Abstract
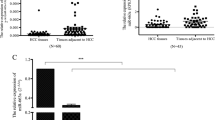
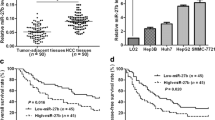
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play vital roles in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). miR-26b has been confirmed as an important regulator in carcinogenesis and other pathological processes. miR-26b-5p is one member of the mature miR-26 family, and its functional role in proliferation, angiogenesis and apoptosis in HCC remains unknown. Here, we demonstrate that miR-26b-5p expression was significantly decreased in HCC tissues and HCC cell lines compared with normal liver tissues and liver cells by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). The relationships between miR-26b-5p and the clinical characteristics of HCC patients were further analysed, and miR-26b-5p was positively correlated with the differentiation of HCC cells. Computational searches were further used to identify the downstream targets and signalling pathways of miR-26b-5p in HCC cells. Cell viability, proliferation and tube formation abilities were assessed by scrape, 3-(4,5 dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and three-dimensional culture assays to confirm that miR-26b-5p inhibited HCC cell growth and impaired the tube formation ability of the HCC cells. Both in vitro and in vivo studies showed that miR-26b-5p could suppress vascular mimicry (VM) and angiogenesis by down-regulating the expression of VE-cadherin, Snail and MMP2 and could inhibit the apoptosis of HCC cells. Using mouse models, we revealed that tumours derived from miR-26b-5p-expressing HCC cells displayed a significant decrease in microvessel density compared with those derived from control cells. Therefore, our data provide further insight into the role of miR-26b-5p as a negative regulator of proliferation, angiogenesis, and apoptosis in HCC.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118–27. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1001683.
Suzuki HI, Katsura A, Matsuyama H, Miyazono K. MicroRNA regulons in tumor microenvironment. Oncogene. 2015;34(24):3085–94. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.254.
Braconi C, Henry JC, Kogure T, Schmittgen T, Patel T. The role of MicroRNAs in human liver cancers. Semin Oncol. 2011;38(6):752–63. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2011.08.001.
Ji JF, Shi J, Budhu A, Yu ZP, Forgues M, Roessler S, et al. MicroRNA expression, survival, and response to interferon in liver cancer. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(15):1437–47. doi:10.1056/Nejmoa0901282.
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA, Ray SD. Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: new perspectives on therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:62–74. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2014.10.029.
Tang J, Li L, Huang W, Sui C, Yang Y, Lin X, et al. MiR-429 increases the metastatic capability of HCC via regulating classic Wnt pathway rather than epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 2015;364(1):33–43. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.023.
Liu JB, Yan JC, Zhou CC, Ma QH, Jin QY, Yang ZB. miR-1285-3p acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via downregulating JUN expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(1):219–25. doi:10.1007/s13277-014-2622-5.
Liu H, Li WZ, Chen CY, Pei YG, Long XY. MiR-335 acts as a potential tumor suppressor miRNA via downregulating ROCK1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2015;36(8):6313–9. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3317-2.
Kim HS, Shen, Park S, Lee KS, SJ Park, Y-K Kang, et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10).
Shen G, Lin Y, Yang X, Zhang J, Xu Z, Jia H. MicroRNA-26b inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting USP9X. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:393. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-393.
Yan Y, Luo YC, Wan HY, Wang J, Zhang PP, Liu M, et al. MicroRNA-10a is involved in the metastatic process by regulating Eph tyrosine kinase receptor A4-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and adhesion in hepatoma cells. Hepatology. 2013;57(2):667–77. doi:10.1002/hep.26071.
Xia H, Ooi LL, Hui KM. MicroRNA-216a/217-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition targets PTEN and SMAD7 to promote drug resistance and recurrence of liver cancer. Hepatology. 2013;58(2):629–41. doi:10.1002/hep.26369.
Xiong Y, Fang J-H, Yun J-P, Yang J, Zhang Y, Jia W-H, et al. Effects of MicroRNA-29 on apoptosis, tumorigenicity, and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2009. doi:10.1002/hep.23380.
Keklikoglou I, Hosaka K, Bender C, Bott A, Koerner C, Mitra D, et al. MicroRNA-206 functions as a pleiotropic modulator of cell proliferation, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by targeting ANXA2 and KRAS genes. Oncogene. 2015;34(37):4867–78. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.408.
Zhao N, Wang RZ, Zhou LJ, Zhu Y, Gong J, Zhuang SM. MicroRNA-26b suppresses the NF-kB signaling and enhances the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting TAK1 and TAB3. Mol Cancer. 2014;13. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-13-35.
Verghese ET, Drury R, Green CA, Holliday DL, Lu X, Nash C, et al. Epithelial-stromal cross-talk in breast cancer: miR-26b within carcinoma-associated fibroblasts regulates epithelial cancer cell migration and invasion. J Pathol. 2013;231:23.
Zhang ZC, Kim K, Li X, Moreno M, Sharp T, Goodheart MJ, et al. MicroRNA-26b represses colon cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting lymphoid enhancer factor 1 expression. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(7):1942–51. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-1000.
Fu X, Meng Z, Liang W, Tian Y, Wang X, Han W, et al. miR-26a enhances miRNA biogenesis by targeting Lin28B and Zcchc11 to suppress tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene. 2014;33(34):4296–306. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.385.
