wildtype allele frequency were not observed in Preah Vihear (from 92.6% in 2001–2002 (25/27) to 84.2% in 2011–2012 (16/19), P = 0.63); or Ratanakiri (from 96.4% in 2001–2002 (54/56) to 94.3% in 2011–2012 (33/35), P = 0.63). The frequency of C580Y increased in Pailin from 45.0% (18/40) in 2001–2002 to 88.1% (74/84) in 2011–2012 (P < 10−6), and in Battambang from 7.8% (5/64) in 2001–2002 to 87.3% (62/71) in 2011–2012 (P < 10−6) indicating its rapid invasion of the population and near fixation in these provinces.
Three-dimensional structure modelling of the K13-propeller
The 3D-structural model of the kelch propeller domain of PF3D7_1343700 (‘K13-propeller’) was obtained by homology modelling satisfying spatial restraints using Modeller v9.11 (http://modbase.compbio.ucsf.edu). The 295 amino acids composing the K13-propeller are 22%, 25% and 25% identical to the kelch propeller domain of the human KEAP1 (Protein Data Bank (PDB; http://www.rcsb.org/) 2FLU), KLHL12 (PDB 2VPJ) and KLHL2 (PDB 2XN4) proteins, respectively, that were used as templates to model the 3D-structure of the K13-propeller. The reliability of the obtained model was assessed using two classical criteria. First, the significance of the sequence alignment between the K13-propeller domain and one template was confirmed by an E-value = 0, as calculated by Modeller using the Built-Profile routine. Second, the model achieved a GA341 model score = 1 (a score ≥ 0.7 corresponds to highly reliable models). Localization of the mutants in the K13-propeller 3D-model was prepared using the PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, version 1.5.0.4 (Schrödinger; http://www.pymol.org).
Statistical analysis
Data were analysed with Microsoft Excel and MedCalc version 12. Quantitative data were expressed as median, interquartile range (IQR). The Mann–Whitney U test (independent samples, two-sided) was used to compare two groups, and the Kruskal–Wallis test (H-test, two-sided) was used to compare more than two groups. The Spearman’s rho rank correlation coefficient (and the 95% confidence interval for the correlation coefficient) was used to measure the strength of relationship between the prevalence of wild-type K13-propeller allele and the frequency of day 3 positivity (defined as persistence of microscopically detectable parasites on the third day of artemisinin-based combination therapy)2. Fisher’s exact test was used to compare frequency data and the Clopper–Pearson exact method based on the beta distribution was used to determine 95% confidence intervals for proportions. Differences were considered statistically significant when P values were less than 0.05.
Extended Data
Extended Data Figure 1. SNP-calling algorithm and sequence and coverage of SNPs.
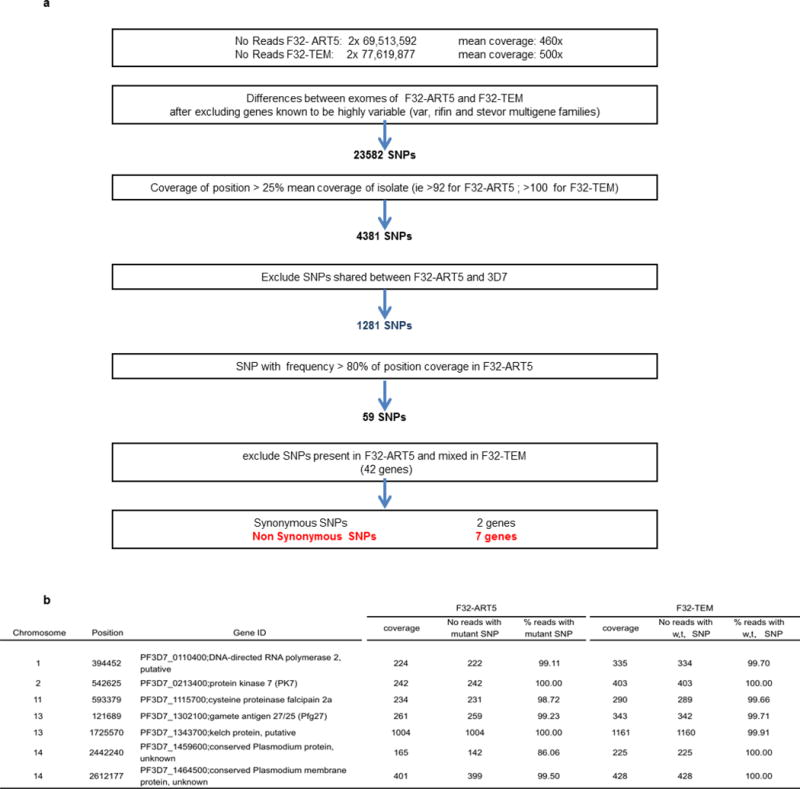
a, SNP-calling algorithm of the whole-genome sequence comparison of F32-ART5 and F32-TEM. b, Sequence and coverage of SNPs in seven candidate genes differing in F32-TEM and F32 ART5.
