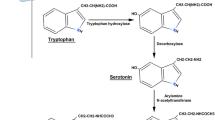
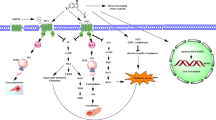
Abstract
Angiogenesis depends on proangiogenic and anti-angiogenic molecules that regulate endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Well-regulated angiogenesis plays a pivotal role in many physiological conditions such as reproduction and embryonic development, while abnormal angiogenesis is also the basis of a variety of pathological processes including tumor metastasis and atherosclerotic plaque formation. Melatonin has a variety of biological effects, including inhibition of tumor metastasis, stabilizing atherosclerotic plaques, and the regulation of seasonal reproductive rhythms, etc. During certain pathophysiological processes, melatonin exerts different functions depending on its ability to regulate angiogenesis. This review reveals that melatonin has different effects on neovascularization under different physiological and pathological conditions. In tumors, in age-related ocular diseases, and in a hypoxic environment, melatonin inhibits neovascularization in tissues, while in gastric ulcers, skin lesions, and some physiologic processes, it promotes angiogenesis. We also speculate that melatonin may inhibit the neovascularization in atherosclerotic plaques, thus preventing the initiation and development of atherosclerosis. Most studies suggest that these effects are related to the role of melatonin in regulating of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors, but the specific regulatory mechanisms remain disparate, which may lead to the differential effects of melatonin on angiogenesis under different conditions. In this review, we thus summarize some seemingly contradictory mechanisms by which melatonin controls angiogenesis under different pathological and physiological conditions, and urge that the regulatory mechanisms be further studied.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J, Shing Y (1992) Angiogenesis. J Biol Chemistry 267(16):10931–10934. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4613-2825-4_42
Vandekeere S, Dewerchin M, Carmeliet P (2015) Angiogenesis revisited: an overlooked role of endothelial cell metabolism in vessel sprouting. Microcirculation 22(7):509–517. https://doi.org/10.1111/micc.12229
Alvarez-Garcia V, Gonzalez A, Alonso-Gonzalez C, Martinez-Campa C, Cos S (2013) Antiangiogenic effects of melatonin in endothelial cell cultures. Microvasc Res 87:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2013.02.008
Rizov M, Andreeva P, Dimova I (2017) Molecular regulation and role of angiogenesis in reproduction. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol 56(2):127–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjog.2016.06.019
Gerbaud P, Murthi P, Guibourdenche J, Guimiot F, Sarazin B, Evain-Brion D, Badet J, Pidoux G (2019) Study of human T21 placenta suggests a potential role of mesenchymal spondin-2 in placental vascular development. Endocrinology 160(3):684–698. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2018-00826
DiPietro LA (2016) Angiogenesis and wound repair: when enough is enough. J Leukoc Biol 100(5):979–984. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.4MR0316-102R
Ribatti D, Crivellato E (2012) "Sprouting angiogenesis", a reappraisal. Dev Biol 372(2):157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.09.018
Folkman J, Cotran R (1976) Relation of vascular proliferation to tumor growth. Int Rev Exp Pathol 16:207–248
Carmeliet P (2003) Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med 9(6):653–660. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0603-653
McCord CP, Allen FP (1917) Evidences associating pineal gland function with alterations in pigmentation. Journal of experimental zoology 23:207–224. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1400230108
Lerner AB, Case JD, Takahashi Y, Lee TH, Mori W (1958) Isolation of melatonin the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocytes. J Am Chem Soc 80(10):2587–2587. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01543a060
Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Brzozowska I, Pawlik M, Sliwowski Z, Czesnikiewicz-Guzik M, Kwiecien S, Brzozowski T, Bubenik GA, Pawlik WW (2007) Localization and biological activities of melatonin in intact and diseased gastrointestinal tract (GIT). J Physiol Pharmacol 58(3):381–405
