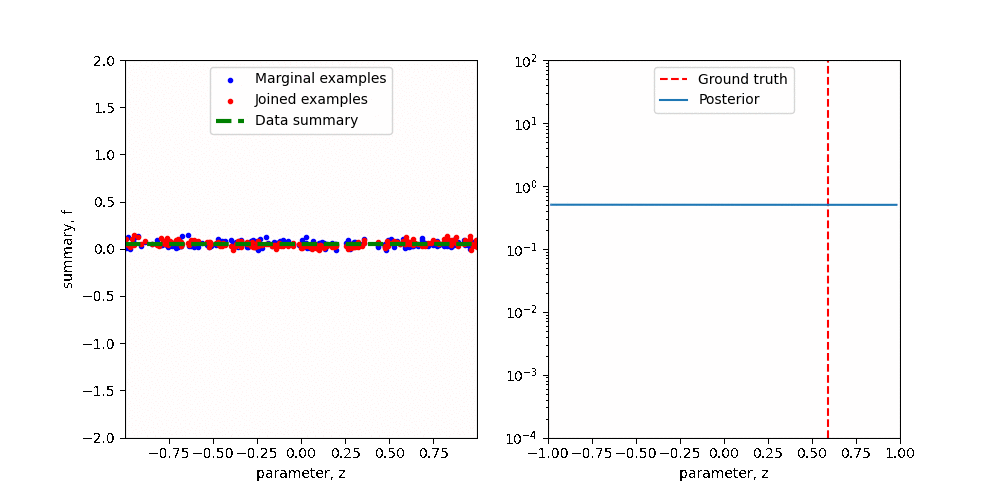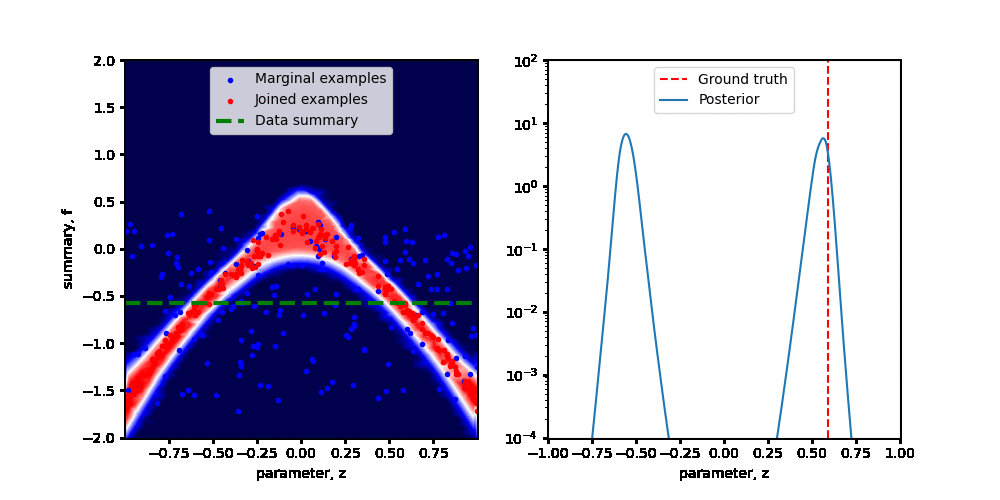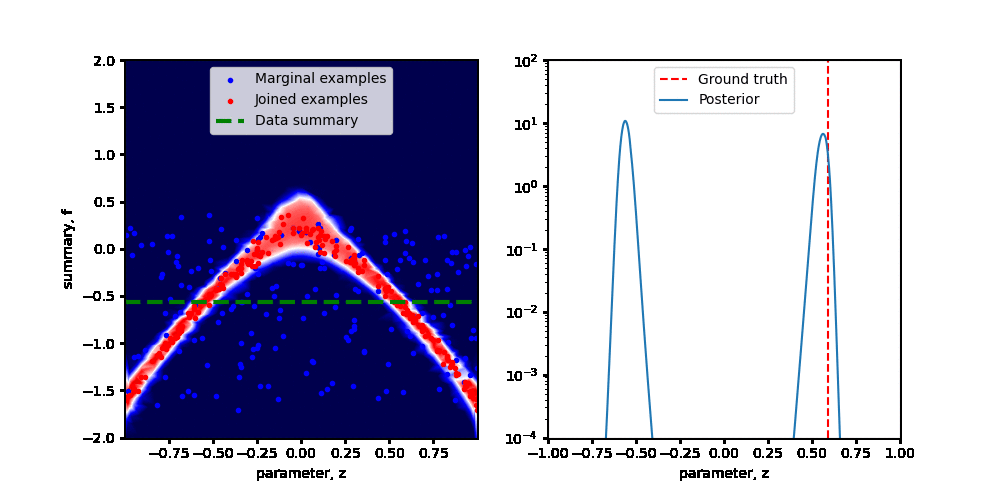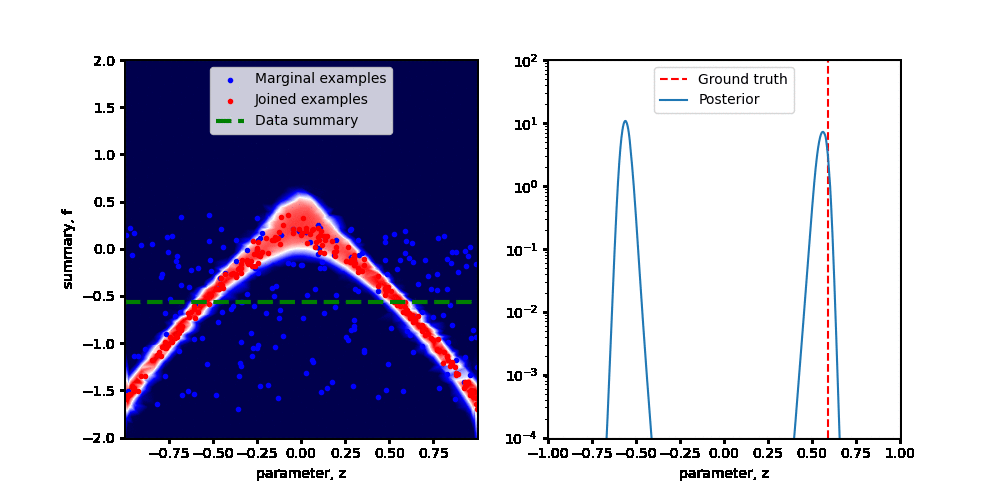
Swyft is a system for scientific simulation-based inference at scale.
Swyft is the official implementation of Truncated Marginal Neural Ratio Estimation (TMNRE), a hyper-efficient, simulation-based inference technique for complex data and expensive simulators.
- Swyft makes it convenient to perform Bayesian or Frequentist inference of hundreds, thousands or millions of parameter posteriors by constructing optimal data summaries.
- To this end, Swyft estimates likelihood-to-evidence ratios for arbitrary marginal posteriors; they typically require fewer simulations than the corresponding joint.
- Swyft performs targeted inference by prior truncation, combining simulation efficiency with empirical testability.
- Swyft is based on stochastic simulators, which map parameters stochastically to observational data. Swyft makes it convenient to define such simulators as graphical models.
- In scientific settings, a cost-benefit analysis often favors approximating the posterior marginality; swyft provides this functionality.
- The package additionally implements our prior truncation technique, routines to empirically test results by estimating the expected coverage, and a simulator manager with zarr storage to simplify use with complex simulators.
2021
- “Fast and Credible Likelihood-Free Cosmology with Truncated Marginal Neural Ratio Estimation“ Cole+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.08030
2022
- “Estimating the warm dark matter mass from strong lensing images with truncated marginal neural ratio estimation” Anau Montel+, https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.09126
- “SICRET: Supernova Ia Cosmology with truncated marginal neural Ratio EsTimation” Karchev+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.06733
- “One never walks alone: the effect of the perturber population on subhalo measurements in strong gravitational lenses” Coogan+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.09918
