This is a fork from the default prometheus monitoring stack, customized for .fmbot.
The below readme is a default description of the project. We should probably improve this, because all the bloat from the fork is not required.
The grafana dashboard is currently not publicly available.
Running:
docker stack deploy -c docker-stack.yml prom
Removing:
docker stack rm prom
Logs for a specific container:
docker service logs prom_prometheus
Required ~/.bashrc variables are SEQ_PASSWORD and GRAFANA_PASSWORD
- Introduction
Here's a quick start using Play-With-Docker (PWD) to start-up a Prometheus stack containing Prometheus, Grafana and Node scraper to monitor your Docker infrastructure. The Try in PWD below allows you to quickly deploy the entire Prometheus stack with a click of the button. This will allow you to quickly test the stack to see if it meets your needs.
Before we get started installing the Prometheus stack. Ensure you install the latest version of docker and docker swarm on your Docker host machine. Docker Swarm is installed automatically when using Docker for Mac or Docker for Windows.
Clone the project locally to your Docker host.
If you would like to change which targets should be monitored or make configuration changes edit the /prometheus/prometheus.yml file. The targets section is where you define what should be monitored by Prometheus. The names defined in this file are actually sourced from the service name in the docker-compose file. If you wish to change names of the services you can add the "container_name" parameter in the docker-compose.yml file.
Once configurations are done let's start it up. From the /prometheus project directory run the following command:
$ HOSTNAME=$(hostname) docker stack deploy -c docker-stack.yml prom
That's it the `docker stack deploy' command deploys the entire Grafana and Prometheus stack automagically to the Docker Swarm. By default cAdvisor and node-exporter are set to Global deployment which means they will propogate to every docker host attached to the Swarm.
The Grafana Dashboard is now accessible via: http://<Host IP Address>:3000 for example http://192.168.10.1:3000