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Galano A (2014) Melatonin: exceeding expectations. Physiology (Bethesda) 29(5):325–333. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiol.00011.2014
Claustrat B, Leston J (2015) Melatonin: physiological effects in humans. Neurochirurgie 61(2–3):77–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuchi.2015.03.002
Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2019) Mitochondria: the birth place, battle ground and the site of melatonin metabolism in cells. Melatonin Res 2(1):44–66. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250011
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Fuentes-Broto L (2010) Melatonin: a multitasking molecule. Prog Brain Res 181:127–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(08)81008-4
Lee HY, Back K (2018) Melatonin plays a pivotal role in conferring tolerance against endoplasmic reticulum stress via mitogen-activated protein kinases and bZIP60 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Melatonin Res 1(1):94–108. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250006
Gonzalez AG, Revilla NR, Emilio J (2019) Clinical uses of melatonin: evaluation of human trials on cancer treatment. Melatonin Res 2(2):47–69. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250021
Pfeffer M, Korf HW, Wicht H (2018) Synchronizing effects of melatonin on diurnal and circadian rhythms. Gen Comp Endocrinol 258:215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.05.013
Dominguez-Rodriguez A, Abreu-Gonzalez P, Chen Y (2019) Cardioprotection and effects of melatonin administration on cardiac ischemia reperfusion: Insight from clinical studies. Melatonin Res 2(2):100–105. https://doi.org/10.32794/mr11250024
Jardim-Perassi BV, Arbab AS, Ferreira LC, Borin TF, Varma NR, Iskander AS, Shankar A, Ali MM, de Campos Zuccari DA (2014) Effect of melatonin on tumor growth and angiogenesis in xenograft model of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85311. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085311
Gonzalez A, Gonzalez-Gonzalez A, Alonso-Gonzalez C, Menendez-Menendez J, Martinez-Campa C, Cos S (2017) Melatonin inhibits angiogenesis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells by downregulation of VEGF. Oncol Rep 37(4):2433–2440. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5446
Ganguly K, Sharma AV, Reiter RJ, Swarnakar S (2010) Melatonin promotes angiogenesis during protection and healing of indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer: role of matrix metaloproteinase-2. J Pineal Res 49(2):130–140. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00776.x
Bizzarri M, Proietti S, Cucina A, Reiter RJ (2013) Molecular mechanisms of the pro-apoptotic actions of melatonin in cancer: a review. Expert Opin Ther Targets 17(12):1483–1496. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2013.834890
Ferrara N, Henzel WJ (1989) Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161(2):851–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(89)92678-8
Cook KM, Figg WD (2010) Angiogenesis inhibitors: current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J Clin 60(4):222–243. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20075
Shulman K, Rosen S, Tognazzi K, Manseau EJ, Brown LF (1996) Expression of vascular permeability factor (VPF/VEGF) is altered in many glomerular diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 7(5):661–666
Ourradi K, Blythe T, Jarrett C, Barratt SL, Welsh GI, Millar AB (2017) VEGF isoforms have differential effects on permeability of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Respir Res 18(1):116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-017-0602-1
Shibuya M (2011) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptor (VEGFR) signaling in angiogenesis: a crucial target for anti- and pro-angiogenic therapies. Genes Cancer 2(12):1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601911423031
Ferrara N (1999) Molecular and biological properties of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Mol Med (Berl) 77(7):527–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001099900019
Gupta K, Kshirsagar S, Li W, Gui L, Ramakrishnan S, Gupta P, Law PY, Hebbel RP (1999) VEGF prevents apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells via opposing effects on MAPK/ERK and SAPK/JNK signaling. Exp Cell Res 247(2):495–504. https://doi.org/10.1006/excr.1998.4359