Extended Data Figure 2. Geographic distribution of K13-propeller alleles in Cambodia in 2011–2012.
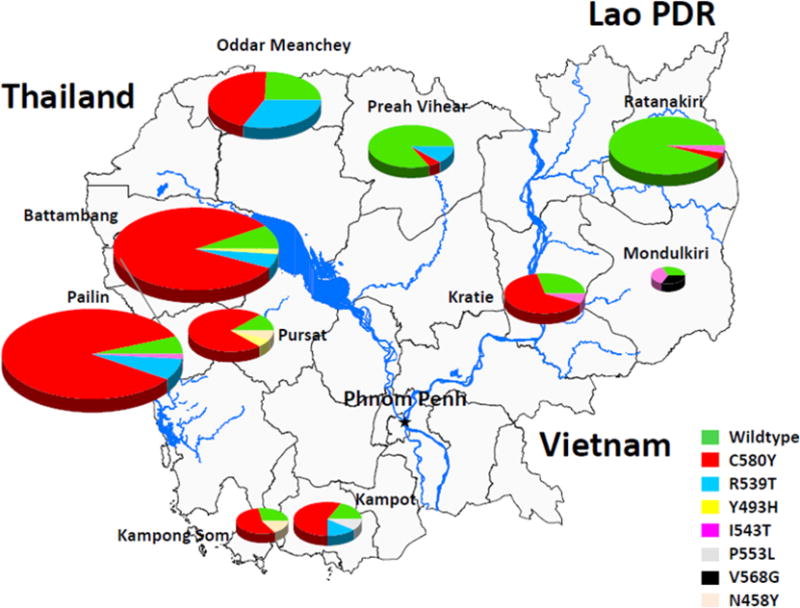
Pie charts show K13-propeller allele frequencies among 300 parasite isolates in ten Cambodian provinces. Pie sizes are proportional to the number of isolates and the different alleles are colour-coded as indicated. The frequencies (95% confidence interval) of mutant K13-propeller alleles are: Pailin (95%, 88–99, n = 84), Battambang (93%, 87–99, n = 71), Pursat (89%, 67–99, n = 19), Kampot (83%, 52–98, n = 12), Kampong Som (71%, 29–96, n = 7), Oddar Meanchey (76%, 58–89, n = 33), Preah Vihear (16%, 3–40, n = 19), Kratie (71%, 44–90, n = 17), Mondulkiri (67%, 9–99, n = 3) and Ratanakiri (6%, 1–19, n = 35).
Extended Data Figure 3. Correlation between the frequency of wild-type K13-propeller alleles and the prevalence of day 3 positivity after ACT treatment in eight Cambodian provinces.
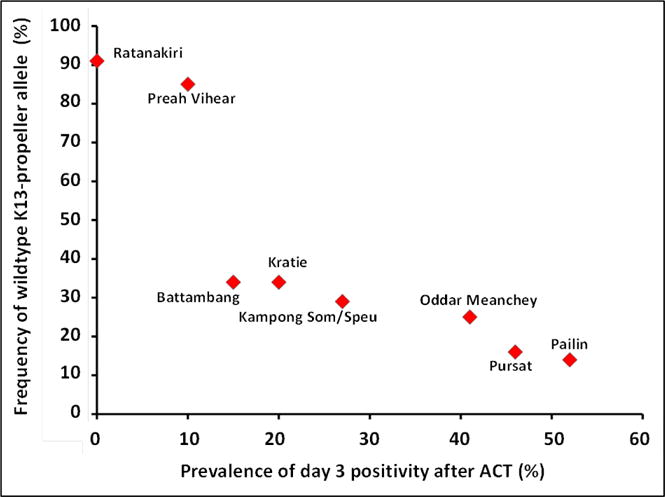
The frequency of day 3 positivity is plotted against the frequency of wild-type K13-propeller alleles. Data are derived from patients treated with an ACT for P. falciparum malaria in 2010–2012 in eight Cambodian provinces (Extended Data Figure 2): Pailin (n = 86, 2011 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, artesunate-mefloquine); Pursat (n = 32, 2012 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine); Oddar Meanchey (n = 32, 2010 NAMRU-2 therapeutic efficacy study, artesunate-mefloquine); Kampong Som/Speu (n = 7, 2012 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine); Battambang (n = 18, 2012 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine); Kratie (n = 15, 2011 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine); Preah Vihear (n =19, 2011 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine); Ratanakiri (n = 32, 2010 WHO therapeutic efficacy study, dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine). Spearman’s coefficient of rank correlation (8 sites): r = −0.99, 95% confidence interval −0.99 to −0.96, P < 0.0001.
Extended Data Figure 4. Schematic representation of homology between P. falciparumK13 and human KEAP1 proteins and structural 3D model of the K13-propeller domain.
