Abstract
A wide spectrum of clinical manifestations has become a hallmark of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) COVID-19 pandemic, although the immunological underpinnings of diverse disease outcomes remain to be defined. We performed detailed characterization of B cell responses through high-dimensional flow cytometry to reveal substantial heterogeneity in both effector and immature populations. More notably, critically ill patients displayed hallmarks of extrafollicular B cell activation and shared B cell repertoire features previously described in autoimmune settings. Extrafollicular activation correlated strongly with large antibody-secreting cell expansion and early production of high concentrations of SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibodies. Yet, these patients had severe disease with elevated inflammatory biomarkers, multiorgan failure and death. Overall, these findings strongly suggest a pathogenic role for immune activation in subsets of patients with COVID-19. Our study provides further evidence that targeted immunomodulatory therapy may be beneficial in specific patient subpopulations and can be informed by careful immune profiling.
In 2019, a novel single-stranded RNA coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) emerged and caused the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic. A defining feature of SARS-CoV-2 infection is the diversity of clinical manifestations and outcomes ranging from asymptomatic disease to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multiorgan failure and death. Severe manifestations are strongly associated with an overactive inflammatory response; multiple reports show associations with interferon (IFN)-γ-regulated cytokine interleukin (IL)-6 and chemokine CXCL10 (also known as IP-10)1, and others in the development of cytokine storms2. Modulating inflammation through corticosteroids has substantial clinical benefit and is now the standard of care. More targeted approaches to modulating cytokine-induced inflammation through single or combination therapies continue to be investigated despite the failure of anti-IL-6 studies to meet their primary endpoints3–5.
Despite the critical role of the inflammatory response in COVID-19 infection, specific immunological underpinnings of different clinical outcomes remain to be understood. Neutralizing antibodies have been a natural avenue of investigation with studies identifying rapid antigen-specific responses in patients with severe disease6 and robust viral-specific responses capable of in vitro virus neutralization in patients who recovered from COVID-19 (refs.7,8). Yet, anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody responses may have limited longevity, and rapid decay may characterize asymptomatic patients that effectively control the infection9,10. Taken together, these findings strongly suggest important differences in the nature and regulation of the effector B cell responses associated with mild versus severe disease, and indicate the need to dissect the B cell origins of the antibody-secreting cells (ASCs) responsible for different antibody responses.
Effector B and T cell responses control acute viral infections and provide the foundation for the subsequent development of specific immunological memory. In contrast to extensive T cell studies, human effector B cell responses remain poorly understood beyond the expansion of ASCs. In mice, early primary antiviral responses are mediated by extrafollicular (EF) differentiation of naive B cells into short-lived ASCs independent of traditional germinal center incorporation11. While EF responses in different models are heterogeneous in their requirement for T cell help, it is now established that mouse EF B cell responses can undergo affinity maturation and generate both memory and long-lived plasma cells even under T cell independent conditions12,13. Driven by IFN-γ and IL-21, Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7-dependent EF B cells express high levels of T-bet+ and CD11c and play critical roles in viral clearance in mouse models14. Of note, this same pathway is also highly inflammatory, and pathogenic in models of autoimmunity15,16.
However, studies of EF B cell responses in human protective and pathogenic responses were long hampered by lack of proper phenotypic identification of their cellular components. We described these components and their contribution to the generation of pathogenic autoreactive ASC responses in human systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)17. Exploiting the vigorous ASC responses characteristic of active SLE, we reported that human EF effector B cell responses are mediated by the expansion of a unique population of CD11c+ activated naive (aN) B cells that differentiate into effector cells lacking naive (IgD) and memory (CD27) markers or ‘double-negative’ (DN) B cells18. The fraction of DN B cells lacking CXCR5 and CD21 (DN2 cells) is greatly expanded in patients with active SLE, and this expansion correlates with increased disease activity and poorer outcomes. We also showed that DN2 cells are induced through IFN-γ–IL-21 in a TLR7-dependent fashion18, correlate with IL-6 and IP-10 serum concentrations19 and are epigenetically poised for ASC differentiation through T-bet-driven networks20.
Here, we show that critically ill patients with COVID-19 displayed hallmarks of EF B cell responses similar to those we have previously reported in autoimmune settings18. EF activation correlated strongly with class-switched ASC expansions, high concentrations of SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing antibodies and poor clinical outcomes.
Results
High-dimensional B cell phenotyping of acute COVID-19.
The identification of new human B cell subsets18,21,22 and their integration in a coherent classification23 enable the application of high-dimensional flow cytometry (FCM) to accurately identify B cell profiles while providing functional context to understand infection response course. To this end, we studied 17 patients with confirmed COVID-19 infection using 24 marker FCM panels (plus non-B cell dump and viability staining) that accurately identify B cell populations, assess activation status and indicate homing potential through integrin and chemokine receptor modulation (Supplementary Table 1). Of the COVID-19 cohort, 10 patients were critically ill and required intensive care unit (ICU) admission (severe COVID-19; ICU-C), and 4 of the 10 patients died (Supplementary Table 2). This group was compared to 7 outpatients with milder illness (outpatient COVID; OUT-C) and 17 healthy donors (HD).
Despite reports of lymphocytopenia24, patients with COVID-19 displayed elevated numbers of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), with CD19+ B cells significantly increased relative to HDs (Extended Data Fig. 1). B cell profiling with high-dimensional FCM identified primary cell populations (transitional (Tr), naive (N), DN, memory (M) and ASCs), which could be then fractionated into 14 nonredundant, secondary B cell populations of established significance (Fig. 1a–f and Table 1)23. The three clinical groups displayed distinct B cell profiles characterized by either expansions of ASCs and DN2 cells (ICU-C) or transitional cells (OUT-C; Fig. 1a–f).
Fig. 1 |. B cell characterization in acute COVID-19 infection by high-dimensional FCM.
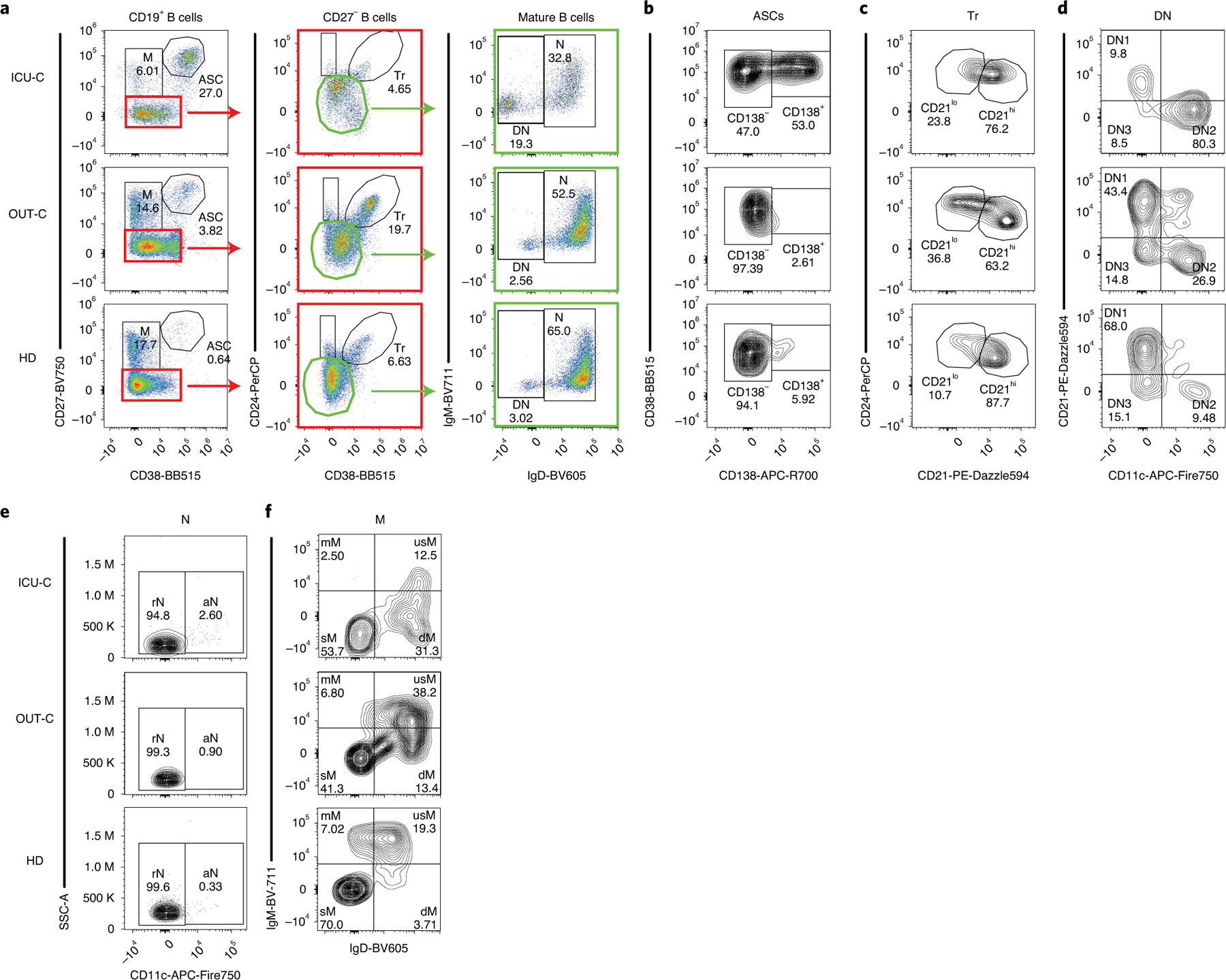
a–f, PBMCs from HD (n = 17), OUT-C (n = 7) or ICU-C (n = 10) patients were analyzed by FCM. Representative patient samples were selected for display (OUT-C: day 4 after symptom onset; ICU-C: day 7 after symptom onset). a, Primary population gating of representative patient samples. b, ASC sub-gating (CD138+ ASC and CD138− ASC) of representative patient samples. c, Transitional B cell sub-gating (CD21lo Tr and CD21hi Tr) of representative patient samples. d, Double-negative B cell sub-gating (DN1, DN2 and DN3) of representative patient samples. e, Naive B cell sub-gating (resting naive (rN) and aN) of representative patient samples. f, Memory B cell sub-gating (mM, usM, dM and sM) of representative patient samples displayed a decrease in usM in ICU-C. dM, IgD-only memory; mM, IgM-only memory; usM, unswitched memory.