Beazley-Long N, Hua J, Jehle T, Hulse RP, Dersch R, Lehrling C, Bevan H, Qiu Y, Lagreze WA, Wynick D, Churchill AJ, Kehoe P, Harper SJ, Bates DO, Donaldson LF (2013) VEGF-A165b is an endogenous neuroprotective splice isoform of vascular endothelial growth factor A in vivo and in vitro. Am J Pathol 183(3):918–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.05.031
Cerezo AB, Hornedo-Ortega R, Alvarez-Fernandez MA, Troncoso AM, Garcia-Parrilla MC (2017) Inhibition of VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 activation and HUVEC migration by melatonin and other bioactive indolic compounds. Nutrients 9(3):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9030249
Ramirez-Fernandez MP, Calvo-Guirado JL, de-Val JE, Delgado-Ruiz RA, Negri B, Pardo-Zamora G, Penarrocha D, Barona C, Granero JM, Alcaraz-Banos M (2013) Melatonin promotes angiogenesis during repair of bone defects: a radiological and histomorphometric study in rabbit tibiae. Clin Oral Invest 17(1):147–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-012-0684-6
Emet M, Ozcan H, Ozel L, Yayla M, Halici Z, Hacimuftuoglu A (2016) A review of melatonin, its receptors and drugs. Eurasian J Med 48(2):135–141. https://doi.org/10.5152/eurasianjmed.2015.0267
Zonta YR, Martinez M, Camargo IC, Domeniconi RF, Lupi Junior LA, Pinheiro PF, Reiter RJ, Martinez FE, Chuffa LG (2017) Melatonin reduces angiogenesis in serous papillary ovarian carcinoma of ethanol-preferring rats. Int J Mol Sci 18(4):763
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285(21):1182–1186. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM197111182852108
Reiter RJ, Rosales-Corral SA, Tan DX, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Qin L, Yang SF, Xu K (2017) Melatonin, a Full Service Anti-Cancer Agent: Inhibition of Initiation, Progression and Metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 18(4):843. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040843
Wang RX, Liu H, Xu L, Zhang H, Zhou RX (2016) Melatonin downregulates nuclear receptor RZR/RORgamma expression causing growth-inhibitory and anti-angiogenesis activity in human gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Lett 12(2):897–903. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2016.4729
Kim KJ, Choi JS, Kang I, Kim KW, Jeong CH, Jeong JW (2013) Melatonin suppresses tumor progression by reducing angiogenesis stimulated by HIF-1 in a mouse tumor model. J Pineal Res 54(3):264–270. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.01030.x
Carbajo-Pescador S, Ordonez R, Benet M, Jover R, Garcia-Palomo A, Mauriz JL, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2013) Inhibition of VEGF expression through blockade of Hif1alpha and STAT3 signalling mediates the anti-angiogenic effect of melatonin in HepG2 liver cancer cells. Br J Cancer 109(1):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.285
Goradel NH, Asghari MH, Moloudizargari M, Negahdari B, Haghi-Aminjan H, Abdollahi M (2017) Melatonin as an angiogenesis inhibitor to combat cancer: mechanistic evidence. Toxicol Appl Pharmcol 335:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2017.09.022
Alvarez-Garcia V, Gonzalez A, Alonso-Gonzalez C, Martinez-Campa C, Cos S (2013) Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by melatonin in human breast cancer cells. J Pineal Res 54(4):373–380. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12007
Menendez-Menendez J, Martinez-Campa C (2018) Melatonin: an anti-tumor agent in hormone-dependent cancers. Int J Endocrinol 2018:3271948. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3271948
Calvo-Guirado JL, Ramirez-Fernandez MP, Gomez-Moreno G, Mate-Sanchez JE, Delgado-Ruiz R, Guardia J, Lopez-Mari L, Barone A, Ortiz-Ruiz AJ, Martinez-Gonzalez JM, Bravo LA (2010) Melatonin stimulates the growth of new bone around implants in the tibia of rabbits. J Pineal Res 49(4):356–363. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00801.x
Shino H, Hasuike A, Arai Y, Honda M, Isokawa K, Sato S (2016) Melatonin enhances vertical bone augmentation in rat calvaria secluded spaces. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 21(1):e122–e126. https://doi.org/10.4317/medoral.20904
Yildirimturk S, Batu S, Alatli C, Olgac V, Firat D, Sirin Y (2016) The effects of supplemental melatonin administration on the healing of bone defects in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Appl Oral Sci 24(3):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-775720150570