username - admin
password - foobar (Password is stored in the `/grafana/config.monitoring` env file)
In order to check the status of the newly created stack:
$ docker stack ps prom
View running services:
$ docker service ls
View logs for a specific service
$ docker service logs prom_<service_name>
Grafana version 5.0.0 has introduced the concept of provisioning. This allows us to automate the process of adding Datasources & Dashboards. The /grafana/provisioning/ directory contains the datasources and dashboards directories. These directories contain YAML files which allow us to specify which datasource or dashboards should be installed.
If you would like to automate the installation of additional dashboards just copy the Dashboard JSON file to /grafana/provisioning/dashboards and it will be provisioned next time you stop and start Grafana.
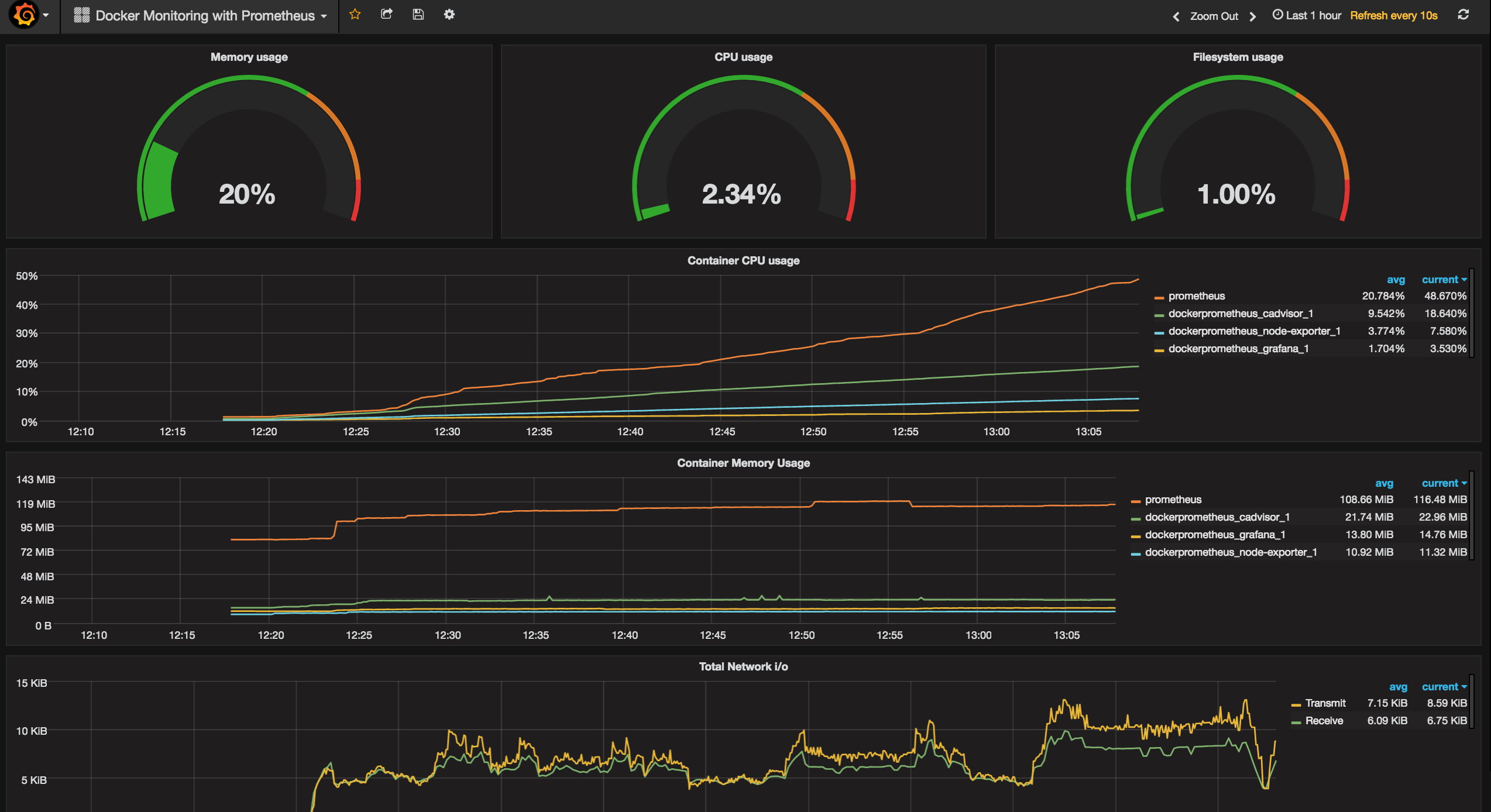
I created a Dashboard template which is available on Grafana Docker Dashboard. Simply select Import from the Grafana menu -> Dashboards -> Import and provide the Dashboard ID #179
This dashboard is intended to help you get started with monitoring. If you have any changes you would like to see in the Dashboard let me know so I can update Grafana site as well.
Here's the Dashboard Template
Grafana Dashboard - dashboards/Grana_Dashboad.json
Alerting Dashboard
Alerting has been added to the stack with Slack integration. 2 Alerts have been added and are managed
Alerts - prometheus/alert.rules
Slack configuration - alertmanager/config.yml
View Prometheus alerts http://<Host IP Address>:9090/alerts
View Alert Manager http://<Host IP Address>:9093
A quick test for your alerts is to stop a service. Stop the node_exporter container and you should notice shortly the alert arrive in Slack. Also check the alerts in both the Alert Manager and Prometheus Alerts just to understand how they flow through the system.
High load test alert - docker run --rm -it busybox sh -c "while true; do :; done"
Let this run for a few minutes and you will notice the load alert appear. Then Ctrl+C to stop this container.