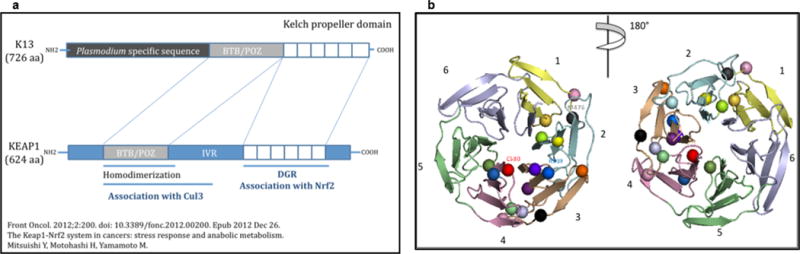
a, Schematic representation of the predicted PF3D7_1343700 protein and homology to human KEAP1. Similar to KEAP1, PF3D7_1343700 contains a BTB/POZ domain and a C-terminal 6-blade propeller, which assembles kelch motifs consisting of four anti-parallel beta sheets. b, Structural 3D model of the K13-propeller domain showing the six kelch blades numbered 1 to 6 from N to C terminus and colour-coded as in Supplementary Fig. 1. The level of amino-acid identity between the K13-propeller and kelch domains of proteins with solved 3D structures, including human KEAP146,47, enabled us to model the 3D structure of the K13-propeller and to map the mutations selected under ART pressure (Extended data Table 5). The accuracy of the K13-propeller 3D model was confirmed by Modeller-specific model/fold criteria of reliability (see Methods). We predict that the K13-propeller folds into a 6-bladed β-propeller structure48 closed by the interaction between a C-terminal beta-sheet and the N-terminal blade46,48. The first domain has three β-sheets, the fourth one being contributed by an extra C-terminal β-sheet called β’1 in Supplementary Fig. 1. The human KEAP1 kelch propeller scaffold is destabilized by a variety of mutations affecting intra- or inter-blade interactions in human lung cancer46 and hypertension47. The positions of the various mutations are indicated by a sphere, colour-coded as in Figs 2–4. The M476 residue mutated in F32-ART5 is indicated in dark grey. Like the mutations observed in human KEAP146,47, many K13-propeller mutations are predicted to alter the structure of the propeller or modify surface charges, and as a consequence alter the biological function of the protein. Importantly, the two major mutations C580Y (red) and R539T (blue) observed in Cambodia are both non-conservative and located in organized secondary structures: a β-sheet of blade 4 where it is predicted to alter the integrity of this scaffold and at the surface of blade 3, respectively. The kelch propeller domain of KEAP1 is involved in protein–protein interactions like most kelch containing modules43. KEAP1 is a negative regulator of the inducible Nrf2-dependent cytoprotective response, sequestering Nrf2 in the cytoplasm under steady state. Upon oxidative stress, the Nrf2/KEAP1 complex is disrupted, and Nrf2 translocates to the nucleus, where it induces transcription of cytoprotective ARE-dependent genes49,50. We speculate that similar functions may be performed by PF3D7_1343700 in P. falciparum, such that mutations of the K13-propeller impair its interactions with an unknown protein partner, resulting in a deregulated anti-oxidant/cytoprotective response. The P. falciparum anti-oxidant response is maximal during the late trophozoite stage, when haemoglobin digestion and metabolism are highest51. Its regulation is still poorly understood and no Nrf2 orthologue could be identified in the Plasmodium genome.
Extended Data Table 1.
Sequence of the primers used to amplify the genes containing nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphisms in F32-ART5
| Targeted gene | Primer forward sequence | Primer reverse sequence |
|---|---|---|
| PF3D7_0110400 | 5′-ttgagcttctttttcccaataatggc-3′ | 5′-tgatatatgtttgtaggagctgtgag-3′ |
| PF3D7_0213400 | 5′-gtgaaaaggataataaattctatgcc-3′ | 5′-tatctaccatatattctgattctcc-3′ |
| PF3D7_1115700 | 5′-agcaagaacgttttgtgtaaa-3′ | 5′-gaattctttaatggttttgaagat-3′ |
| PF3D7_1302100 | 5′-taatatgtaaagtgattatgtatatcgc-3′ | 5′-atgctagagaagttaaagagaagaagcg-3′ |
| PF3D7_1343700 | 5′-agaagagccatcatatccccc-3′ | 5′-agtggaagacatcatgtaaccag-3′ |
| PF3D7_1459600 | 5′-atatgagtaaaatgtcaggttttgg-3′ | 5′-tgcttgttgtgattcatgggg-3′ |
| PF3D7_1464500 | 5′-aaatagttgggcgtagctcag-3′ | 5′-tatcacaattaagtgtatcacaacg-3′ |
Extended Data Table 2.