Table 1 |.
Standard B cell definitions
| B cell type | Primary population | Secondary populations |
|---|---|---|
| Transitional |
Tr: CD19+
CD27− CD38int CD24+ |
CD21lo Tr: CD24hi CD21− |
| CD21hi Tr: CD24lo CD21+ | ||
| Naive |
N: CD19+
CD27− CD38− CD24− lgD+ |
aN: CD11c+ |
| rN: CD11c− | ||
| Double negative |
DN: CD19+
CD27− CD38− CD24− IgD− |
DN1: CD11c− CD21+ |
| DN2: CD11c+ CD21− | ||
| DN3: CD11c− CD21− | ||
| Memory |
M: CD19+
CD27+ CD38−/lo |
mM: lgM+ IgD− |
| dM: IgM− lgD+ | ||
| usM: lgM+ lgD+ | ||
| sM: IgM− IgD− | ||
| ASCs |
ASC: CD19+
CD27+ CD38hi |
CD138neg ASC: CD138− |
| CD138pos ASC: CD138+ |
To aid in exploration of the dataset, a composite sample was created by representative downsampling (1,000 cells per patient) of FCM results obtained from HD (n = 12), OUT-C (n = 7) and ICU-C (n = 10) patients using an identical staining panel (Methods; FCM panel V2), and results were recombined for combined analysis. A uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) algorithm for dimensionality reduction25 was applied to the composite sample for all assessed fluorescence parameters, and cells from the composite sample were mapped in Cartesian space (Fig. 2a). Overlaying a 90% equal probability contour from each cohort revealed clear phenotypic B cell separation in the three clinical groups (Fig. 2b). Three major cell clusters are visually apparent in the projection (Fig. 2a–c). Cluster 1 is highly diverse, predominantly composed of transitional, naive and IgM+ memory B cell subsets (Fig. 2c,d). Cluster 2 is more homogeneous, consisting of DN populations 1–3 and the switched memory (sM) compartment (Fig. 2c,d). Importantly, in keeping with our previous identification of close transcriptional similarity between DN1 and sM cells18, there is a clear overlay between these populations, while DN2 B cells formed a distinct cluster within the larger DN density (Fig. 2c,d). Of note, these projections indicated a split in the DN1 and DN3 compartments seemingly driven by expression of human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR and CD19—an indication of heterogeneity within these populations that requires further interrogation (Fig. 2e). ASC populations split by the CD138 expression pattern defined cluster 3 (Fig. 2c,d). To aid in visual exploration of the dataset, selected marker expression mapped onto these UMAP projections are provided in Fig. 2e. Together, these data provide unique insight into the stark transitions in the B cell compartment following severe SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Fig. 2 |. UMAP projections of compiled COVID-19 FCM dataset.
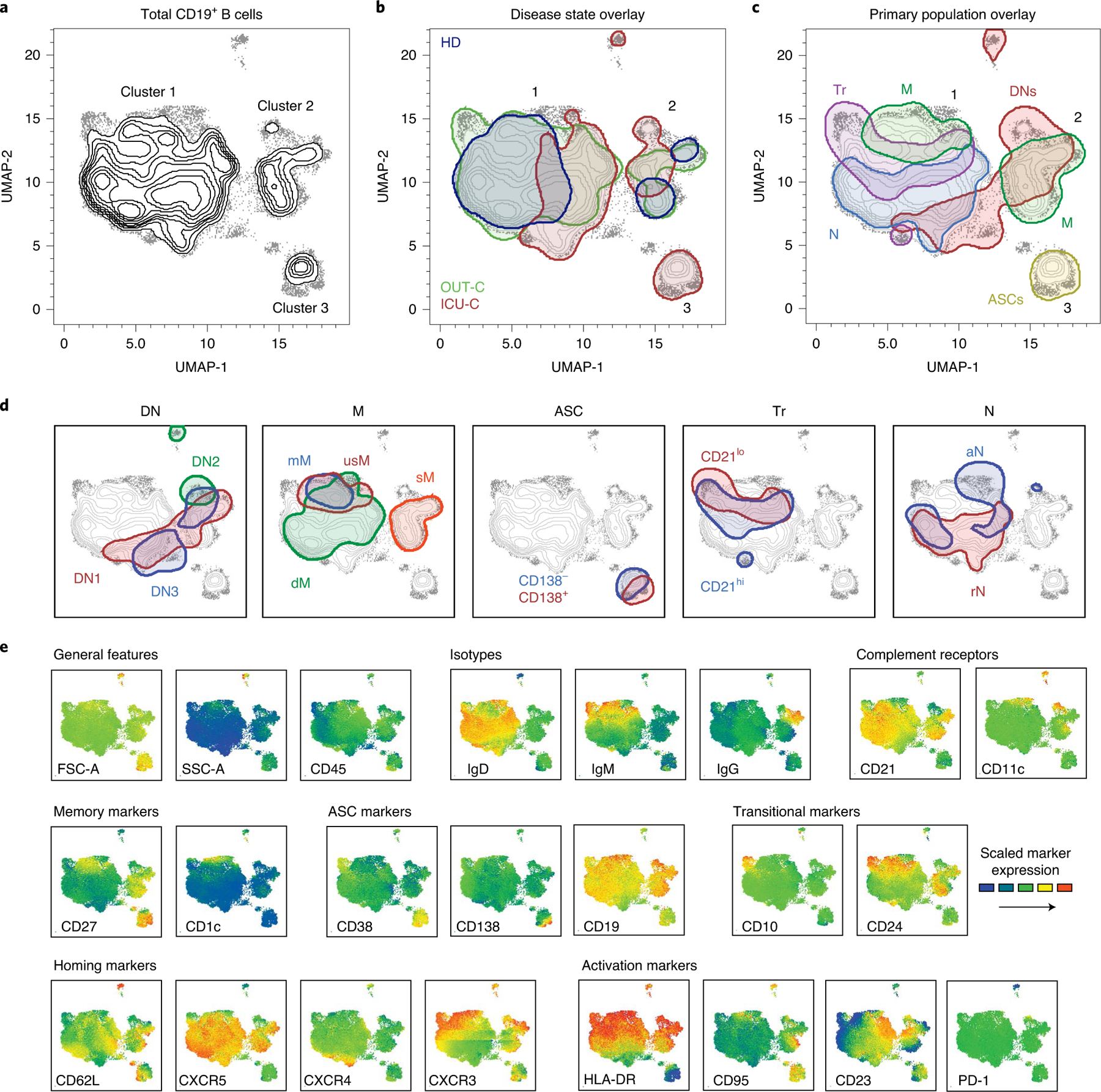
a, UMAP projection of composite patient samples. Composite sample was derived from 1,000 representative cells from patients analyzed with spectral panel V2 (Methods; HD: n = 12; OUT-C: n = 7; ICU-C: n = 10). b–d, Outlined regions represent the 90% equal probability contouring from the indicated classification. b, Patient disease status overlaid on the composite UMAP projection from a. c, Primary populations as gated in Fig. 1a and Table 1 overlaid on the composite UMAP projection from a. d, Secondary populations as gated in Fig. 1b–f and Table 1 overlaid on the composite UMAP projection from a. e, Heat maps of select marker expression overlaid on composite UMAP projection from a. b–d, Outlined regions contain 90% of cells derived from the indicated classification.
Increased DN2 B cells and ASCs correlate with severe COVID-19.
By overlaying disease states onto the composite sample and subtracting overlapping densities, differential cellular signatures became visually apparent (Fig. 3a), with three main regions of interest (ROIs) distinguishing ICU-C and OUT-C patients, both from each other and from HD. Region 1 highlights an area of high CD11c expression by the ICU-C cohort demarcating aN and DN2 populations (Fig. 3b), which were significantly enriched in ICU-C patients (Fig. 3c,d). In accordance with previous studies18, both aN and DN2 cells expressed the highest levels of CD11c and the IFN-γ-inducible transcription factor T-bet (Fig. 3e,f). Region 2 comprises ASCs, a population whose expansion was readily observed following vaccination and other instances of acute infection26,27. In COVID-19 infection, robust ASC formation correlated with negative disease outcomes, with ICU-C patients presenting with significantly higher frequencies of ASCs than other groups (Fig. 3g). Notably, ASC responses in ICU-C patients were highly enriched in more mature CD138+ cells relative to both OUT-C and HDs—a response feature previously observed in SLE17 (Fig. 3h,i). Finally, region 3 mapped neatly to the CD21lo Tr subset (Fig. 3a), which was significantly increased in OUT-C patients. Overall, transitional cells constituted more than 10% of the total B cell compartment in OUT-C patients, with CD21lo cells making up more than half of the overall frequency gain (Fig. 3j,k). CD21lo Tr cells expressed higher levels of markers of the early transitional compartment (IgM, CD24, CD10), but less CD21 and CXCR5 (Fig. 3l), than CD21hi cells. Of note, in comparison with similarly identified cells from the HD cohort, CD21lo Tr cells from OUT-C patients exhibited higher expression of CD138, a marker whose expression is typically considered to be restricted to ASCs (Fig. 3l). Altogether, these data suggest a robust activation of effector B cells in severe COVID-19, unmatched by the responses observed in more mild disease courses.