Soybir G, Topuzlu C, Odabas O, Dolay K, Bilir A, Koksoy F (2003) The effects of melatonin on angiogenesis and wound healing. Surg Today 33(12):896–901. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-003-2621-3
Pugazhenthi K, Kapoor M, Clarkson AN, Hall I, Appleton I (2008) Melatonin accelerates the process of wound repair in full-thickness incisional wounds. J Pineal Res 44(4):387–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00541.x
Mehraein F, Kabir K (2011) The effects of melatonin on open wounds of aged mice skin. Wounds 23(6):166–170
Abdelraheim SR, Okasha AM, Ghany HM, Ibrahim HM (2015) Ghrelin gene expression in rats with ethanol-induced gastric ulcers: a role of melatonin. Endocr Regul 49(1):3–10
Colucci R, Fornai M, Antonioli L, Ghisu N, Tuccori M, Blandizzi C, Del Tacca M (2009) Characterization of mechanisms underlying the effects of esomeprazole on the impairment of gastric ulcer healing with addition of NSAID treatment. Dig Liver Dis 41(6):395–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2008.10.004
Celinski K, Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Cichoz-Lach H, Slomka M, Malgorzata P, Bielanski W, Reiter RJ (2011) Melatonin or L-tryptophan accelerates healing of gastroduodenal ulcers in patients treated with omeprazole. J Pineal Res 50(4):389–394. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00855.x
Konturek PC, Konturek SJ, Celinski K, Slomka M, Cichoz-Lach H, Bielanski W, Reiter RJ (2010) Role of melatonin in mucosal gastroprotection against aspirin-induced gastric lesions in humans. J Pineal Res 48(4):318–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00755.x
Konturek SJ, Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Bubenik GA (2007) Role of melatonin in upper gastrointestinal tract. J Physiol Pharmacol 58 Suppl 6:23–52
Ahluwalia A, Brzozowska IM, Hoa N, Jones MK, Tarnawski AS (2018) Melatonin signaling in mitochondria extends beyond neurons and neuroprotection: Implications for angiogenesis and cardio/gastroprotection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(9):E1942-E1943. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1722131115
Ganguly K, Swarnakar S (2012) Chronic gastric ulceration causes matrix metalloproteinases-9 and – 3 augmentation: alleviation by melatonin. Biochimie 94(12):2687–2698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2012.08.004
Pradeepkumar Singh L, Vivek Sharma A, Swarnakar S (2011) Upregulation of collagenase-1 and – 3 in indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer in diabetic rats: role of melatonin. J Pineal Res 51(1):61–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00845.x
Ganguly K, Swarnakar S (2009) Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and – 3 in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced acute gastric ulcers in mice: regulation by melatonin. J Pineal Res 47(1):43–55. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00687.x
Rudra DS, Pal U, Maiti NC, Reiter RJ, Swarnakar S (2013) Melatonin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity by binding to its active site. J Pineal Res 54(4):398–405. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12034
Brzozowska I, Strzalka M, Drozdowicz D, Konturek SJ, Brzozowski T (2014) Mechanisms of esophageal protection, gastroprotection and ulcer healing by melatonin. implications for the therapeutic use of melatonin in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and peptic ulcer disease. Curr Pharm Des 20(30):4807–4815. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612819666131119110258
Bruick RK, McKnight SL (2001) A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294(5545):1337–1340. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066373
Ivan M, Haberberger T, Gervasi DC, Michelson KS, Gunzler V, Kondo K, Yang H, Sorokina I, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Kaelin WG Jr (2002) Biochemical purification and pharmacological inhibition of a mammalian prolyl hydroxylase acting on hypoxia-inducible factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(21):13459–13464. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.192342099