Description of the eight nonsynonymous, single-nucleotide polymorphisms acquired in the F32-ART5 compared to the F32-TEM lineage during an effective 5-year discontinuous exposure to increasing concentrations of artemisinin
| Gene ID (Plasmodb 9.1) |
Annotation | Chromosome/ position mutated |
Nucleotide position in coding sequence |
F32- TEM codon# |
Codon F32-ART5 lineage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Drug pressure cycle# | Mutant codon |
||||||||
| 23 | 39 | 56 | 120 | |||||||
| – | 0.2 μM ART* |
1,8 μM ART* |
9 μM ART* |
9 μM ART* |
||||||
| PF3D7_0110400 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase 2 complex subunit RPB9, putative | 01/39452 | 173 | gAt | gAt | gAt | gTg | gTg | gTg | D56V |
| PF3D7_1343700a | kelch protein, putative, called here ‘K13’ | 13/1725570 | 1428 | atG | atG | atG | atA | atA | atA | M476I |
| PF3D7_0213400 | protein kinase 7 (PK7) | 02/542625 02/542627 |
310 312 |
GaA | GaA | GaA | GaA | GaA | TaG | E104stop |
| PF3D7_1115700 | cysteine proteinase falcipain 2a | 11/593378 | 206 | tCa | tCa | tCa | tCa | tCa | tGa | S69stop |
| PF3D7_1302100 | gamete antigen 27/25 (Pfg27) | 13/121689 | 601 | Cca | Cca | Cca | Cca | Cca | Aca | P201T |
| PF3D7_1459600a | conserved Plasmodium protein, unknown function | 14/2442240 | 896 | aGt | aGt | aGt | aGt | aGt | aCt | S299T |
| PF3D7_1464500 | conserved Plasmodium membrane protein unknown function | 14/2612177 | 4886 | aAt | aAt | aAt | aAt | aAt | aGt | N1629S |
3D7-type sequence; the same codon sequence is also observed in the parental F32-Tanzania line.
Artemisinin (ART) dose used for selection during the corresponding drug-pressure cycle.
Genes found in the chromosomal location of top-ranked signatures of selection in ref. 16.
Extended Data Table 3.
Reported characteristics of the genes mutated in F32-ART5 parasites
| PF3D7_0110400 (PFA0505c), is a two-exon gene, codes for the RNA Polymerase II subunit 9 (RPB9), a small integral Pol II subunit, which is highly conserved among eukaryotes. The yeast RPB9 ortholog has been shown to have a role in assuring the fidelity of transcription in vivo. Deletion of the gene results in error-prone transcription52. The protein has a predicted zinc ribbon domain similar to the zinc ribbon domain of TFIIS (RNA Polymerase II elongation factor) that contains the essential catalytic Asp-Glu dipeptide53. Very little is known on the protein in Plasmodia, although the gene is expressed and the protein is present in blood stages (www.plasmodb.org). It is difficult to make any prediction on the possible phenotypic consequences of the D56V mutation, which is located in a Plasmodium-specific, well-conserved domain. |
| PF3D7_1343700 (PF13_0238), is a one-exon gene (called here K13) that codes for a putative kelch protein. K13 has a predicted 3-domain structure, with an approx. 225 residue long, Plasmodium-specific and well conserved N-terminal domain, followed by a BTB/POZ domain and a 6-blade C-terminal propeller domain formed of canonical kelch motifs43,48. Little is known about the protein in malaria parasites. Proteomics data indicate that it is produced by asexual (trophozoites, schizonts, merozoites and rings) and sexual blood stages (gametocytes) of P. falciparum, and that it possesses phosphorylated residues in the N-terminal Plasmodium-specific domain (www.plasmodb.org). The M476I mutation is located between the first and second blade of the propeller domain. |
| PF3D7_0213400 (PFB0605w), is a four-exon gene that codes for protein kinase 7 (PK7) expressed during the asexual blood stage development, in gametocytes and ookinetes. The E104 stop mutation (two SNPs affecting the same codon) observed in F32-ART5 interrupts the gene resulting in a truncated putative translation product lacking more than 2/3 of its sequence. Studies with genetically inactivated parasites have shown that PK7-KO P. falciparum parasites have an asexual growth defect due to a reduced number of merozoites per schizont54. Furthermore, PK7 is important for mosquito transmission, with a collapsed number of ookinetes in P. falciparum54 and in P. berghei, where no sporoblasts and consequently no sporozoites are formed55. This transmission defective phenotype is unlikely to survive in the field. |
| PF3D7_1115700 (PF11_0165), is a one-exon gene that codes for falcipain 2a, a cysteine proteinase produced by maturing blood stages (trophozoites and schizonts) and involved in hemoglobin degradation56. The S69stop mutation located in the pro-enzyme region precludes expression of an active enzyme by F32-ART5 parasites. Gene inactivation has shown to induce a transient reduction of hemoglobin degradation compensated by expression of other members of the cysteine proteinases family, with minimal impact on growth rate57,58. However, falcipain 2a is the only gene from the list of seven affected loci that has been associated with the in vitro response to artemisinin. Indeed, it has been convincingly shown that inhibition of falcipain2a-dependent hemoglobin digestion by specific inhibitors or by gene inactivation reduced parasite susceptibility to artemisinins19. Moreover, ring stages that do not massively digest hemoglobin display a reduced susceptibility to artemisinins59. |
