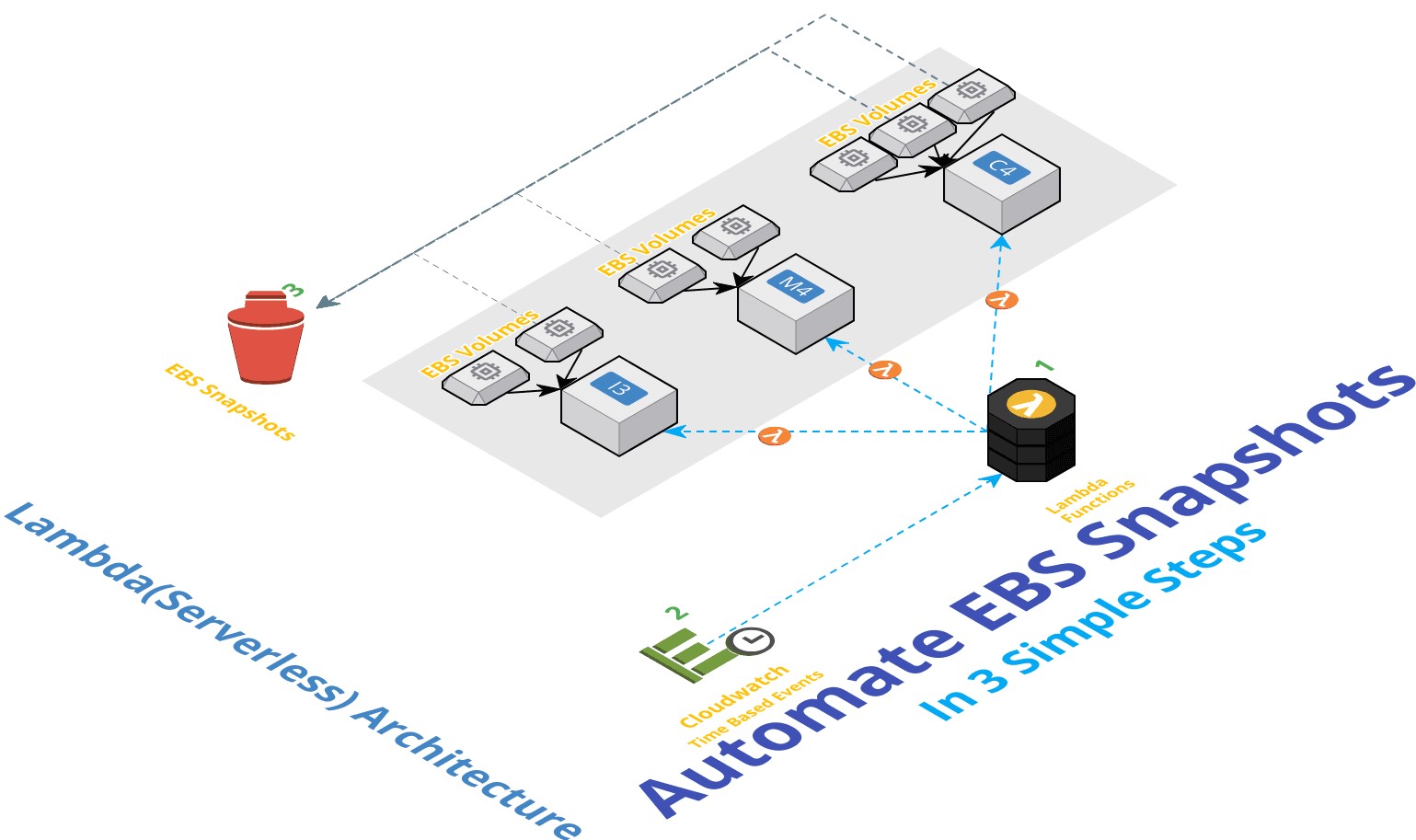
Taking EBS snapshots is often a routine activity that is well suited to be automated using Lambda functions. So we are going to write a simple Boto3 script to trigger EBS Snapshots using AWS Lambda Functions
Serverless EBS Volume Snapshots using Lambda
In 3 simple steps, we are going to setup our serverless backup automation,
- Step 1 - Setup Lambda Function - The Lambda Function will, (
codegiven below)- Find out
Instancesin the currentRegion - Filter Instances based on
Tags- In this case the key should be "Backup or "backup" - Identify block devices attached to those instances
- Initiate Backup
- Add Tags to Snapshots
- Report Status
- Find out
- Step 2 - Configure Lambda Triggers - Cloudwatch Events
- Step 3 - Verify EBS Snapshots in
EC2 Dashboard
We will need the following pre-requisites to successfully complete this activity,
- EC2 Server(s) - with Tag "Key = BackUp" and "Value = Yes" Remember the tag is case sensitive
- IAM Role - i.e
Lambda Service Role- withEC2FullAccesspermissions
Create a AWS Lambda Function, and choose Python 2.7 as the runtime and copy paste the below code.