- “Detection is truncation: studying source populations with truncated marginal neural ratio estimation” Anau Montel+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.04291
2023
- “Debiasing Standard Siren Inference of the Hubble Constant with Marginal Neural Ratio Estimation” Gagnon-Hartman+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05241
- “Constraining the X-ray heating and reionization using 21-cm power spectra with Marginal Neural Ratio Estimation” Saxena+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.07339
- “Peregrine: Sequential simulation-based inference for gravitational wave signals”, Bhardwaj+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.02035
- “Albatross: A scalable simulation-based inference pipeline for analysing stellar streams in the Milky Way”, Alvey+ https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.02032
- Documentation & installation: https://swyft.readthedocs.io/
- Example usage: https://swyft.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorial-notebooks.html
- Source code: https://github.com/undark-lab/swyft
- Support & discussion: https://github.com/undark-lab/swyft/discussions
- Bug reports: https://github.com/undark-lab/swyft/issues
- Contributing: https://swyft.readthedocs.io/en/latest/contributing-link.html
- Citation: https://swyft.readthedocs.io/en/latest/citation.html
- As of v0.4.0, Swyft is based on pytorch-lightning, with a completely updated
- v0.3.2 is the version that was submitted to JOSS.
- tmnre is the implementation of the paper Truncated Marginal Neural Ratio Estimation.
- v0.1.2 is the implementation of the paper Simulation-efficient marginal posterior estimation with swyft: stop wasting your precious time.
- sbi is a collection of simulation-based inference methods. Unlike Swyft, the repository does not include our truncation scheme nor marginal estimation of posteriors.
- lampe is an implementation of amoritzed simulation-based inference methods aimed at simulation-based inference researchers due to its flexibility.