Fig. 3 |. Unique B cell utilization by ICU patients and outpatients with COVID-19.
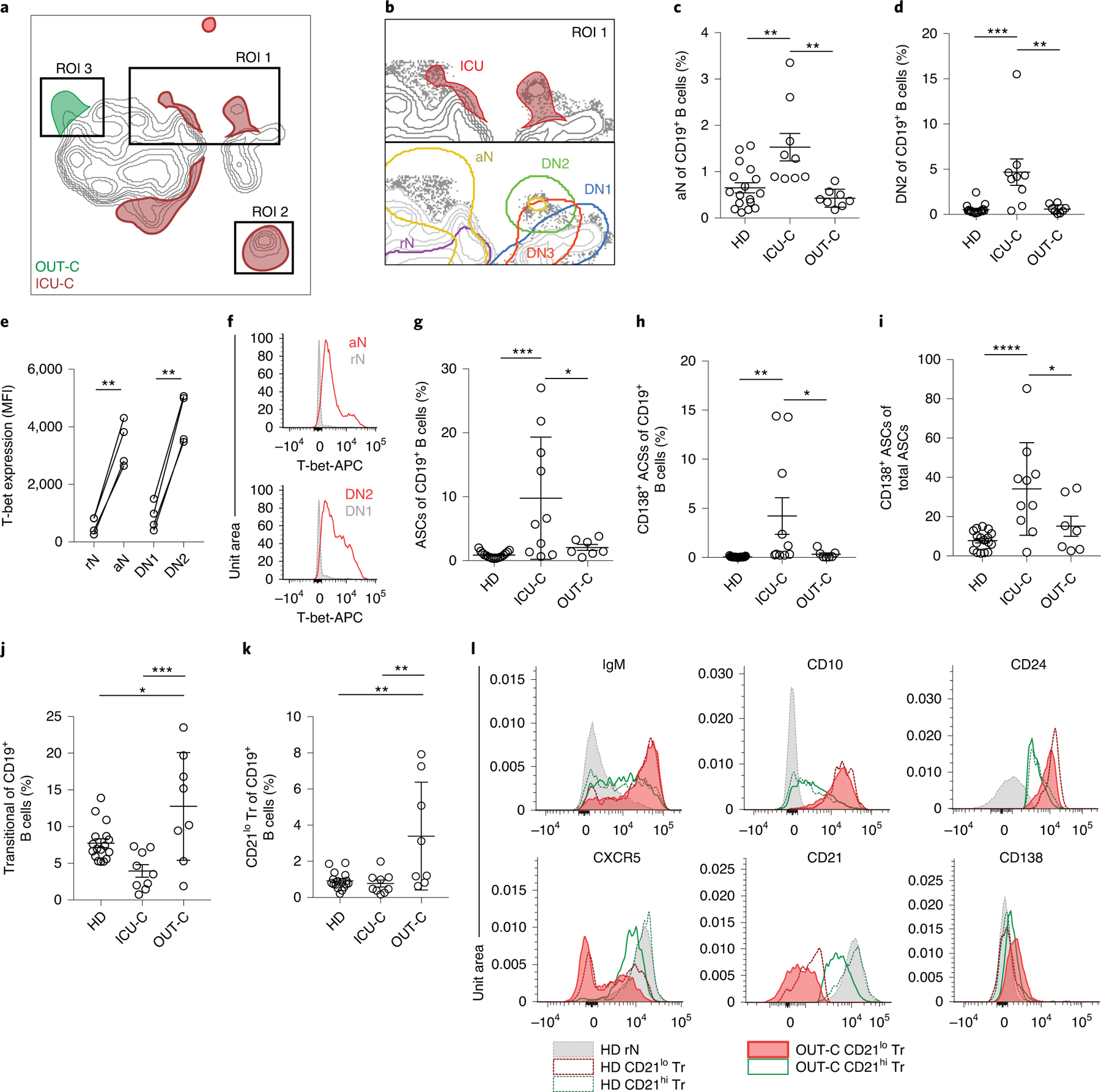
a, Overlay of patient disease status on the composite UMAP projection as in Fig. 2a (HD: n = 12; OUT-C: n = 7; ICU-C: n = 10). Regions of overlapping density are subtracted to display ROIs indicating unique population use. b, Top: magnification of ROI 1 from a. Bottom: indicated secondary populations overlaid on a magnification of region 1 from a. c, aN frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD (n = 17), ICU-C (n = 10) or OUT-C (n = 7) cohorts. d, DN2 frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohorts. e, T-bet expression in indicated secondary populations from ICU-C patients by intracellular FCM (n = 4). MFI, median fluorescence intensity. f, Representative histograms of T-bet expression as in e. APC, antigen-presenting cell. g, ASC frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohorts. h, CD138+ ASC frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohorts. i, CD138+ ASC frequency of total ASCs in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohorts. j, Tr frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohorts. k, CD21lo Tr frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohorts. l, Histograms of indicated marker expression by FCM. c–k, Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons testing between all groups. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001. Summary statistics (c–k): mean ± standard deviation (s.d.).
Severe COVID-19 drives SLE-like extrafollicular responses.
The use of secondary population frequencies as features for the hierarchical clustering of patients with COVID-19 demonstrated a near-perfect separation between the ICU-C and OUT-C cohorts, driven primarily by a coordinated increase in the more severe group of both aN and DN2 cell populations (Fig. 4a). A novel DN population (DN3), previously unreported in other conditions and defined by the absence of both CD21 and CD11c, consistently fell alongside aN and DN2 populations (Fig. 4a). Their association with these EF constituents and similarly reduced expression of CD21 suggests relevance to this effector pathway (Fig. 4a and Extended Data Fig. 2a,b). Increased frequency of all three activated CD21− populations was highly correlated with the ASC expansion described above (Fig. 4a), forming a population cluster that defined the responses within the critically ill patients. EF pathway activation was not a reflection of infection duration as both EF-high (CoV-A) and EF-low (CoV-B) clusters were sampled at similar times after symptom onset (Fig. 4b).
Fig. 4 |. Severe COVID-19 correlates with SLE-like activation of the EF pathway.

a, Heat map of secondary population frequency z-scores by outpatient (purple; n = 7), ICU (green; n = 6) or deceased (red; n = 4) patients who tested positive for COVID-19. Multivariate clustering of patients by Ward’s method is represented by dendrograms. Clusters were designated as CoV-A and CoV-B for downstream analysis. Black boxes highlight transitional B cells or populations previously (DN2, aN) or currently (DN3) implicated in EF responses. The red box and dagger indicate patients analyzed by single-cell V(D)J analysis in Fig. 5. preMZ, precursors of marginal zone B cells. b, Patient sample collection times following symptom onset in CoV-A (n = 9) and CoV-B (n = 8) clusters. c, Representative plots of DN population composition in HD, CoV-A, CoV-B and SLE patient groups. d, DN composition analysis in HD (n = 17), CoV-A (n = 9), CoV-B (n = 8) and SLE (n = 7) patient groups. e, Outer ring represents the mean DN population composition of patient groups. Inner ring represents the mean DN2:DN1 ratios of patient groups. f, DN2:DN1 ratios in HD, CoV-A, CoV-B and SLE patient groups. g, usM frequency of CD19+ B cells in HD (n = 17), CoV-A (n = 9) and CoV-B (n = 8) groups. h, Homing receptor surface expression in follicular (rN and DN1) versus EF (aN and DN2) populations observed in CoV-A (n = 9) patients. b, Differences between groups were analyzed by a two-tailed Student’s t-test. d–h, Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons testing between groups. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001; NS, not significant. Summary statistics (b–g): mean ± s.d.
We have previously observed that EF pathway activation, particularly the increased frequency of DN2 B cells, was accompanied by concordant reductions in the DN1 compartment17,18,20. Direct comparison of the CoV-A cluster to patients with active SLE revealed highly similar DN features (Fig. 4c) with strong skewing toward the ASC-associated DN2 subset in both groups (Fig. 4d,e). Thus, DN2:DN1 ratios, an important reflection of EF to follicular response dynamics, were significantly higher in both CoV-A and active SLE groups (Fig. 4f). This phenotype was associated with a contraction of unswitched memory cells, a feature consistently observed in SLE and other autoimmune diseases17,28,29 (Fig. 4g). In keeping with an EF nature, chemokine receptor analysis in patients with COVID-19 showed a decrease in follicular homing predisposition through CXCR5 and a corresponding increase in CXCR3—a mediator of homing to tissue undergoing IFN-γ-driven inflammation (Fig. 4h).