| PF3D7_1302100 (PF13_0011), is a one-exon gene that codes for the gamete antigen 27/25 (Pfg27) produced at the onset of gametocytogenesis. The gene is specific to P. falciparum and its close relatives such as P. reichnowi. This is an abundant, dimeric phosphorylated cytoplasmic protein that binds RNA. The various KO lines generated display conflicting phenotypes some being deficient in gametocyogenesis60, while other Pfg27-defective lines undergo unimpaired gametocytogenesis up to stage V, mature gametocytes although absence of Pfg27 is associated with abnormalities in intracellular architecture of gametocytes61. The crystal structure shows that the protein forms a dimer, displays a particular RNA binding fold and possesses two Pro-X-X-Pro motifs (known ligands for various domains, including SH3 modules), which combine to form a receptacle for SH3 modules62. The P201T mutation is located in the C-terminal ProX-X-Pro motif and predicted to alter the spatial structure of the interaction domain and thus have functional consequences. |
| PF3D7_1459600 (PF14_0569), is a two-exon gene that codes for a 806 residue-long, conserved protein of unknown function. The P. yoelii ortholog has been annotated as the CAAT-box DNA binding subunit B. Close orthologs can be found only among the Plasmodium species. Proteomics data indicate that the protein is present in asexual (trophozoites, schizonts, merozoites and rings) and sexual (gametocytes) blood stages of P. falciparum. A predicted approx. 130 aa-long Interpro domain suggests presence of an N-terminal multi-helical, alpha-alpha 2-layered structural VHS fold, possibly involved in intracellular membrane trafficking. The rest of the coding sequence carries no specific domain signature. The S299T mutation is located within this “unknown” region. |
| PF3D7_1464500 (PF14_0603), is a five-exon gene that codes for a 3251 residue-long protein of unknown function, with 4 predicted transmembrane domains, but otherwise no specific domain signature. Apart from proteomics data indicating its expression and phosphorylation in schizonts, with possible expression in gametocytes and sporozoites as well, little is known about its putative function. The N1629S mutation is located in the middle of the protein, with unpredictable phenotypic impact. |
Extended Data Table 4.
Geographic origin and year of collection of archived blood samples studied for K13-propeller polymorphism
| Region | Province | Year of collection
|
Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001–2002 | 2003–2004 | 2005–2006 | 2007–2008 | 2009–2010 | 2011–2012 | |||
| Western Cambodia | Battambang | 64 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 71 | 135 |
| Pailin | 40 | 43 | 46 | 95 | 66 | 84 | 374 | |
| Pursat | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 43 | 19 | 72 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Southern Cambodia | Kampot | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Kampong Som | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 7 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Northern Cambodia | Oddar Meanchey | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 33 | 33 |
| Preah Vihear | 27 | 27 | 25 | 24 | 0 | 19 | 122 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Eastern Cambodia | Kratie | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 32 |
| Mondulkiri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| Ratanakiri | 56 | 30 | 22 | 0 | 8 | 35 | 151 | |
|
| ||||||||
| Total | 202 | 110 | 93 | 119 | 117 | 300 | 941 | |
Extended Data Table 5.
Polymorphisms observed in the K13-propeller in Cambodian P. falciparum isolates collected in 2001–2012 and in The Gambia (ref. 42)
| Codon Position | Amino Acid reference | Nucleotide reference | Amino Acid mutation | Nucleotide mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 449 | G | ggt | A | gCt |
| 458 | N | aat | Y | Tat |
| 474 | T | aca | I | aTa |
| 476* | M | atg | I | atA |
| 481 | A | gct | V | gTt |
| 493 | Y | tac | H | Cac |
| 508 | T | act | N | aAt |
| 527 | P | cct | T | Act |
| 533 | G | ggt | S | Agt |
| 537 | N | aat | I | aTt |
| 539 | R | aga | T | aCa |
| 543 | I | att | T | aCt |
| 553 | P | ccg | L | cTg |
| 561 | R | cgt | H | cAt |
| 568 | V | gtg | G | gGg |
| 574 | P | cct | L | cTt |
| 580 | C | tgt | Y | tAt |
| 584 | D | gat | V | gTt |
| 612** | E | gaa | D | gaT |
| 623 | S | agt | C | Tgt |
Observed in F32-ART5, not observed in Cambodia
Reported in The Gambia42, not observed in Cambodia
Extended Data Table 6.