Wu TW, Chen WQ, Liu SY, Lu HD, Wang H, Kong DY, et al. Huaier suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human pulmonary cancer cells via upregulation of miR-26b-5p. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(12):2107–14. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.044.
Sun T, Zhao N, Zhao XL, Gu Q, Zhang SW, Che N, et al. Expression and functional significance of twist1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: its role in vasculogenic mimicry. Hepatology. 2010;51(2):545–56. doi:10.1002/hep.23311.
Sun T, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhao N, Dong XY, Che N, et al. Promotion of tumor cell metastasis and vasculogenic mimicry by way of transcription coactivation by Bcl-2 and Twist1: a study of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2011;54(5):1690–706. doi:10.1002/hep.24543.
Meng J, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhang DF, Zhao XM, Gu Q, et al. Doxycycline as an inhibitor of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and vasculogenic mimicry in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(12):3107–22. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-13-1060.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(−Delta Delta C) method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Kuwana T, Newmeyer DD. Bcl-2-family proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15(6):691–9. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2003.10.004.
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y, Sakuragi N. Apoptosis and Molecular Targeting Therapy in Cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014;Artn 150845. doi:10.1155/2014/150845.
Basu A, Haldar S. The relationship between Bcl-2, Bax, and p53: consequences for cell cycle progression and cell death. Mol Hum Reprod. 1998;4(12):1099–109.
Wang XY, Li C, Dai QQ. Down-regulation of microRNA-26b rescued hypoxia-induced apoptosis in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes by regulating PTEN. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(3):4073–9.
Kulshreshtha R, Ferracin M, Wojcik SE, Garzon R, Alder H, Agosto-Perez FJ, et al. A microRNA signature of hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(5):1859–67. doi:10.1128/MCB.01395-06.
Liu XX, Li XJ, Zhang B, Liang YJ, Zhou CX, Cao DX, et al. MicroRNA-26b is underexpressed in human breast cancer and induces cell apoptosis by targeting SLC7A11. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(9):1363–7. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2011.04.018.
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, Yang J, Liu Y, Huang X, et al. MicroRNA-29b suppresses tumor angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis by regulating matrix metalloproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology. 2011;54(5):1729–40. doi:10.1002/hep.24577.
Wang J, Huang R, Chu ES, Lan HY, Chen H-Y, JJ Sung, et al. microRNA-29b prevents liver fibrosis by attenuating hepatic stellate cell activation and inducing apoptosis through targeting PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6(9).
Wu DW, Hsu NY, Wang YC, Lee MC, Cheng YW, Chen CY, et al. c-Myc suppresses microRNA-29b to promote tumor aggressiveness and poor outcomes in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting FHIT. Oncogene. 2015;34(16):2072–82. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.152.
Habata S, Iwasaki M, Sugio A, Suzuki M, Tamate M, Satohisa S, et al. BAG3 increases the invasiveness of uterine corpus carcinoma cells by suppressing miR-29b and enhancing MMP2 expression. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(5):2613–21. doi:10.3892/or.2015.3831.
Wolf Jr JE, Hubler Jr WR. Tumor angiogenic factor and human skin tumors. Arch Dermatol. 1975;111(3):321–7.
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA, Gardner LMG, Pe’er J, et al. Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 1999;155(3):739–52. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65173-5.
Wang JY, Sun T, Zhao XL, Zhang SW, Zhang DF, Gu Q, et al. Functional significance of VEGF-a in human ovarian carcinoma—role in vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7(5):758–66. doi:10.4161/Cbt.7.5.5765.
Zhang SW, Li M, Zhang DF, Xu SY, Wang XY, Liu ZY, et al. Hypoxia influences linearly patterned programmed cell necrosis and tumor blood supply patterns formation in melanoma. Lab Invest. 2009;89(5):575–86. doi:10.1038/labinvest.2009.20.
Sun BC, Zhang SW, Zhang DF, Du J, Guo H, Zha XL, et al. Vasculogenic mimicry is associated with high tumor grade, invasion and metastasis, and short survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2006;16(4):693–8.
Hess AR, Seftor EA, Seftor REB, Hendrix MJC. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and MMP-2 activity during melanoma cell vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Res. 2003;63(16):4757–62.
Chung HJ, Mahalingam M. Angiogenesis, vasculogenic mimicry and vascular invasion in cutaneous malignant melanoma—implications for therapeutic strategies and targeted therapies. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2014;14(5):621–39. doi:10.1586/14737140.2014.883281.
Lynam-Lennon N, Maher SG, Reynolds JV. The roles of microRNA in cancer and apoptosis. Biol Rev. 2009;84(1):55–71. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.2008.00061.x.
Guo XZ, Shao XD, Liu MP, Xu JH, Ren LN, Zhao JJ, et al. Effect of bax, bcl-2 and bcl-xL on regulating apoptosis in tissues of normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroentero. 2002;8(6):1059–62.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Key project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81230050), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81172046, no. 81173091 and no. 81301813), the Key project of the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (no. 12JCZDJC23600) and the project of the Tianjin Natural Science Foundation (No. 14JCYBJC27700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Yong Wang and Baocun Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Sun, B., Sun, H. et al. Regulation of proliferation, angiogenesis and apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by miR-26b-5p. Tumor Biol. 37, 10965–10979 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4964-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4964-7