An important consideration in this study cohort was the heavy skewing of the ICU-C cohort toward African American (AA) patients, while HD and OUT-C groups included more patients of European ancestry. As AA patients have been previously shown to have higher baseline B cell responsiveness, and EF responses specifically18, it was important to understand if this activation signature was attributable to baseline demographic differences. Hence, we evaluated a retrospective cohort of AA HDs (n = 24), by FCM, to assess ASC response, DN2:DN1 ratio and usM reduction, relative to HD, OUT-C and ICU-C groups (Extended Data Fig. 3). In all three metrics, AA HDs were slightly skewed from our current HD cohort, but significantly different from the ICU-C cohort, giving confidence that the responses identified in the ICU-C cohort were not due to changes in baseline B cell composition across demographics. Accordingly, these data confirm that patients with severe COVID-19 display many of the hallmarks of dominant EF responses previously reported in SLE (Extended Data Fig. 4).
Germline clonotypes dominate the COVID-19 ASC repertoire.
To understand the nature of the repertoire in severe COVID-19, ASCs from a critically ill patient from the CoV-A cluster (Fig. 4a) was analyzed by single-cell V(D)J repertoire sequencing. Isotype analysis revealed that ASCs utilized a balanced IgM, IgG1 and IgA1 signature (Fig. 5a). Moreover, a large fraction of all the clonotypes identified (>3% of all clonotypes and 60% of the top 15 clonotypes) displayed contemporaneous connections between IgM and IgG1 or IgA1, demonstrating ongoing isotype switching (Fig. 5b). Also consistent with ongoing maturation and antigen selection, the ASC V(D)J repertoire was characterized by the presence of oligoclonal expansions, with the top ten clonotypes making up more than 12% of the overall repertoire (n = 2,017 clonotypes; Fig. 5c). Bulk V(D)J sequencing of CD138-enriched ASCs from two additional ICU-C patients demonstrated similar oligoclonality, but with more pronounced clonotype expansions, individually contributing 1–8% of the total repertoire (Fig. 5c). This observation was similar to previous studies characterizing ASCs in both flaring SLE and in response to influenza or tetanus vaccination17. In addition, single-cell sequencing identified individual multimember clonal lineages, including the two largest clonotypes, with complex branching patterns, class switching and broad ranges of somatic hypermutation (SHM) indicative of robust antigen selection (Fig. 5c,d). Nevertheless, a majority of the clonotypes identified in this patient had remarkably low mutation frequencies, especially clonotypes making up the IgA1 and IgG1 compartments (Fig. 5e). Indeed, more than half of the clonotypes obtained expressed germline VH genes (Fig. 5f). This pattern is consistent with the presence of newly recruited EF clones, as we previously reported in SLE17.
Fig. 5 |. ASC compartment displays low levels of SHM across diverse isotypes.

a, Isotype usage in naive B cells and ASCs through single-cell V(D)J analysis of ICU-C patient samples (Figs. 4a and 6i; day 12 after symptom onset). b, Circos plot from ASCs in a connecting observed clonotypes containing cellular members in both unswitched (IgM) and switched compartments. c, Sample clonality of ICU patient ASCs assessed through single-cell (scVDJ patient 1) or bulk (bVDJ patients 2 and 3) V(D)J repertoire sequencing. d, Representative lineage trees from patient 1 displaying evidence of SHM. e, Distribution of average clonotype mutation frequencies by isotype in patient 1. f, Percentage of clonotypes in each isotype that display exclusively germline IgHV sequences. g, Representative clonotypes using IGHV4–34 with intact AVY hydrophobic patches in patient 1. h, Concentrations of serum 9G4-idiotype antibodies in HD (n = 52), OUT-C (n = 6) or ICU-C (n = 9) cohorts. Red coloring and dagger indicate the patient analyzed by single-cell V(D)J analysis (a–g). Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison testing between groups. ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001. Summary statistics: mean ± s.d.
Another hallmark of the SLE repertoire is defective tolerance resulting in increased frequencies of disease-specific IgHV4–34 B cells and VH4–34-encoded 9G4-idiotype autoantibodies. These antibodies display intrinsic autoreactivity against a variety of self-antigens (nucleic acids and blood-group antigens among others), which is mediated by a hydrophobic patch encoded in the germline framework 1 (FR1)30. In healthy individuals, elimination of the FR1 patch through somatic mutation allows the expression of non-autoreactive, protective IgHV4–34 antibodies (clonal redemption)31. In contrast, the FR1 patch was present in 85% of all VH4–34-expressing clonotypes from the single-cell sequencing, including expanding lineages with evidence of SHM (Fig. 5g). In keeping with the sequencing data, ICU-C patients expressed significantly higher concentrations of serum 9G4 antibodies whose detection relies on the preservation of the VH4–34 FR1 patch (Fig. 5h). These data suggest that, in addition to effector pathway activation, perturbations in the ASC repertoire are highly consistent with those previously characterized in EF-driven responses.
Robust extrafollicular responses correlate with neutralizing antibody titers.
EF response characterization has identified the pathway as peripherally focused, inflammatory, and highly associated with IL-6 and IP-10 (refs.19,20,32). Both of these factors have now been identified as biomarkers of poor prognosis in the COVID-19 literature1 and could be identified at increased expression in the CoV-A cluster (Fig. 6a,b). In keeping with those studies, four of the five patients with the highest concentrations of IL-6 did not survive (Fig. 6b). C-reactive protein (CRP), an acute phase reactant in the IL-6 pathway commonly used as a biomarker of COVID-19 severity, was also increased in the ICU-C cohort (Fig. 6c) and correlated with IL-6 and IP-10 concentrations in patients with COVID-19 (Fig. 6d,e). Importantly, the DN2 magnitude within the DN compartment was also significantly associated with CRP concentrations, indicating that the extent of EF activation may serve as a correlate of disease severity (Fig. 6f).
Fig. 6 |. EF response intensity is correlated with inflammatory biomarkers and high neutralizing antibody titers.

a, CXCL10 (IP-10) plasma concentration in HD (n = 13), CoV-A (n = 8) or CoV-B (n = 5) cohort. The asterisk denotes the highest value exceeding the testing range and was identified to be a statistical outlier (P < 0.00001). P-value reporting in parentheses indicates testing with outlier removed. b, IL-6 plasma concentration of HD (n = 13), CoV-A (n = 8) or CoV-B (n = 5) cohort. c, CRP concentration in the plasma of HD (n = 13), CoV-A (n = 8) or CoV-B (n = 5) cohort. d, Linear regression of CRP values as a function of IP-10 plasma levels (with outlier removed). e, Linear regression of CRP values as a function of IL-6 plasma levels. f, Linear regression of log(CRP) values as a function of DN2 B cell frequency of total DN B cells. g, RBD-specific responses grouped by indicated isotype in HD (n = 13), ICU-C (n = 10) or OUT-C (n = 7) cohort. h, RBD-specific responses as a function of time in HD, ICU-C or OUT-C cohort. Solid lines represent quadratic regression; shaded areas denote 95% confidence intervals of quadratic regression. i, Regression analyses of in vitro viral neutralization as a function of patient serum dilution in HD (n = 3), CoV-A (n = 4) or CoV-B (n = 3) clusters. Dagger indicates patient analyzed by single-cell V(D)J analysis (Fig. 5a–g). a–c,g, Statistical significance was determined using ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparisons testing between groups. a–g, *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001. Summary statistics: median (a–c); mean ± s.d. (g).
While mouse EF responses can effectively undergo antigen-driven affinity maturation13, and human SLE EF responses are enriched for autoreactivity even in clones with low frequency of SHM17, we wondered whether such responses would be associated with low titers of SARS-CoV-2-specific serum antibodies in COVID-19 infection. Instead, serum antibody responses against the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein were higher in the more severe group (Fig. 6g). Consistent with the B cell antigen receptor-sequencing data, SARS-CoV-2-specific responsiveness was broad, with participation of IgM, IgA and IgG antibodies (Fig. 6g). Importantly, and in accordance with previous findings6, ICU-C responses were higher than outpatient responses and occurred very early in the infection course with significantly elevated titers by day 5 after symptom onset (Fig. 6h). To understand if these elevated titers were capable of neutralization, selected serums were tested using an in vitro neutralization assay. Concordant with anti-RBD activity, CoV-A cohort serums were consistently higher in neutralization capacity than CoV-B or HD serums, thereby confirming antibody functionality (Fig. 6i). In total, these data suggest that high concentrations of neutralizing antibodies are correlated with robust EF response activation but are insufficient to resolve the disease course in severe COVID-19.
Discussion
SARS-CoV-2 infection presents major challenges with its spectrum of illness severity and seemingly maladaptive immune response33. An abundance of evidence indicates that immune response quality may contribute to heterogeneous clinical manifestations and adverse outcomes. By and large, this model stems from the study of soluble inflammatory mediators and the cellular correlates of severe disease, while their mechanistic underpinnings remain poorly understood1,34,35. Here, we report that, in COVID-19, disease severity and poor clinical outcomes are closely correlated with intense activation of the EF B cell pathway despite the presence of high titers of anti-SARS-CoV-2 RBD antibodies with serum-neutralizing activity. This model is validated by recent work identifying a lack of germinal center formation in the spleens and lymph nodes of patients that have succumbed to COVID-1936. The immunological landscape associated with this effector B cell mobilization in COVID-19 is highly similar to the one observed in patients with active autoimmune processes, and in particular with active SLE. Although detailed antigen-specific studies are needed, meaningful similarities between these groups extend beyond the cellular B cell profile and also include the molecular properties of the B cell antigen receptor repertoire expressed by the responding ASCs.