Association between polymorphisms observed in the K13-propeller and KH subpopulations (ref. 15) in 150 P. falciparum isolates collected in 2009–2010 in Pursat (n=103) and Ratanakiri (n=47) provinces, Cambodia
| KH group | Province | Mutations in the K13-propeller
|
Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wildtype | C580Y | R539T | Y493H | |||
| KH1 | Pursat | 7 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 9 |
| Ratanakiri | 46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 46 | |
|
| ||||||
| KH2 | Pursat | 0 | 25 | 0 | 1 | 26 |
| Ratanakiri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
|
| ||||||
| KH3 | Pursat | 3 | 7 | 4 | 0 | 14 |
| Ratanakiri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
|
| ||||||
| KH4 | Pursat | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 |
| Ratanakiri | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
|
| ||||||
| KHA | Pursat | 15 | 19 | 2 | 6 | 42 |
| Ratanakiri | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |
|
| ||||||
| Total | 72 | 51 | 6 | 21 | 150 | |
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients and field staff involved in clinical trials and sample collections. We are grateful to the provincial health department directors and other staff of the Cambodian Ministry of Health. Clinical trials and sample collections were supported in part by the Global Fund Grant Malaria Program Rounds 6 (CAM-607-G10M-CNM3) and 9 (CAM-S10-G14-M), the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and USAID (through the World Health Organization), the US DOD Global Epidemic Information System, and the Intramural Research Program, NIAID, NIH. Laboratory work was supported by grants from Banque Natixis (to O.M.-P. and D.M.) and Laboratoire d’Excellence IBEID (Agence Nationale de la Recherche, France) and Institut Pasteur, Division International (ACIP A-10-2010). B.W. was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from Institut Pasteur, Division International; J.B. by an Institut Pasteur Paris Master-Pro fellowship; and D.M.by the French Ministry of Foreign Affairs. We are grateful to the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute and the MalariaGEN resource centre for sequencing, genotyping and population structure analysis of some Cambodian clinical samples, funded by the Wellcome Trust (098051; 090770/Z/09/Z) and the MRC (G0600718). We thank the Rotary Club-Versailles for funding computer equipment. P.R., D.M.B. and W.O.R. are staff members of the World Health Organization and the US Navy, respectively. They alone are responsible for the views expressed in this publication, and they do not necessarily represent the decisions, policy or views of the World Health Organization or the US Navy.
Footnotes
Online Content Any additional Methods, Extended Data display items and Source Data are available in the online version of the paper; references unique to these sections appear only in the online paper.
Supplementary Information is available in the online version of the paper.
Author Contributions B.W., S.M., A.B. and F.B.-V. produced the F32-ART5 and F32-TEM clonal lines and analysed their survival rates. F.A. and J.B. developed computational components of the whole-genome sequence analysis. C.B. and L.M. performed whole-genome sequencing. F.A., C.A., S.K., V.D., P.L., R.L., S.D., Se.S., So.S., C.M.C., D.M.B., W.O.R., B.G., T.F., P.R., J.L.B., R.M.F. and D.M. conducted clinical studies and collected parasite isolates. A.-C.L., N.K., S.K., V.D., S.M. and A.B. performed PCR and sequencing analyses. B.W., F.B.-V., V.D. and D.M. performed in vitro assays (RSA0–3h). O.M. provided genotyping and population structure data for Cambodian parasite isolates. J.-C.B. and O.M.-P. performed three-dimensional structure modelling. F.A., R.M.F., F.B.-V., O.M.-P. and D.M. conceived of the study, supervised the project, processed the data and wrote the manuscript with contributions from B.W., C.A., A.B. and J.-C.B.
Author Information The following reagents have been deposited to the MR4/BEI by D.M.:MRA-1236 (Plasmodium falciparum IPC3445 Pailin Cambodia 2010), MRA-1237 (Plasmodium falciparum IPC 3663 Pailin Cambodia 2010), MRA-1238 (Plasmodium falciparum IPC 4884 Pursat Cambodia 2011), MRA-1239 (Plasmodium falciparum IPC 5188 Ratanakiri Cambodia 2011), MRA-1240 (Plasmodium falciparum IPC 5202 Battambang Cambodia 2011) and MRA-1241 (Plasmodium falciparum IPC 4912 Mondulkiri Cambodia 2011).