Jardim-Perassi BV, Lourenco MR, Doho GM, Grigolo IH, Gelaleti GB, Ferreira LC, Borin TF, Moschetta MG, Pires de Campos Zuccari DA (2016) Melatonin regulates angiogenic factors under hypoxia in breast cancer cell line. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 16(3):347–358
Cheng J, Yang HL, Gu CJ, Liu YK, Shao J, Zhu R, He YY, Zhu XY, Li MQ (2019) Melatonin restricts the viability and angiogenesis of vascular endothelial cells by suppressing HIF-1alpha/ROS/VEGF. Int J Mol Med 43(2):945–955. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.4021
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wang F, Ling EA, Liu S, Wang L, Yang Y, Yao L, Chen X, Wang F, Shi W, Gao M, Hao A (2013) Melatonin antagonizes hypoxia-mediated glioblastoma cell migration and invasion via inhibition of HIF-1alpha. J Pineal Res 55(2):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12052
Sohn EJ, Won G, Lee J, Lee S, Kim SH (2015) Upregulation of miRNA3195 and miRNA374b mediates the anti-angiogenic properties of melatonin in hypoxic PC-3 prostate cancer cells. J Cancer 6(1):19–28. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.9591
Goncalves Ndo N, Rodrigues RV, Jardim-Perassi BV, Moschetta MG, Lopes JR, Colombo J, Zuccari DA (2014) Molecular markers of angiogenesis and metastasis in lines of oral carcinoma after treatment with melatonin. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 14(9):1302–1311
Guzy RD, Hoyos B, Robin E, Chen H, Liu L, Mansfield KD, Simon MC, Hammerling U, Schumacker PT (2005) Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and cellular oxygen sensing. Cell Metab 1(6):401–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2005.05.001
Guzy RD, Schumacker PT (2006) Oxygen sensing by mitochondria at complex III: the paradox of increased reactive oxygen species during hypoxia. Exp Physiol 91(5):807–819. https://doi.org/10.1113/expphysiol.2006.033506
Park SY, Jang WJ, Yi EY, Jang JY, Jung Y, Jeong JW, Kim YJ (2010) Melatonin suppresses tumor angiogenesis by inhibiting HIF-1alpha stabilization under hypoxia. J Pineal Res 48(2):178–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2009.00742.x
Cho SY, Lee HJ, Jeong SJ, Lee HJ, Kim HS, Chen CY, Lee EO, Kim SH (2011) Sphingosine kinase 1 pathway is involved in melatonin-induced HIF-1alpha inactivation in hypoxic PC-3 prostate cancer cells. J Pineal Res 51(1):87–93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00865.x
Vriend J, Reiter RJ (2016) Melatonin and the von Hippel-Lindau/HIF-1 oxygen sensing mechanism: a review. Biochim Biophys Acta 1865(2):176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2016.02.004
Dorrell M, Uusitalo-Jarvinen H, Aguilar E, Friedlander M (2007) Ocular neovascularization: basic mechanisms and therapeutic advances. Surv Ophthalmol 52 Suppl 1:S3–S19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.survophthal.2006.10.017
Amaral J, Becerra SP (2010) Effects of human recombinant PEDF protein and PEDF-derived peptide 34-mer on choroidal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51(3):1318–1326. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.09-4455
Du H, Sun X, Guma M, Luo J, Ouyang H, Zhang X, Zeng J, Quach J, Nguyen DH, Shaw PX, Karin M, Zhang K (2013) JNK inhibition reduces apoptosis and neovascularization in a murine model of age-related macular degeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110(6):2377–2382. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1221729110
Sakamoto K, Liu C, Tosini G (2004) Circadian rhythms in the retina of rats with photoreceptor degeneration. J Neurochem 90(4):1019–1024. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02571.x
Crooke A, Huete-Toral F, Colligris B, Pintor J (2017) The role and therapeutic potential of melatonin in age-related ocular diseases. J Pineal Res 63(2):e12430. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12430
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Yong Z, Lu J, Foulds WS, Ling EA (2007) Blood-retinal barrier disruption and ultrastructural changes in the hypoxic retina in adult rats: the beneficial effect of melatonin administration. J Pathol 212(4):429–439. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2195
Lv XD, Liu S, Cao Z, Gong LL, Feng XP, Gao QF, Wang J, Hu L, Cheng XC, Yu CH, Xing YQ (2016) Correlation between serum melatonin and aMT6S level for age-related macular degeneration patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20(20):4196–4201