A striking feature of severe COVID-19 is the strong expansion of the ASC compartment relative to milder disease, a finding that could be explained in several, non-mutually exclusive ways. Perhaps the most straightforward interpretation is that greater ASC expansions reflect more severe infection with higher viral load/antigen burden. In this model, the high number of ASCs represents a productive humoral response that, for reasons that are yet unclear, fails to resolve the disease course despite prolonged, elevated, neutralizing antibody titers across multiple isotypes. It would suggest that, for a subset of patients, robust humoral immune responses are insufficient to provide protection from severe disease. Elucidating whether our results may be explained by a direct relationship between viral load and the intensity of downstream immunological events would require precise longitudinal measurements of antigenic load in multiple sites, including the lung. However, mitigating this possibility are reports of similar viral loads in respiratory samples at early time points following infection between mild and severe patients and by the observation that asymptomatic patients may fail to generate a sustained antibody response despite having high viral loads9.
Alternatively, the distinct B cell response in severe COVID-19 could be consistent with a direct pathogenic role, or reflective of the upstream activation of T cells or innate immune responses33,35,37,38. In the latter scenario, disease-associated B cell profiles would represent a proxy for the associated pathogenic mechanisms. In either case, distinct B cell responses in patients with COVID-19 might serve as biomarkers of disease severity and outcome, a possibility that needs to be formally established through larger prospective studies.
Direct B cell pathogenesis has been demonstrated across multiple disease states, through both antibody-dependent and antibody-independent mechanisms39–42. Antibody-independent B cell functions are well established in infections and autoimmunity, and can be mediated through multiple mechanisms, including the generation of inflammatory cytokines such as IFN-γ, IL-6, GM-CSF and tumor-necrosis factor (TNF)-α, a cytokine now implicated in the lack of germinal center formation in COVID-19 (ref.36). In addition to B cells, production of proinflammatory cytokines can also be carried out by ASCs43,44, potentially explaining the correlation between the expansion of these cells and severe COVID-19 infection. The production of pathogenic cytokines by ASCs and/or EF B cells in COVID-19 remains to be experimentally addressed.
Antibody-mediated pathogenesis can also be mediated by multiple mechanisms, including the induction of tissue damage through the activation of inflammatory macrophages, as recently described in COVID-19 (ref.45). It is also possible that antibodies generated through enhanced EF B cell responses could be pathogenic on the basis of autoreactivity, as previously demonstrated in human SLE17,46. Our work has demonstrated that, in active SLE, this pathway is greatly enriched in disease-specific autoreactive cells that contribute a major fraction of contemporaneous serum autoantibodies. Low mutation IGHV4–34 ASCs, known contributors of autoreactive antibodies in SLE, are enriched in severe COVID-19 and, as in SLE, are closely correlated with both disease severity and AA ancestry. Thus, our data are broadly consistent with defective enforcement of B cell tolerance both in severe COVID-19 and active SLE resulting in significant increases of autoreactive serum 9G4 autoantibodies. Whether defective B cell tolerance is a general feature of sustained EF responses remains to be determined. It also unknown whether autoantibodies play a pathogenic role in acute severe COVID-19 infection; however, this model would be supported by the previous description of cross-reactivity between anti-spike antibodies and the lung epithelial marker Annexin 2 in SARS-CoV-1 infection47 and the reported relationship between anti-phospholipid antibodies and COVID-19 severity48,49.
A parsimonious explanation of the data might include features of several models. A lack of viral control at the infection site for a variety of reasons might result in germinal center suppression and skewing toward an EF response. While capable of functional antibody production, intense or prolonged activation could result in pathogenic B cell responses, whether through autoantibody production, antigen presentation, cytokine production or abnormal follicular helper T cell modulation39–42. Murine CD11c+T-bet+ B cells can contribute to autoimmunity through all four of these functions15,50–52, and we have shown the contribution of these cells to autoantibody production in human SLE18,21. It will be important to understand if EF effector pathways might contribute, at least in part, to the more severe COVID-19 courses observed in AA patients due to the known hyperresponsiveness within the T-bet+ B cell compartment53 and the much higher prevalence of severe SLE in this minority population18.
Finally, it will be important to understand whether infection-induced autoreactive B cell responses may persist after infection. The potential for EF responses to generate memory in humans is strongly supported by recent studies of vaccine responses to yellow fever, another single-stranded RNA virus, where antigen-specific EF pathway constituent persistence was comparable to CD27+ memory cells 1 year after vaccination54. Our COVID-19 study confirms the engagement of EF responses during the acute phase of a primary viral infection in humans. Should these B cells and/or autoantibodies also persist for prolonged periods after infection, it would be important to ascertain whether autoimmunity may contribute to the increasingly recognized entity of COVID-19 ‘long-haulers’, where patients manifest symptoms commonly observed in chronic autoimmune disease long after the virus has been cleared55.
Our study is complicated by unavoidable confounding factors created by the nature of the pandemic, including time-sensitive clinical imperatives. Critical illness could have induced non-specific immunological changes, thereby skewing the profiling results. This concern, however, is mitigated by the fact that expansions of ASCs and activation of EF response pathways are not regularly observed in patients with sepsis56. Careful longitudinal assessment of critical illness in other infectious diseases will be required to fully elucidate the contribution of different components of the B cell response to determine whether it is just a feature of severe disease or could also represent a predictor and inducer of disease course. Should that be the case, B cell profiles could be used to guide targeted therapies to prevent disease progression45. In addition, immunological features could also be modified by the timing of sampling and by the use of immunomodulatory therapies. In our study, 50% of the ICU-C cohort was treated with hydroxychloroquine, a drug that would be expected to dampen SLE-like B cell responses and whose use did not correlate with enhanced responses. Moreover, as this dataset was obtained before corticosteroids became the standard of care for patients with COVID-19 who are mechanically ventilated or have respiratory failure but are not yet intubated, it will serve as an important reference to evaluate the impact of immunomodulators on acute disease course57.
Finally, clinical restrictions and the importance of quickly studying patients in the early phases of the pandemic precluded the inclusion of larger, demographically matched cohorts of patients and HDs. While the incorporation of matched historical controls helps address the impact of this variable, additional studies during the current surge will permit us to rigorously control for the effect of ethnicity and investigate in additional detail the mechanisms underlying the disproportionate rate of mortality in AA and other minorities in general and the contribution of skewed B cell responses in particular. Importantly, the data here suggest that disease heterogeneity, and specifically the strong activation of the EF pathway previously associated with AA cohorts, may result in immunomodulatory therapy having discordant effects on different patient groups. This consideration will be particularly consequential given the increasing interest in the use of immunomodulatory therapies in the treatment of severe COVID-19 infection58,59.
Methods
Human participants.
All research was approved by the Emory University Institutional Review Board (Emory IRB nos. IRB00058507, IRB00057983 and IRB00058271) and was performed in accordance with all relevant guidelines and regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants or, if they were unable to provide informed consent, from designated healthcare surrogates. Healthy individuals (n = 36) were recruited using promotional materials approved by the Emory University Institutional Review Board. Individuals with COVID-19 (n = 19) were recruited from Emory University Hospital, Emory University Hospital Midtown and Emory St. Joseph’s Hospital (all Atlanta, USA). All non-healthy individuals were diagnosed with COVID-19 by PCR amplification of SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA obtained from nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal swabs. Individuals with COVID-19 were included in the study if they were between 18 to 80 years of age, were not immunocompromised and had not been given oral or intravenous corticosteroids within the preceding 14 d. Peripheral blood was collected in either heparin sodium tubes (PBMCs) or serum tubes (serum; both BD Diagnostic Systems). Baseline individual demographics are included in Supplementary Table 2. Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at Emory University60.
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell isolation and plasma collection.
Peripheral blood samples were collected in heparin sodium tubes and processed within 6 h of collection. PBMCs were isolated by density gradient centrifugation at 1,000g for 10 min. Aliquots from the plasma layer were collected and stored at −80 °C until use. PBMCs were washed twice with RPMI at 500g for 5 min. Viability was assessed using trypan blue exclusion, and live cells were counted using an automated hemocytometer.
Flow cytometry.
Isolated PBMCs (2 × 106) were centrifuged and resuspended in 75 μl FACS buffer (PBS + 2% FBS) and 5 μl Fc receptor block (BioLegend, no. 422302) for 5 min at room temperature. For samples stained with anti-IgG, it was observed that Fc block inappropriately interfered with staining, so a preincubation step of the anti-IgG alone for 5 min at 22 °C was added before the addition of the block. Next, 25 μl of antibody cocktail (Supplementary Table 3) was added (100 μl staining reaction), and samples were incubated for 20 min at 4 °C. Cells were washed in PBS, and resuspended in a PBS dilution of Zombie NIR fixable viability dye (BioLegend, no. 423106). Cells were washed and fixed at 0.8% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min at 22 °C in the dark before a final wash and resuspension for analysis.
For intracellular staining, the 0.8% PFA fixation step was omitted, and an additional wash was added following viability staining. Fixation and permeabilization of the cells were carried out per the manufacturer’s instructions using the True-Nuclear Transcription Factor Buffer Set (BioLegend, no. 424401). Following permeabilization, cells were stained with antibodies for intracellular cytokine staining (ICS) and diluted in permeabilization buffer (Supplementary Table 3).
Cells were analyzed on a Cytek Aurora flow cytometer using Cytek SpectroFlo software. Up to 3 × 106 cells were analyzed using FlowJo v10 (Treestar) software with DownSample (v3.3) and UMAP (V3.1) plugins for UMAP generation and visualization (see below).
UMAP visualization of flow cytometric data.