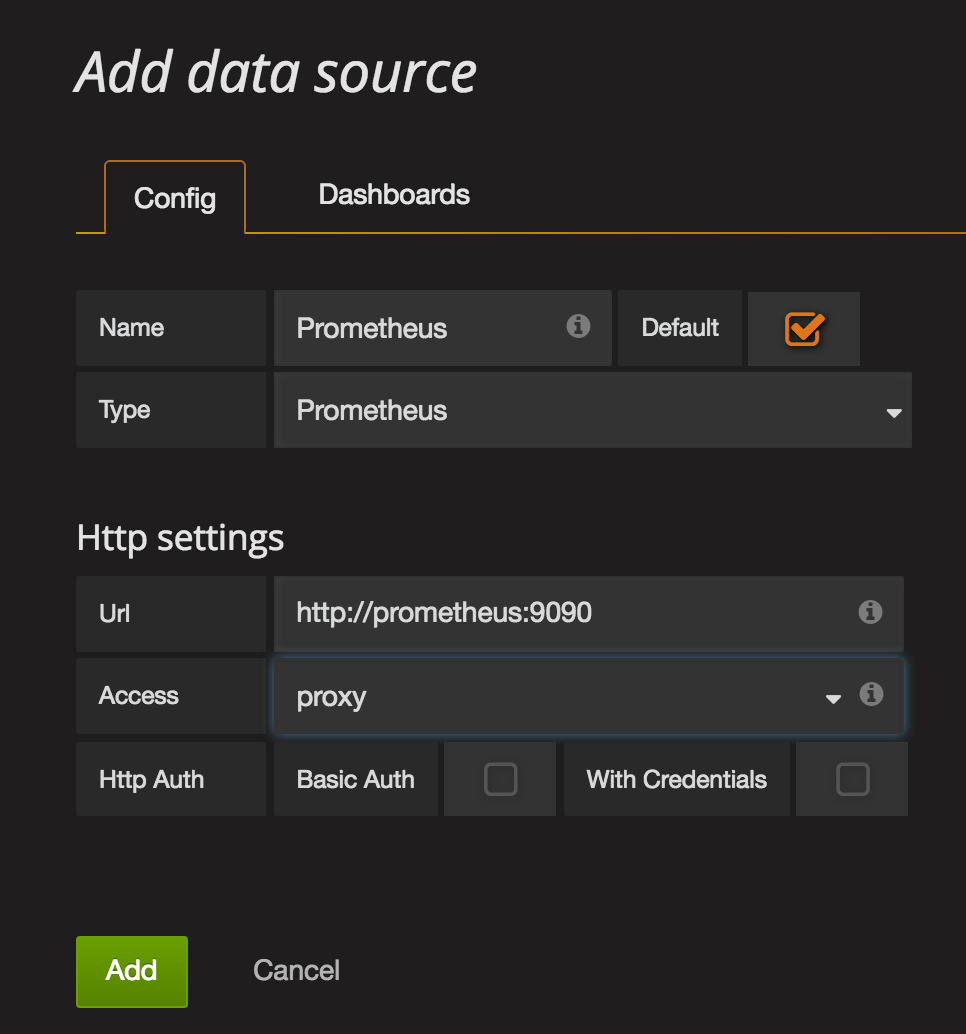
Now we need to create the Prometheus Datasource in order to connect Grafana to Prometheus
- Click the
GrafanaMenu at the top left corner (looks like a fireball) - Click
Data Sources - Click the green button
Add Data Source.
Ensure the Datasource name Prometheusis using uppercase P
- Grafana - http://grafana.localhost
- Prometheus - http://prometheus.localhost
Here are just a couple security considerations for this stack to help you get started.
- Remove the published ports from Prometheus and Alerting servicesi and only allow Grafana to be accessed
- Enable SSL for Grafana with a Proxy such as jwilder/nginx-proxy or Traefik with Let's Encrypt
- Add user authentication via a Reverse Proxy jwilder/nginx-proxy or Traefik for services cAdvisor, Prometheus, & Alerting as they don't support user authenticaiton
- Terminate all services/containers via HTTPS/SSL/TLS