Abstract
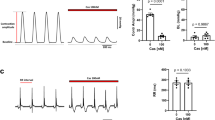
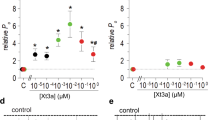
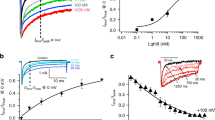
The biophysical properties of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels are well suited to pacemaking and to supporting calcium flux near the resting membrane potential in both excitable and non-excitable cells. We have identified a new scorpion toxin (kurtoxin) that binds to the α 1G T-type calcium channel with high affinity and inhibits the channel by modifying voltage-dependent gating. This toxin distinguishes between α 1G T-type calcium channels and other types of voltage-gated calcium channels, including α 1A , α 1B , α 1C and α 1E . Like the other α-scorpion toxins to which it is related, kurtoxin also interacts with voltage-gated sodium channels and slows their inactivation. Kurtoxin will facilitate characterization of the subunit composition of T-type calcium channels and help determine their involvement in electrical and biochemical signaling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llinas, R. & Yarom, Y. Properties and distribution of ionic conductances generating electroresponsiveness of mammalian inferior olivary neurons in vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 315, 569–584 (1981).
Carbone, E. & Lux, H. D. A low voltage activated, fully inactivating Ca2+ channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature 310, 501–511 ( 1984).
Bossu, J. L., Feltz, A. & Thomann, J. M. Depolarization elicits two distinct calcium currents in vertebrate sensory neurones. Pflügers Arch. 403, 360–368 (1985).
Bean, B. P. Two kinds of calcium channels in canine atrial cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 86, 1–30 (1985 ).
Armstrong, C. M. & Matteson, D. R. Two distinct populations of calcium channels in a clonal line of pituitary cells. Science 227, 65–67 ( 1985).
Nilius, B., Hess, P., Lansman, J. B. & Tsien, R. W. A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature 316, 443–446 (1985).
Kostyuk, P. G., Shuba, Y. M. & Savchenko, A. N. Three types of calcium channels in the membranes of mouse sensory neurons. Pflügers Arch. 411, 611–669 (1988).
Chen, C. & Hess, P. Mechanism of gating of T-type calcium channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 96, 603– 630 (1990).
Hagiwara, N., Irisawa, H. & Kameyama, M. Contribution of two types of calcium currents to the pacemaker potentials of rabbit sino-atrial node cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 395, 233–253 ( 1988).
Jahnsen, H. & Llinas, R. J. Ionic basis for the electro-responsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones in vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 349, 227–247 (1984).
Huguenard, J. R. Low-threshold calcium currents in central nervous system neurons. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 58, 329–348 (1996).
Cohen, C. J., McCarthy, R. T., Barrett, P. Q. & Rasmussen, H. Ca2+ channels in adrenal glomerulosa cells: K+ and angiotensin II increase T-type Ca2+ current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 2412– 2416 (1988).
Chen, C., Corbley, M., Roberts, T. & Hess, P. Voltage-sensitive calcium channels in normal and transformed 3T3 fibroblasts. Science 239, 1024–1026 ( 1988).
Santi, C. M., Darszon, A. & Hernandez-Cruz, A. A dihydropyridine-sensitive T-type Ca2+ current is the main Ca2+ current carrier in mouse primary spermatocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 271, C1583– C1593 (1996).
Bezprozvanny, I. & Tsien R. W. Voltage-dependent blockade of diverse types of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes by the Ca2+ channel antagonist mibefradil (Ro 40–5967). Mol. Pharmacol. 48, 540–549 (1995).
Perez-Reyes, E. et al. Molecular characterization of a neuronal low-voltage-activated T-type calcium channel. Nature 391, 896– 900 (1998).
Liman, E. R., Tytgat, J. & Hess, P. Subunit stoichiometry of a mammalian K+ channel determined by construction of mutimeric cDNAs. Neuron 9, 861–871 (1992).
Meves, H., Simard, J. M. & Watt, D. D. Interactions of scorpion toxins with the sodium channel. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 479,113– 132 (1986).
McDonough, S. I., Lampe, R. A., Keith, R. A. & Bean, B. P Voltage-dependent inhibition of N- and P-type calcium channels by the peptide toxin w-grammotoxin-SIA. Mol. Pharmacol. 52, 1095–1104 (1997).
McDonough, S. I., Mintz, I. M. & Bean, B. P. Alteration of P-type calcium channel gating by the spider toxin w-Aga-IVA. Biophys. J. 72, 2117–2128 (1997).
Swartz, K. J. & MacKinnon, R. Hanatoxin modifies the gating of a voltage-dependent K+ channel through multiple binding sites. Neuron 18, 665–673. (1997).