Contour plots were generated using ‘contour’ visualization in FlowJo (equal probability contouring). For UMAP projections, all samples stained with panel 2 were downsampled to 1,000 cells using the DownSample plugin (v3.3) available on the FlowJo Exchange. All samples were concatenated to create a single, 29,000-cell composite, and a UMAP algorithm for dimensionality reduction was applied using the UMAP plugin (v3.1) available on the FlowJo Exchange. The composite sample then was re-gated as indicated for all primary and secondary populations (Table 1) to aid in visual overlays in exploration of the UMAP projections. Density plots with levels set to 10% of gated populations were then projected onto the UMAP coordinates, with the outermost density representing 90% of the total gated cells (Fig. 2c,d). Alternatively, 90% densities were identified from total B cells from HD, OUT-C or ICU-C cohorts (Fig. 2b). These densities and underlying UMAP projections were exported to be superimposed and processed for display in Adobe Illustrator. Overlapping densities were removed using Adobe Illustrator’s intersection tools to reveal only densities occupied by OUT-C or ICU-C groups (Fig. 2a).
Analysis software.
Computational analysis was carried out in R (v3.6.2; release 12 Dec 2019). Heat maps were generated using the pheatmap library (v1.0.12), with data prenormalized (log-transformed z-scores calculated per feature) before plotting. Clustering was carried out using Ward’s method. Custom plotting, such as antigen-specific response curves, was performed using the ggplot2 library for base analysis, and then post-processed in Adobe Illustrator. Circos plotting was carried out using Circos software (v0.69–9). Lineage trees were calculated using GLaMST (Grow Lineages along Minimum Spanning Tree) software61,62, run on MATLAB and then visualized in R using the iGraph package (v1.2.4.2). Exported trees then were post-processed in Adobe Illustrator. Statistical analyses were performed directly in R, or in GraphPad Prism (v8.2.1).
Flow cytometry and sorting of B cell subsets for repertoire sequencing.
Frozen cell suspensions were thawed at 37 °C in RPMI + 10% FCS and then washed and resuspended in FACS buffer (PBS + 2% FCS). The cells were incubated with a mix of fluorophore-conjugated antibodies for 30 min on ice. The cells were washed in PBS and then incubated with the live/dead fixable aqua dead cell stain (Thermo Fisher) for 10 min at 22 °C. After a final wash in FACS buffer, the cells were resuspended in FACS buffer at 107 cells per ml for cell sorting on a three-laser BD FACS (BD Biosciences).
For single-cell analysis, total ASCs were gated as CD3−CD14−CD16−CD19+CD38+CD27+ single live cells, whereas naive B cells were gated as CD3−CD14−CD16−CD19+CD27−IgD+CD38+ single live cells.
For bulk sequencing preparations, B cells were enriched using StemCell’s Human Pan-B Cell Enrichment Kit (no. 19554; negative selection of CD2, CD3, CD14, CD16, CD36, CD42b, CD56, CD66b and CD123). CD138+ ASCs were enriched further using CD138+ selection beads according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Miltenyi Biotec, no. 130-051-301).
V(D)J repertoire library preparation and sequencing.
Single-cell sequencing analysis.
Cells were counted immediately using a hemocytometer and adjusted to 1,000 cells per μl to capture 10,000 single cells per sample loaded in the 10× Genomics Chromium device according to the manufacturer’s standard protocol (Chromium Next GEM Single Cell V(D)J Reagent Kits, v1.1). The 10× Genomics v2 libraries were prepared using the 10x Genomics Chromium Single Cell 5′ Library Construction Kit per the manufacturer’s instructions. Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq (paired-end; 2 × 150 bp; read 1:26 cycles; i7 index: 8 cycles, i5 index: 0 cycles; read 2: 98 cycles) such that more than 70% saturation could be achieved with a sequence depth of 5,000 reads per cell.
Bulk sequencing.
RNA was extracted from enriched cells using Qiagen’s RNeasy Mini Kit according to the manufacturer’s protocol. First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using the iScript cDNA synthesis kit and 8 μl of RNA following the manufacturer’s recommended protocol. First-round amplification of IgG, IgA and IgM was performed with previously described primer sets18, with amplification conditions as follows; PCR1 conditions were: 95 °C for 3 min; 40 cycles of: 30 s at 95 °C, 30 s at 58 °C, 30 s at 72 °C; and 72 °C for 5 min. Samples were then ligated in a second-round PCR with Nextera Index kit (Illumina). PCR2 conditions for this reaction were: 72 °C for 3 min; 98 °C for 30 s; and 5 cycles of: 98 °C for 10 s, 63 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 3 min. Products were purified with Agencourt AMPure XP beads (Beckman Coulter), and the resulting products were run on 1.2% agarose gels (Lonza) to verify amplification. Libraries were denatured using 0.2 N NaOH, and then quenched with cold illumine HT1 hybridization buffer according to manufacturer’s recommended workflow (Illumina). Libraries were mixed with 20% PhiX (Illumina) as a quality control and loaded onto a 600-cycle V3 MiSEQ cartridge (Illumina) for paired-end sequencing.
Cytokine immunoassays.
Plasma concentrations of IL-6 were quantified with ELISA using a Human IL-6 Quantikine ELISA Kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions (R&D Biosystems, no. HS600C). CRP was measured in a singleplex immunoassay (MilliporeSigma) in a Luminex-200 platform following manufacturer’s protocol (25 μl of 1:40,000 dilution in duplicates).
Carbodiimide coupling of microspheres to SARS-CoV-2 antigens.
Two SARS-CoV-2 proteins were coupled to MagPlex Microspheres of different regions (Luminex). Nucleocapsid (N) protein expressed from Escherichia coli (N-terminal His6) was obtained from Raybiotech (230-01104-100) and the RBD of spike (S) protein expressed from HEK293 cells was obtained from the laboratory of J. Wrammert63 at Emory University. Coupling was carried out at 22 °C following standard carbodiimide coupling procedures. Concentrations of coupled microspheres were confirmed by Bio-Rad T20 Cell Counter.
Luminex proteomic assays for measurement of anti-antigen antibody.
Approximately 50 μl of coupled microsphere mix was added to each well of 96-well clear-bottom black polystyrene microplates (Greiner Bio-One) at a concentration of 1,000 microspheres per region per well. All wash steps and dilutions were accomplished using 1% BSA, 1× PBS assay buffer. Sera were assayed at 1:500 dilutions and surveyed for antibodies against N or RBD. After a 1-h incubation in the dark on a plate shaker at 800 r.p.m., wells were washed five times in 100 μl of assay buffer, using a BioTek 405 TS plate washer, then applied with 3 μg ml−1 PE-conjugated goat anti-human IgA, IgG and/or IgM (Southern Biotech). After 30 min of incubation at 800 r.p.m. in the dark, wells were washed three times in 100 μl of assay buffer, resuspended in 100 μl of assay buffer and analyzed using a Luminex FLEXMAP 3D instrument (Luminex) running xPONENT 4.3 software. MFI using combined or individual detection antibodies (anti-IgA, anti-IgG or anti-IgM) was measured using the Luminex xPONENT software. The background value of assay buffer was subtracted from each serum sample result to obtain MFI minus background (MFI-B; net MFI).
Quantification of 9G4-idiotype IgG in serum.
Polysorp 96-well plates (Thermo Fisher, no. 475094) were coated overnight with 0.5 μg ml−1 rat anti-human 9G4 IgG diluted in PBS. SuperBlock (Thermo Fisher, no. 37515) was used as blocking reagent. Serum samples were then incubated for 60 min at 22 °C at a dilution of 1:8,000 (9G4+ IgG) followed with three twofold dilutions. Positive 9G4 IgG sera were detected by AP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG (Fc specific) at a dilution of 1:15,000 (Sigma, no. A9544). The reaction was visualized by the addition of 100 μl KPL BluePhosÒ Microwell Phosphatase Substrate System (SeraCare, no. 5120–0059). The ELISA OD 9G4 IgG results were quantified with a human 9G4+ monoclonal IgG standard curve. Plates were washed three times with washing buffer (PBS (pH 7.4) containing 0.1% (vol/vol) Tween 20) after each step.
Focus-reduction neutralization test.
Indicated dilutions of plasma were incubated with 102 focus-forming units (FFU) of SARS-CoV-2 for 1 h at 37 °C. Antibody–virus complexes were added to indicated cell monolayers in 96-well plates and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. Subsequently, cells were overlaid with 1% (wt/vol) methylcellulose in MEM supplemented with 2% FBS. Plates were harvested 30 h later by removing overlays and fixed with 4% PFA in PBS for 20 min at 22 °C. Plates were washed and sequentially incubated with 1 mg ml−1 of CR3022 anti-S antibody64,65 and HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG in PBS supplemented with 0.1% saponin and 0.1% BSA. SARS-CoV-2-infected cell foci were visualized using TrueBlue peroxidase substrate (KPL) and quantified on an ImmunoSpot microanalyzer (Cellular Technologies). Data were processed using Prism software v8.0 (GraphPad).
Statistical analysis.
Statistical analysis was carried out using Prism (GraphPad). For each experiment, the type of statistical testing, summary statistics and levels of significance can be found in the figures and corresponding legends. All measurements displayed were taken from distinct samples.
Reporting Summary.
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Extended Data
Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Cellularity of COVID-19 patient blood samples.