Blasiak J, Reiter RJ, Kaarniranta K (2016) Melatonin in retinal physiology and pathology: the case of age-related macular degeneration. Oxidative Med Cell Long. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6819736
Dehdashtian E, Mehrzadi S, Yousefi B, Hosseinzadeh A, Reiter RJ, Safa M, Ghaznavi H, Naseripour M (2018) Diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis and the ameliorating effects of melatonin; involvement of autophagy, inflammation and oxidative stress. Life Sci 193:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.001
Arranz-Romera A, Davis BM, Bravo-Osuna I, Esteban-Perez S, Molina-Martinez IT, Shamsher E, Ravindran N, Guo L, Cordeiro MF, Herrero-Vanrell R (2019) Simultaneous co-delivery of neuroprotective drugs from multi-loaded PLGA microspheres for the treatment of glaucoma. J Control Release 297:26–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.01.012
Calderon GD, Juarez OH, Hernandez GE, Punzo SM, De la Cruz ZD (2017) Oxidative stress and diabetic retinopathy: development and treatment. Eye 31(8):1122–1130. https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2017.64
Wang J, Xu X, Elliott MH, Zhu M, Le YZ (2010) Muller cell-derived VEGF is essential for diabetes-induced retinal inflammation and vascular leakage. Diabetes 59(9):2297–2305. https://doi.org/10.2337/db09-1420
Wang JJ, Zhu M, Le YZ (2015) Functions of Muller cell-derived vascular endothelial growth factor in diabetic retinopathy. World J Diabetes 6(5):726–733. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i5.726
Bai Y, Ma JX, Guo J, Wang J, Zhu M, Chen Y, Le YZ (2009) Muller cell-derived VEGF is a significant contributor to retinal neovascularization. J Pathol 219(4):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.2611
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Foulds WS, Luu CD, Ling EA (2009) Cellular and vascular changes in the retina of neonatal rats after an acute exposure to hypoxia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50(11):5364–5374. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.09-3552
Jiang T, Chang Q, Zhao Z, Yan S, Wang L, Cai J, Xu G (2012) Melatonin-mediated cytoprotection against hyperglycemic injury in Muller cells. PLoS ONE 7(12):e50661. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0050661
Hellings WE, Peeters W, Moll FL, Piers SR, van Setten J, Van der Spek PJ, de Vries JP, Seldenrijk KA, De Bruin PC, Vink A, Velema E, de Kleijn DP, Pasterkamp G (2010) Composition of carotid atherosclerotic plaque is associated with cardiovascular outcome: a prognostic study. Circulation 121(17):1941–1950. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.887497
Crea F, Libby P (2017) Acute coronary syndromes: the way forward from mechanisms to precision treatment. Circulation 136(12):1155–1166. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029870
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2015) Contribution of neovascularization and intraplaque haemorrhage to atherosclerotic plaque progression and instability. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 213(3):539–553. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.12438
Sedding DG, Boyle EC, Demandt JAF, Sluimer JC, Dutzmann J, Haverich A, Bauersachs J (2018) Vasa vasorum angiogenesis: key player in the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis and potential target for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Front Immunol 9:706. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00706
Jaipersad AS, Lip GY, Silverman S, Shantsila E (2014) The role of monocytes in angiogenesis and atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 63(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.09.019
Favero G, Rodella LF, Reiter RJ, Rezzani R (2014) Melatonin and its atheroprotective effects: a review. Molecular cellular endocrinology 382(2):926–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2013.11.016
Zhang Y, Koradia A, Kamato D, Popat A, Little PJ, Ta HT (2019) Treatment of atherosclerotic plaque: perspectives on theranostics. J Pharm Pharmacol 71(7):1029–1043. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.13092
Ding S, Lin N, Sheng X, Zhao Y, Su Y, Xu L, Tong R, Yan Y, Fu Y, He J, Gao Y, Yuan A, Ye L, Reiter RJ, Pu J (2019) Melatonin stabilizes rupture-prone vulnerable plaques via regulating macrophage polarization in a nuclear circadian receptor RORalpha-dependent manner. Journal of pineal research:e12581. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12581