Change the global variables at the top of the script to suit your needs. For example change the default Rentention period the Backup Tag to filter etc
import boto3
import collections
import datetime
# Set the global variables
globalVars = {}
globalVars['Owner'] = "Miztiik"
globalVars['Environment'] = "Test"
globalVars['REGION_NAME'] = "ap-south-1"
globalVars['tagName'] = "Valaxy-Serverless-Automated-Backup"
globalVars['findNeedle'] = "BackUp"
globalVars['RetentionTag'] = "DeleteOn"
globalVars['RetentionInDays'] = "70"
#Please mention your region name
ec = boto3.client('ec2', region_name='ap-south-1')
def backup_bot():
snapsCreated = { 'Snapshots':[], }
filters = [
{'Name': 'tag-key', 'Values': [ globalVars['findNeedle'] ]},
{'Name': 'tag-value', 'Values': ['Yes']},
]
reservations = ec.describe_instances( Filters=filters ).get( 'Reservations', [] )
instances = sum(
[
[i for i in r['Instances']]
for r in reservations
], [])
# print "Number of the Instances : %d" % len(instances)
snapsCreated['InstanceCount']=len(instances)
to_tag = collections.defaultdict(list)
# Iterate for all Instances in the Region
for instance in instances:
try:
retention_days = [
int(t.get('Value')) for t in instance['Tags']
if t['Key'] == 'Retention'][0]
except IndexError:
retention_days = int(globalVars['RetentionInDays'])
# Get all the Block Device Mappings
for dev in instance['BlockDeviceMappings']:
if dev.get('Ebs', None) is None:
continue
vol_id = dev['Ebs']['VolumeId']
# Iterate Tags to collect the instance name tag
DescriptionTxt = ''
for tag in instance['Tags']:
if tag['Key'] == 'Name' :
DescriptionTxt = tag['Value']
snap = ec.create_snapshot( VolumeId=vol_id, Description=DescriptionTxt )
to_tag[retention_days].append(snap['SnapshotId'])
# Tag all the snaps that were created today with Deletion Date
# Processing "DeleteOn" here to allow for future case of each disk having its own Retention date
for retention_days in to_tag.keys():
delete_date = datetime.date.today() + datetime.timedelta(days=retention_days)
# to mention the current date formet
delete_fmt = delete_date.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
# below code is create the name and current date as instance name
ec.create_tags(
Resources=to_tag[retention_days],
Tags=[
{'Key': globalVars['RetentionTag'], 'Value': delete_fmt},
{'Key': 'Name', 'Value': snap['Description'] },
]
)
snapsCreated['Snapshots'].append({ 'SnapshotId':snap['SnapshotId'], 'VolumeId' : vol_id, 'InstanceId' : instance['InstanceId'], 'DeleteOn': delete_fmt })
to_tag.clear()
return snapsCreated
def lambda_handler(event, context):
return backup_bot()
if __name__ == '__main__':
lambda_handler(None, None)We are going to use Cloudwatch Scheduled Events to take backup everyday.
rate(1 minute)
or
rate(5 minutes)
or
rate(1 day)
or
# The below example creates a rule that is triggered every day at 12:00pm UTC.
cron(0 12 * * ? *)
If you want to learn more about the above Scheduled expressions, Ref: CloudWatch - Schedule Expressions for Rules
You can use many of the lamdba configurations to customize it suit your needs,
Concurrency:Increase as necessary to manage all your instancesMemory&Timeout: If you have a large number of instances, you want to increase theMemory&TimeoutSecurity: Run your lambda inside yourVPCfor added securityCloudTrail: You can also enableCloudTrailfor audit & governance