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
References
- 1.Dondorp AM, et al. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:455–467. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization. Global Report on Antimalarial Drug Efficacy and Drug Resistance: 2000–2010. World Health Organization; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mita T, et al. Limited geographical origin and global spread of sulfadoxine-resistant dhps alleles in Plasmodium falciparum populations. J Infect Dis. 2011;204:1980–1988. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Roper C, et al. Intercontinental spread of pyrimethamine-resistant malaria. Science. 2004;305:1124. doi: 10.1126/science.1098876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wootton JC, et al. Genetic diversity and chloroquine selective sweeps in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 2002;418:320–323. doi: 10.1038/nature00813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Amaratunga C, et al. Artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Pursat province, western Cambodia:a parasite clearance rate study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:851–858. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(12)70181-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kyaw MP, et al. Reduced susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum to artesunate in southern Myanmar. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e57689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Noedl H, et al. Evidence of artemisinin-resistant malaria in western Cambodia. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2619–2620. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc0805011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Phyo AP, et al. Emergence of artemisinin-resistant malaria on the western border of Thailand: a longitudinal study. Lancet. 2012;379:1960–1966. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60484-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hien TT, et al. In vivo susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum to artesunate in Binh Phuoc Province, Vietnam. Malar J. 2012;11:355. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Flegg JA, et al. Standardizing the measurement of parasite clearance in falciparum malaria: the parasite clearance estimator. Malar J. 2011;10:339. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.White NJ. The parasite clearance curve. Malar J. 2011;10:278. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Witkowski B, et al. Novel phenotypic assays for the detection of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria in Cambodia: in-vitro and ex-vivo drug-response studies. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013;13:1043–1049. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70252-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cheeseman IH, et al. Amajor genome region underlying artemisinin resistance in malaria. Science. 2012;336:79–82. doi: 10.1126/science.1215966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Miotto O, et al. Multiple populations of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum in Cambodia. Nature Genet. 2013;45:648–655. doi: 10.1038/ng.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Takala-Harrison S, et al. Genetic loci associated with delayed clearance of Plasmodium falciparum following artemisinin treatment in Southeast Asia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:240–245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1211205110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lopera-Mesa TM, et al. Plasmodium falciparum clearance rates in response to artesunate in Malian children with malaria: effect of acquired immunity. J Infect Dis. 2013;207:1655–1663. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Witkowski B, et al. Increased tolerance to artemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum is mediated by a quiescence mechanism. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:1872–1877. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01636-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Klonis N, et al. Artemisinin activity against Plasmodium falciparum requires hemoglobin uptake and digestion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108:11405–11410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1104063108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vigan-Womas I, et al. An in vivo and in vitro model of Plasmodium falciparum rosetting and autoagglutination mediated by varO, a group A var gene encoding a frequent serotype. Infect Immun. 2008;76:5565–5580. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00901-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cui L, et al. Mechanisms of in vitro resistance to dihydroartemisinin in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Microbiol. 2012;86:111–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leang R, et al. Efficacy of dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine for treatment of uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax in Cambodia, 2008 to 2010. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:818–826. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00686-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sidhu AB, et al. Chloroquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites conferred by pfcrt mutations. Science. 2002;298:210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.1074045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Valderramos SG, et al. Identification of a mutant PfCRT-mediated chloroquine tolerance phenotype in Plasmodium falciparum. PLoS Pathog. 2010;6:e1000887. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bhisutthibhan J, et al. The Plasmodium falciparum translationally controlled tumor protein homolog and its reaction with the antimalarial drug artemisinin. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:16192–16198. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.26.16192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Eichhorn T, et al. Molecular interaction of artemisinin with translationally controlled tumor protein (TCTP) of Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85:38–45. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.10.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sanchez CP, et al. Polymorphisms within PfMDR1 alter the substrate specificity for anti-malarial drugs in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Microbiol. 2008;70:786–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Veiga MI, et al. Novel polymorphisms in Plasmodium falciparum ABC transporter genes are associated with major ACT antimalarial drug resistance. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e20212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Raj DK, et al. Disruption of a Plasmodium falciparum multidrug resistance-associated protein (PfMRP) alters its fitness and transport of antimalarial drugs and glutathione. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:7687–7696. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M806944200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Anderson TJ, et al. Are transporter genes other than the chloroquine resistance locus (pfcrt) and multidrug resistance gene (pfmdr) associated with antimalarial drug resistance? Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49:2180–2188. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.6.2180-2188.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Jambou R, et al. Resistance of Plasmodium falciparum field isolates to in-vitro artemether and point mutations of the SERCA-type PfATPase6. Lancet. 2005;366:1960–1963. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)67787-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Krishna S, et al. Artemisinins and the biological basis for the PfATP6/SERCA hypothesis. Trends Parasitol. 2010;26:517–523. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2010.06.