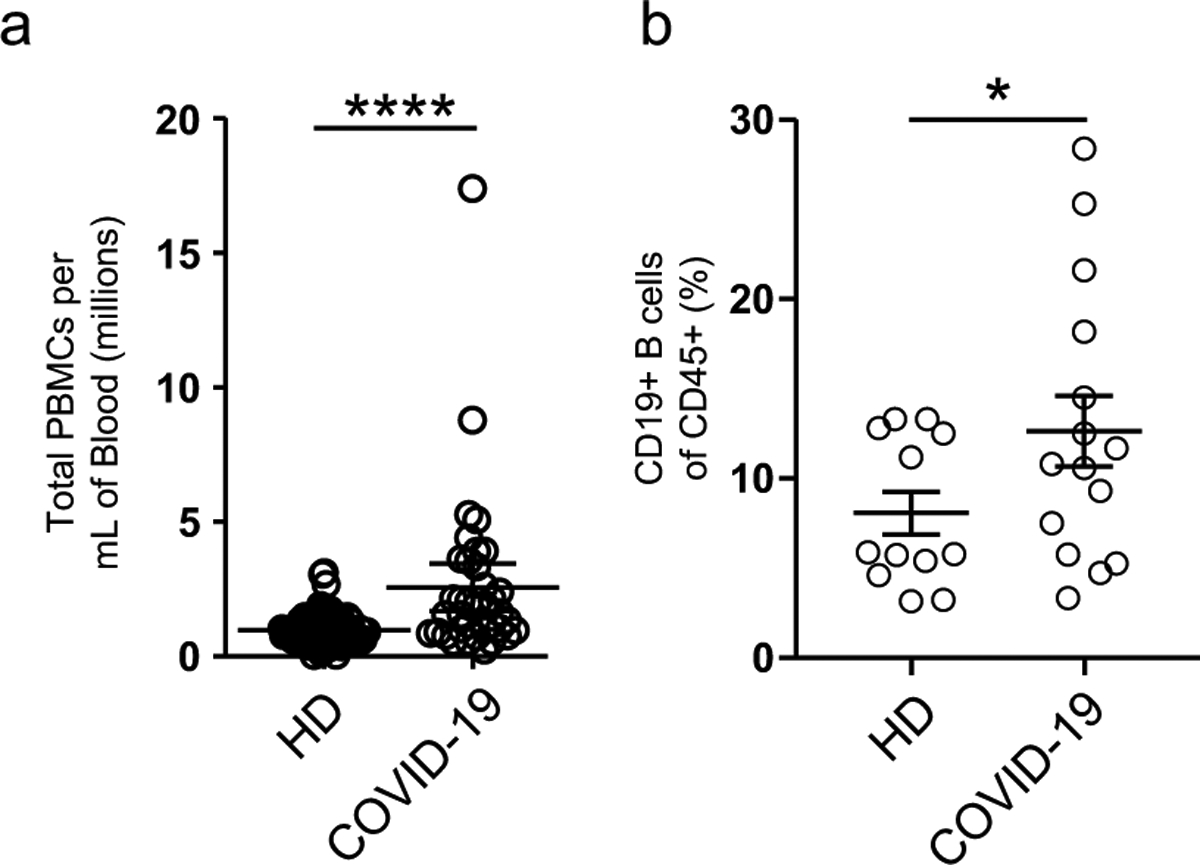
a, Calculated total PBMC yield per mL of patient blood from HD, or donors with COVID-19. b, Frequency of CD19+ B cells of CD45+ cells in HD vs donors with COVID-19.
Extended Data Fig. 2 |. DN3 cells are expanded in the ICu-C cohort.

a, CD38 expression by DN3 cells in two ICU-C patients. b, DN3 frequency of total CD19+ B cells in HD, OUT-C, and ICU-C cohorts.
Extended Data Fig. 3 |. COVID-19 infection comparisons with African American HD cohorts.
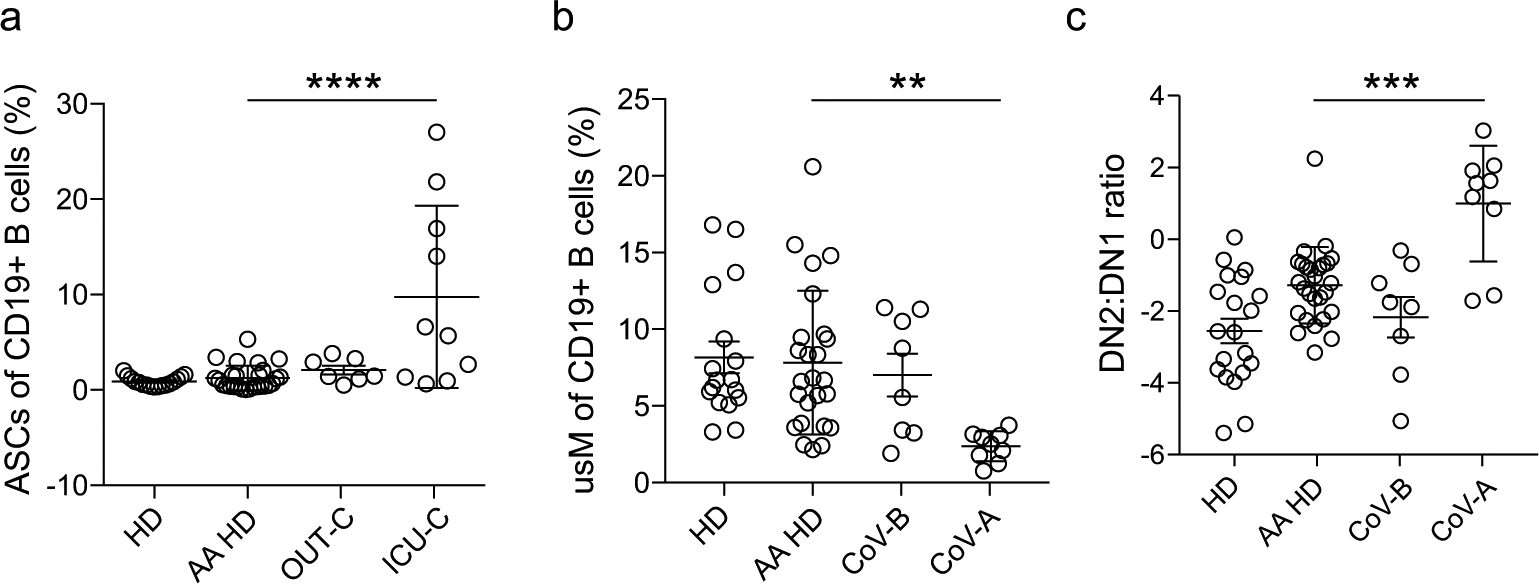
Critical indicators of EF response activation were compared between the current HD cohort (recruited for this study), historically collected HD cohorts of AA descent (AA-HD), and patients groups as in [Figs. 2 and 3]. a, ASC frequency of total CD19+ B cells in HD, AA HD, OUT-C, and ICU-C cohorts. b, usM frequency of total CD19+ B cells in HD, AA HD, CoV-B, and CoV-A cohorts. (a) DN2:DN1 ratios in HD, AA HD, CoV-B, and CoV-A cohorts.
Extended Data Fig. 4 |. Cartoon of EF vs. follicular response pathway intermediates.

Center table summarizes documented features of EF responses in primary infection and highlights open questions about the formation of memory and long-lived ASC responses as a result of pathway activation to be answered in follow up studies.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank all of the healthy individuals, patients and their families for their selfless participation in this study. We also thank the nurses, staff and providers in the 71 ICU in Emory University Hospital Midtown and the 2E ICU in Emory Saint Joseph’s Hospital without whom our work would not have been possible. We acknowledge the contributions of D. Murphy, W. Bender, C. Swenson, C. Coleman, M. Horwath, D. Alter, V. Engineer, M. Hernandez and J. Varghese and their time and expertise. Extensive efforts by the Pediatric/Winship Flow Cytometry Core and the Flow Cytometry Core at the Emory Vaccine Center made this work possible. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants UL TR000424 (Emory Library IT), R01-AG054991 (to W.T.H.), U19-AI110483 Emory Autoimmunity Center of Excellence (to I.S.), P01-AI125180-01 (to I.S. and F.E.-H.L.), R37-AI049660 (to I.S.), 1R01AI121252 (to F.E.-H.L.), 1U01AI141993 (to F.E.-H.L.), R01 AI127828 (to J.E.C. and M.S.D.) and T32-HL116271-07 (to R.P.R.); HHS/NIAID/NIH contract 75N93019C00074 (to J.E.C.); Defense Advanced Research Project Agency grant HR001117S0019 (to J.E.C.); the Dolly Parton COVID-19 Research Fund at Vanderbilt; and a Fast Grants Award (to J.E.C.)
Footnotes
Online content
Any methods, additional references, Nature Research reporting summaries, source data, extended data, supplementary information, acknowledgements, peer review information; details of author contributions and competing interests; and statements of data and code availability are available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z.
Data availability
All FCM and sequencing data presented here are publicly available in alignment with current requirements for public disclosure before peer review. All FCM data presented and analyzed in this manuscript (Figs. 1–3) are publicly available in the FlowRepository at http://flowrepository.org/id/FR-FCM-Z2XF/. Single-cell V(D) J sequencing (Fig. 4) is available in the Sequence Read Archive at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/642962/.