Cribbs, L. L. et al. Cloning and characterization of α1H from human heart, a member of the T-type Ca2+ channel gene family. Circ. Res. 83, 103–109 (1998).
Dubel, S. J. et al. Molecular cloning of the α-1 subunit of an ω-conotoxin-sensitive calcium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 5058–5062 (1992).
Mori, Y. et al. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of a brain calcium channel. Nature 350, 398–402 (1991).
Wei, X. et al. Increase in Ca2+ channel expression by deletions at the amino terminus of the cardiac α1C subunit. Receptors Channels 4, 205–215 ( 1996).
Schneider, T. et al. Molecular analysis and functional expression of the human type E neuronal Ca2+ channel α1 subunit. Receptors Channels 2, 255–270 (1994).
Auld, V. J. et al. A rat brain Na+ channel α subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron 1, 449– 461 (1988).
Isom, L. L. et al. Primary structure and functional expression of the β1 subunit of the rat brain sodium channel. Science 256 , 839–842 (1992).
Catterall, W. A. Binding of scorpion toxin to receptor site associated with sodium channels in frog muscle: correlation of voltage-dependent binding with activation. J. Gen. Physiol. 74, 357– 391 (1979).
Wang, G. K. & Strichartz, G. Kinetic analysis of the action of Leiurus scorpion toxin on ionic currents in myelinated nerve. J. Gen. Physiol. 86, 739–762 (1985).
Gonoi, T. & Hille, B. Gating of Na+ channels: inactivation modifiers discriminate among models. J. Gen. Physiol . 89, 253–274 ( 1987).
Rogers, J. C., Qu, Y., Tanada, T. N., Scheuer, T. & Catterall, W. Molecular determinants of high affinity binding of α-scorpion toxin and sea anemone toxin in the S3-S4 extracellular loop in domain IV of the Na+ channel α subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 15950–15962 (1996).
Li-Smerin Y. & Swartz, K. J. Gating modifier toxins recognize a conserved structural motif in voltage-gated Ca2+ and K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 8585–8589 (1998).
Swartz, K. J. & MacKinnon, R. Mapping the receptor site for hanatoxin, a gating modifier of voltage-dependent K+ channels. Neuron 18, 675–682 (1997).
Soong, T. W. et al. Structure and functional expression of a member of the low voltage-activated calcium channel family. Science 260 , 1133–1136 (1993).
Bourinet, E. et al. The α1E calcium channel exhibits permeation properties similar to low-voltage-activated calcium channels. J. Neurosci. 16, 4983–4993 (1996).
Meir, A. & Dolphin, A. C. Known calcium channel α1 subunits can form low threshold small conductance channels with similarities to native T-type channels. Neuron 20, 341 –351.
Bean, B. P. & McDonough, S. I. Two for T. Neuron 20, 825–828 ( 1998).
Pragnell, M., Sakamoto, J., Jay, S. D. & Campbell, K. P. Cloning and tissue-specific expression of the brain calcium channel β-subunit. FEBS Lett. 291, 253–258 (1991).
Ellis, S. B. et al. Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the α1 and α2 subunits of a DHP sensitive calcium channel. Science 241, 1661–1664 (1988).
Wei, X. et al. Heterologous regulation of the cardiac Ca2+ channel α1 subunit by skeletal muscle β and γ subunits. Implications for the structure of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 21943–21947 ( 1991).
Jaffe, H., Veeranna Shetty, K. T. & Pant, H. C. Characterization of the phosphorylation sites of human high molecular weight neurofilament protein by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry and database searching. Biochemistry 37, 3931–3940 (1998).
Seok, Y-J et al. High affinity binding and allosteric regulation of Escherichia coli glycogen phosphorylase by the histidine phosphocarrier protein, HPr. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26511– 26521 (1997).
Stone, K. L. & Williams, K. R. in A Practical Guide to Protein and Peptide Purification for Microsequencing (ed. Matsudaira, P.) 43–69 (Academic, San Diego, CA, 1993 ).
Acknowledgements
We thank Zhe Lu, Chinfei Chen and Yingying Li-Smerin for discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuang, RI., Jaffe, H., Cribbs, L. et al. Inhibition of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels by a new scorpion toxin. Nat Neurosci 1, 668–674 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/3669
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/3669
This article is cited by
-
CPP-Ts: a new intracellular calcium channel modulator and a promising tool for drug delivery in cancer cells
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Molecular Interactions between Tarantula Toxins and Low-Voltage-Activated Calcium Channels
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
CaV channels and cancer: canonical functions indicate benefits of repurposed drugs as cancer therapeutics
European Biophysics Journal (2016)
-
Block of T-type calcium channels by protoxins I and II
Molecular Brain (2014)
-
Profiling the resting venom gland of the scorpion Tityus stigmurus through a transcriptomic survey
BMC Genomics (2012)