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hunt P, et al. Gene encoding a deubiquitinating enzyme is mutated in artesunate-and chloroquine-resistant rodent malaria parasites. Mol Microbiol. 2007;65:27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hunt P, et al. Experimental evolution, genetic analysis and genome re-sequencing reveal the mutation conferring artemisinin resistance in an isogenic lineage of malaria parasites. BMC Genomics. 2010;11:499. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Borges S, et al. Genome-wide scan reveals amplification of mdr1 as a common denominator of resistance to mefloquine, lumefantrine, and artemisinin in Plasmodium chabaudi malaria parasites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011;55:4858–4865. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01748-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chavchich M, et al. Role of pfmdr1 amplification and expression in induction of resistance to artemisinin derivatives in Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:2455–2464. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00947-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen N, et al. Deamplification of pfmdr1-containing amplicon on chromosome 5 in Plasmodium falciparum is associated with reduced resistance to artelinic acid in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54:3395–3401. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01421-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Picot S, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of evidence for correlation between molecular markers of parasite resistance and treatment outcome in falciparum malaria. Malar J. 2009;8:89. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Price RN, et al. Mefloquine resistance in Plasmodium falciparum and increased pfmdr1 gene copy number. Lancet. 2004;364:438–447. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16767-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Sidhu AB, et al. Decreasing pfmdr1 copy number in Plasmodium falciparum malaria heightens susceptibility to mefloquine, lumefantrine, halofantrine, quinine, and artemisinin. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:528–535. doi: 10.1086/507115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Yuan J, et al. Chemical genomic profiling for antimalarial therapies, response signatures, and molecular targets. Science. 2011;333:724–729. doi: 10.1126/science.1205216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Amambua-Ngwa A, et al. Population genomic scan for candidate signatures of balancing selection to guide antigen characterization in malaria parasites. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Adams J, et al. The kelch repeat superfamily of proteins: propellers of cell function. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:17–24. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(99)01673-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Prag S, Adams JC. Molecular phylogeny of the kelch-repeat superfamily reveals an expansion of BTB/kelch proteins in animals. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003;4:42. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-4-42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Witkowski B, et al. Reduced artemisinin susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum ring stages in western Cambodia. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57:914–923. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01868-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Padmanabhan B, et al. Structural basis for defects of Keap1 activity provoked by its point mutations in lung cancer. Mol Cell. 2006;21:689–700. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2006.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Boyden LM, et al. Mutations in kelch-like 3 and cullin 3 cause hypertension and electrolyte abnormalities. Nature. 2012;482:98–102. doi: 10.1038/nature10814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Li X, Zhang D, Hannink M, Beamer LJ. Crystal structure of the Kelch domain of human Keap1. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:54750–54758. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410073200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Itoh K, et al. Keap1 represses nuclear activation of antioxidant responsive elements by Nrf2 through binding to the amino-terminal Neh2 domain. Genes Dev. 1999;13:76–86. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang DD, Hannink M. Distinct cysteine residues in Keap1 are required for Keap1-dependent ubiquitination of Nrf2 and for stabilization of Nrf2 by chemopreventive agents and oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23:8137–8152. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.22.8137-8151.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Bozdech Z, Ginsburg H. Antioxidant defense in Plasmodium falciparum—data mining of the transcriptome. Malar J. 2004;3:23. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-3-23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nesser NK, Peterson DO, Hawley DK. RNA polymerase II subunit Rpb9 is important for transcriptional fidelity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:3268–3273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511330103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kettenberger H, Armache KJ, Cramer P. Architecture of the RNA polymerase II-TFIIS complex and implications for mRNA cleavage. Cell. 2003;114:347–357. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)00598-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dorin-Semblat D, Sicard A, Doerig C, Ranford-Cartwright L, Doerig C. Disruption of the PfPK7 gene impairs schizogony and sporogony in the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Eukaryot Cell. 2008;7:279–285. doi: 10.1128/EC.00245-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tewari R, et al. The systematic functional analysis of Plasmodium protein kinases identifies essential regulators of mosquito transmission. Cell Host Microbe. 2010;8:377–387. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.09.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Rosenthal PJ, McKerrow JH, Aikawa M, Nagasawa H, Leech JH. A malarial cysteine proteinase is necessary for hemoglobin degradation by Plasmodium falciparum. J Clin Invest. 1988;82:1560–1566. doi: 10.1172/JCI113766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sijwali PS, et al. Plasmodium falciparum cysteine protease falcipain-1 is not essential in erythrocytic stage malaria parasites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:8721–8726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402738101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sijwali PS, Koo J, Singh N, Rosenthal PJ. Gene disruptions demonstrate independent roles for the four falcipain cysteine proteases of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006;150:96–106. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2006.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Klonis N, et al. Altered temporal response of malaria parasites determines differential sensitivity to artemisinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:5157–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217452110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lobo CA, Fujioka H, Aikawa M, Kumar N. Disruption of the Pfg27 locus by homologous recombination leads to loss of the sexual phenotypein P. falciparum. Mol Cell. 1999;3:793–798. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)80011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Olivieri A, et al. The Plasmodium falciparum protein Pfg27 is dispensable for gametocyte and gamete production, but contributes to cell integrity during gametocytogenesis. Mol Microbiol. 2009;73:180–193. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sharma A, Sharma I, Kogkasuriyachai D, Kumar N. Structure of a gametocyte protein essential for sexual development in Plasmodium falciparum. Nature Struct Biol. 2003;10:197–203. doi: 10.1038/nsb899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