Competing interests
F.E.-H.L. is the founder of MicroB-plex and has research grants with Genentech. W.T.H. has consulted for ViveBio, AARP and Biogen; has received research support from Fujirebio; and has a patent on CSF-based diagnosis of FTLD-TDP. M.S.D. is a consultant for Inbios, Vir Biotechnology and NGM Biopharmaceuticals and is on the scientific advisory board of Moderna. The Diamond laboratory has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Moderna, Vir Biotechnology and Emergent BioSolutions. J.E.C. has served as a consultant for Pfizer, Novavax, Lilly and Luna Biologics; is a member of the scientific advisory boards of CompuVax and Meissa Vaccines; and is Founder of IDBiologics. The Crowe laboratory at Vanderbilt University Medical Center has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Moderna, Sanofi-Aventis and IDBiologics.
Extended data is available for this paper at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z.
Supplementary information is available for this paper at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-020-00814-z.
Peer review information L. A. Dempsey was the primary editor on this article and managed its editorial process and peer review in collaboration with the rest of the editorial team.
References
- 1.Chen X et al. Detectable serum SARS-CoV-2 viral load (RNAaemia) is closely correlated with drastically elevated IL-6 level in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Clin. Infect. Dis 10.1093/cid/ciaa449 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Henderson LA et al. On the alert for cytokine storm: immunopathology in COVID-19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 10.1002/art.41285 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Group RC et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19—preliminary report. N Engl. J. Med 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436 (2020). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tang Y et al. Cytokine storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies. Front. Immunol 11, 1708 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Harrison C Focus shifts to antibody cocktails for COVID-19 cytokine storm. Nat. Biotechnol 38, 905–908 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sun B et al. Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgM and IgG responses in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes Infect 9, 940–948 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zost SJ et al. Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Nature 584, 443–449 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Liu L et al. Potent neutralizing antibodies directed to multiple epitopes on SARS-CoV-2 spike. Nature 584, 450–456 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Long QX et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med 26, 1200–1204 (2020). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ibarrondo FJ et al. Rapid decay of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in persons with mild COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med 383, 1085–1087 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lam JH, Smith FL & Baumgarth N B cell activation and response regulation during viral infections. Viral Immunol. 33, 294–306 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Allman D, Wilmore JR & Gaudette BT The continuing story of T cell independent antibodies. Immunol. Rev 288, 128–135 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Di Niro R et al. Salmonella infection drives promiscuous B cell activation followed by extrafollicular affinity maturation. Immunity 43, 120–131 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rubtsova K, Rubtsov AV, Cancro MP & Marrack P Age-associated B cells: a T-bet-dependent effector with roles in protective and pathogenic immunity. J. Immunol 195, 1933–1937 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Manni M et al. Regulation of age-associated B cells by IRF5 in systemic autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol 19, 407–419 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rubtsova K et al. B cells expressing the transcription factor T-bet drive lupus-like autoimmunity. J. Clin. Invest 127, 1392–1404 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tipton CM et al. Diversity, cellular origin and autoreactivity of antibody-secreting cell population expansions in acute systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Immunol 16, 755–765 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jenks SA et al. Distinct effector B cells induced by unregulated Toll-like receptor 7 contribute to pathogenic responses in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 49, 725–739 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zumaquero E et al. IFN-γ induces epigenetic programming of human T-bethi B cells and promotes TLR7/8- and IL-21-induced differentiation. Elife 8, e41641 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Scharer CD et al. Epigenetic programming underpins B cell dysfunction in human SLE. Nat. Immunol 20, 1071–1082 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang S et al. IL-21 drives expansion and plasma cell differentiation of autoreactive CD11chi T-bet+ B cells in SLE. Nat. Commun 9, 1758 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jenks SA, Cashman KS, Woodruff MC, Lee FE & Sanz I Extrafollicular responses in humans and SLE. Immunol. Rev 288, 136–148 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sanz I et al. Challenges and opportunities for consistent classification of human B cell and plasma cell populations. Front. Immunol 10, 2458 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tan L et al. Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: a descriptive and predictive study. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther 5, 33 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Becht E et al. Dimensionality reduction for visualizing single-cell data using UMAP. Nat. Biotechnol 37, 38–44 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wrammert J et al. Rapid and massive virus-specific plasmablast responses during acute dengue virus infection in humans. J. Virol 86, 2911–2918 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lee FE et al. Circulating human antibody-secreting cells during vaccinations and respiratory viral infections are characterized by high specificity and lack of bystander effect. J. Immunol 186, 5514–5521 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rodríguez-Bayona B, Ramos-Amaya A, Pérez-Venegas JJ, Rodríguez C & Brieva JA Decreased frequency and activated phenotype of blood CD27 IgD IgM B lymphocytes is a permanent abnormality in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Arthritis Res.Ther 12, R108 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sellam J et al. Blood memory B cells are disturbed and predict the response to rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 63, 3692–3701 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tipton CM, Hom JR, Fucile CF, Rosenberg AF & Sanz I Understanding B cell activation and autoantibody repertoire selection in systemic lupus erythematosus: a B-cell immunomics approach. Immunol. Rev 284, 120–131 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reed JH, Jackson J, Christ D & Goodnow CC Clonal redemption of autoantibodies by somatic hypermutation away from self-reactivity during human immunization. J. Exp. Med 213, 1255–1265 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stone SL et al. T-bet transcription factor promotes antibody-secreting cell differentiation by limiting the inflammatory effects of IFN-γ on B cells. Immunity 50, 1172–1187 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lucas C et al. Longitudinal analyses reveal immunological misfiring in severe COVID-19. Nature 584, 463–469 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mehta P et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 395, 1033–1034 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Mathew D et al. Deep immune profiling of COVID-19 patients reveals distinct immunotypes with therapeutic implications. Science 369, eabc8511(2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kaneko N et al. Loss of Bcl-6-expressing T follicular helper cells and germinal centers in COVID-19. Cell 10.1016/j.cell.2020.08.025 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kwissa M et al. Dengue virus infection induces expansion of a CD14+CD16+ monocyte population that stimulates plasmablast differentiation. Cell Host Microbe 16, 115–127 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gaya M et al. Initiation of antiviral B cell immunity relies on innate signals from spatially positioned NKT cells. Cell 172, 517–533 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lund FE & Randall TD Effector and regulatory B cells: modulators of CD4+ T cell immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol 10, 236–247 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.León B, Ballesteros-Tato A, Misra RS, Wojciechowski W & Lund FE Unraveling effector functions of B cells during infection: the hidden world beyond antibody production. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 12, 213–221 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zeng Q et al. B cells mediate chronic allograft rejection independently of antibody production. J. Clin. Invest 124, 1052–1056 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Chan OT, Hannum LG, Haberman AM, Madaio MP & Shlomchik MJ A novel mouse with B cells but lacking serum antibody reveals an antibody-independent role for B cells in murine lupus. J. Exp. Med 189, 1639–1648 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Dang VD, Hilgenberg E, Ries S, Shen P & Fillatreau S From the regulatory functions of B cells to the identification of cytokine-producing plasma cell subsets. Curr. Opin. Immunol 28, 77–83 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pioli PD Plasma cells, the next generation: beyond antibody secretion. Front. Immunol 10, 2768 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hoepel W et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG from severely ill COVID-19 patients promotes macrophage hyper-inflammatory responses. Preprint at bioRxiv 10.1101/2020.07.13.190140 (2020). [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.William J, Euler C, Christensen S & Shlomchik MJ Evolution of autoantibody responses via somatic hypermutation outside of germinal centers. Science 297, 2066–2070 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fang YT et al. Annexin A2 on lung epithelial cell surface is recognized by severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus spike domain 2 antibodies. Mol. Immunol 47, 1000–1009 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xiao M et al. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Arthritis Rheumatol. 10.1002/art.41425 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang Y et al. Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med 382, e38 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang W et al. Excessive CD11c+T-bet+ B cells promote aberrant TFH differentiation and affinity-based germinal center selection in lupus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 116, 18550–18560 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rubtsov AV et al. CD11c-expressing B cells are located at the T cell/B cell border in spleen and are potent APCs. J. Immunol 195, 71–79 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liu Y et al. T-bet+CD11c+ B cells are critical for antichromatin immunoglobulin G production in the development of lupus. Arthritis Res. Ther 19, 225 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Menard LC et al. B cells from African American lupus patients exhibit an activated phenotype. JCI Insight 1, e87310 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Wec AZ et al. Longitudinal dynamics of the human B cell response to the yellow fever 17D vaccine. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 117, 6675–6685 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Carfi A, Bernabei R, Landi F & Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group. Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19. JAMA 324, 603–605 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Gustave CA et al. Septic shock shapes B cell response toward an exhausted-like/immunoregulatory profile in patients. J. Immunol 200, 2418–2425 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 treatment guidelines. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ (2020). [PubMed]
- 58.Kiprov D, Conboy MJ & Conboy IM Immunomodulation for the management of COVID-19. Transfus. Apher. Sci 59,102856 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ingraham NE et al. Immunomodulation in COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med 8, 544–546 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Harris PA et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J. Biomed. Inform 95, 103208 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yang J et al. FMST: an automatic neuron-tracing method based on fast marching and minimum spanning tree. Neuroinformatics 17, 185–196 (2019). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Yang X et al. GLaMST: grow lineages along minimum spanning tree for B cell receptor sequencing data. BMC Genomics 21, 583 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Suthar MS et al. Rapid generation of neutralizing antibody responses in COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep. Med 1, 100040 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.ter Meulen J et al. Human monoclonal antibody combination against SARS coronavirus: synergy and coverage of escape mutants. PLoS Med. 3, e237 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yuan M et al. A highly conserved cryptic epitope in the receptor binding domains of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Science 368, 630–633 (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