Li H, Li J, Jiang X, Liu S, Liu Y, Chen W, Yang J, Zhang C, Zhang W (2019) Melatonin enhances atherosclerotic plaque stability by inducing prolyl-4-hydroxylase alpha1 expression. J Hypertens 37(5):964–971. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000001979
Ma S, Chen J, Feng J, Zhang R, Fan M, Han D, Li X, Li C, Ren J, Wang Y, Cao F (2018) Melatonin ameliorates the progression of atherosclerosis via mitophagy activation and NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition. Oxidative Med Cell Long 2018:9286458. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9286458
Hussein MR, Ahmed OG, Hassan AF, Ahmed MA (2007) Intake of melatonin is associated with amelioration of physiological changes, both metabolic and morphological pathologies associated with obesity: an animal model. Int J Exp Pathol 88(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2613.2006.00512.x
Pita ML, Hoyos M, Martin-Lacave I, Osuna C, Fernandez-Santos JM, Guerrero JM (2002) Long-term melatonin administration increases polyunsaturated fatty acid percentage in plasma lipids of hypercholesterolemic rats. J Pineal Res 32(3):179–186. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1600-079x.2002.1o851.x
Sartori C, Dessen P, Mathieu C, Monney A, Bloch J, Nicod P, Scherrer U, Duplain H (2009) Melatonin improves glucose homeostasis and endothelial vascular function in high-fat diet-fed insulin-resistant mice. Endocrinology 150(12):5311–5317. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2009-0425
Cardinali DP, Cano P, Jimenez-Ortega V, Esquifino AI (2011) Melatonin and the metabolic syndrome: physiopathologic and therapeutical implications. Neuroendocrinology 93(3):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1159/000324699
Kwon TG, Lerman LO, Lerman A (2015) The vasa vasorum in atherosclerosis: the vessel within the vascular wall. J Am Coll Cardiol 65(23):2478–2480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.04.032
Castle-Miller J, Bates DO, Tortonese DJ (2017) Mechanisms regulating angiogenesis underlie seasonal control of pituitary function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114(12):E2514–E2523. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1618917114
Korf HW (2018) Signaling pathways to and from the hypophysial pars tuberalis, an important center for the control of seasonal rhythms. Gen Comp Endocrinol 258:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.05.011
Reiter RJ (1980) The pineal and its hormones in the control of reproduction in mammals. Endocr Rev 1(2):109–131. https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv-1-2-109
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Kim SJ, Cruz MH (2014) Delivery of pineal melatonin to the brain and SCN: role of canaliculi, cerebrospinal fluid, tanycytes and Virchow-Robin perivascular spaces. Brain Struct Funct 219(6):1873–1887. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-014-0719-7
Reiter RJ (1993) The melatonin rhythm: both a clock and a calendar. Experientia 49(8):654–664. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01923947
Basini G, Bussolati S, Ciccimarra R, Grasselli F (2017) Melatonin potentially acts directly on swine ovary by modulating granulosa cell function and angiogenesis. Reprod Fertil Dev 29(12):2305–2312. https://doi.org/10.1071/RD16513
Kandemir YB, Konuk E, Katirci E, Xxx F, Behram M (2019) Is the effect of melatonin on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 associated with angiogenesis in the rat ovary? Clinics 74:e658. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2019/e658
Li Y, Fang L, Yu Y, Shi H, Wang S, Guo Y, Sun Y (2019) Higher melatonin in the follicle fluid and MT2 expression in the granulosa cells contribute to the OHSS occurrence. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 17(1):37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-019-0479-6
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81827808 and 81870178)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Q., Reiter, R.J. & Chen, Y. Role of melatonin in controlling angiogenesis under physiological and pathological conditions. Angiogenesis 23, 91–104 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-019-09689-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-019-09689-7