Obtaining and using time zones in Windows is not simple. It involves API calls and reading the Registry. Some information is localised, and some are not. Here you will find a complete set of functions that wraps the difficult steps, eases common tasks, and helps when designing user interfaces. The documentation (see link below) demonstrates how to create tables to store time zones and how to display and select a time zone in Microsoft Access and Excel.
Even though time zones as such origin from the astronomical fact, that the Earth is spinning, time zones are not purely defined by science, math, or coordinates but are often a result of political decisions. Take, for example, daylight saving time or the date line that zigzags its way down the Pacific Ocean because some small countries adjacent the true date line have decided to belong to another time zone to "stay ahead" of the other countries. In 1940, Spain decided to move to the Central European Time time zone even though the country lines up with the United Kingdom.
It would be nice and convenient if the time zone of a location could be calculated directly from its coordinates. That is not so and, even worse, the time zone may change over time. Therefore, it is necessary to track the changes and record these to be able to obtain the time zone of a location at a given time.
For the IT industry, this is taken care of by IANA, which maintains a database, IANA Time Zone Database, holding all information about past and planned future changes of time zones and their locations. Due to its nature, however, this database is not just a set of tables you can look up; to query this vast database, special tools are needed.
With the functions presented, all time zones can be retrieved and listed like this:
| MUI | Bias | Name (key) |
|---|---|---|
| -80 | 240 | Atlantic Standard Time |
| -650 | -570 | AUS Central Standard Time |
| -2490 | -525 | Aus Central W. Standard Time |
| -670 | -600 | AUS Eastern Standard Time |
or full info for a single time zone:
| Field | Data |
|---|---|
| Name | Central Europe Standard Time |
| UTC Zone | UTC+01:00 |
| Bias | -60 |
| MUI | -280 |
| MUI Std | -282 |
| MUI Dlt | -281 |
| Std | Centraleuropa, normaltid |
| Dlt | Centraleuropa, sommertid |
| Bias Std | 0 |
| Bias Dlt | -60 |
| Date Std | 2019-10-27 03:00:00 |
| Date Dlt | 2019-03-31 02:00:00 |
| Locations | Beograd , Bratislava, Budapest, Ljubljana, Prag |
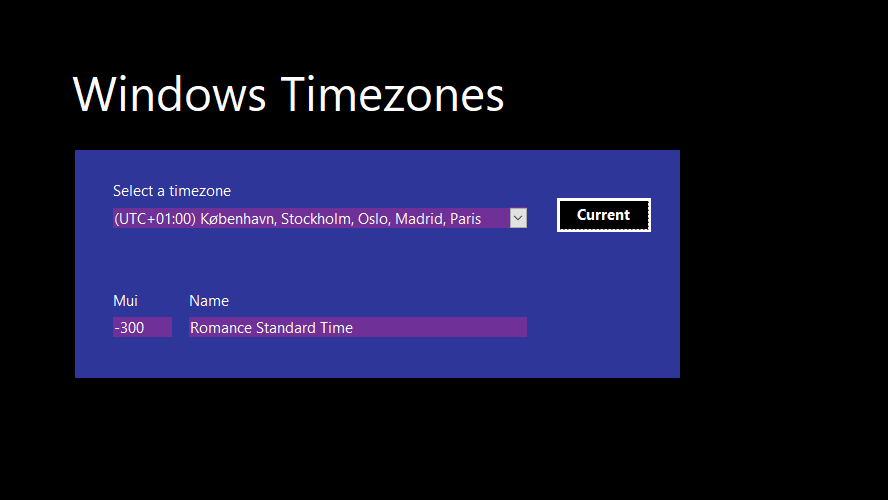
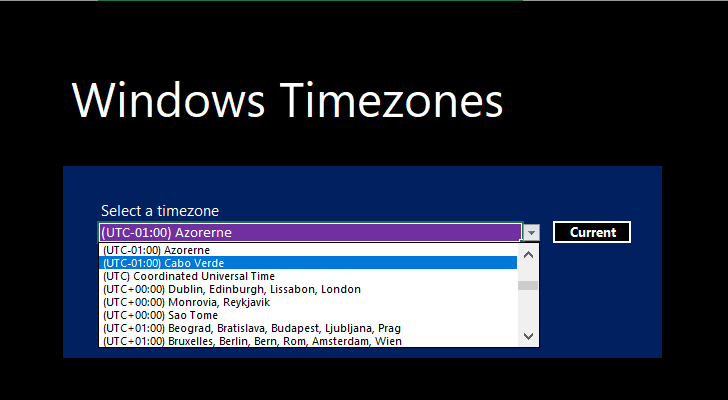
The time zones may be formatted identical to their listing in Windows 10:
Two examples are provided on how to achieve this - one using a CallBack function in Microsoft Access:
and using Data Validation in Microsoft Excel:
Code has been tested with both 32-bit and 64-bit Microsoft Access and Excel 365.
Full documentation can be found in the two articles here:
Time Zones, Windows, and VBA - Part 1
Time Zones, Windows, and Microsoft Office - Part 2
Included is a Microsoft Access example application and a Microsoft Excel example workbook.
If you wish to support my work or need extended support or advice, feel free to: