Abstract
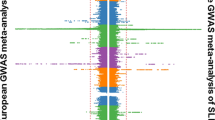
We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) in a Chinese Han population by genotyping 1,047 cases and 1,205 controls using Illumina Human610-Quad BeadChips and replicating 78 SNPs in two additional cohorts (3,152 cases and 7,050 controls). We identified nine new susceptibility loci (ETS1, IKZF1, RASGRP3, SLC15A4, TNIP1, 7q11.23, 10q11.22, 11q23.3 and 16p11.2; 1.77 × 10−25 ≤ Pcombined ≤ 2.77 × 10−8) and confirmed seven previously reported loci (BLK, IRF5, STAT4, TNFAIP3, TNFSF4, 6q21 and 22q11.21; 5.17 × 10−42 ≤ Pcombined ≤ 5.18 × 10−12). Comparison with previous GWAS findings highlighted the genetic heterogeneity of SLE susceptibility between Chinese Han and European populations. This study not only advances our understanding of the genetic basis of SLE but also highlights the value of performing GWAS in diverse ancestral populations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
04 December 2009
In the version of this article initially published, there were two errors in the author affiliations and corresponding author details. Jian-Jun Liu is also affiliated with footnote 17, and Sen Yang and Xue-Jun Zhang are the corresponding authors. These errors have been corrected in the HTML and PDF versions of the article.
References
Hopkinson, N.D., Doherty, M. & Powell, R.J. Clinical features and race-specific incidence/prevalence rates of systemic lupus erythematosus in a geographically complete cohort of patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 53, 675–680 (1994).
Wang, J. et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus: a genetic epidemiology study of 695 patients from China. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 298, 485–491 (2007).
Lau, C.S., Yin, G. & Mok, M.Y. Ethnic and geographical differences in systemic lupus erythematosus: an overview. Lupus 15, 715–719 (2006).
Zeng, Q.Y. et al. Rheumatic diseases in China. Arthritis Res. Ther. 10, R17 (2008).
Danchenko, N., Satia, J.A. & Anthony, M.S. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: a comparison of worldwide disease burden. Lupus 15, 308–318 (2006).
Hom, G. et al. Association of systemic lupus erythematosus with C8orf13-BLK and ITGAM-ITGAX. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 900–909 (2008).
Harley, J.B. et al. Genome-wide association scan in women with systemic lupus erythematosus identifies susceptibility variants in ITGAM, PXK, KIAA1542 and other loci. Nat. Genet. 40, 204–210 (2008).
Kozyrev, S.V. et al. Functional variants in the B-cell gene BANK1 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 40, 211–216 (2008).
Graham, R.R. et al. Genetic variants near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 40, 1059–1061 (2008).
Yang, W. et al. Population differences in SLE susceptibility genes: STAT4 and BLK, but not PXK, are associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in Hong Kong Chinese. Genes Immun. 10, 219–226 (2009).
Cunninghame Graham, D.S. et al. Polymorphism at the TNF superfamily gene TNFSF4 confers susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 40, 83–89 (2008).
Beyaert, R., Heyninck, K. & Van Huffel, S. A20 and A20-binding proteins as cellular inhibitors of nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent gene expression and apoptosis. Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 1143–1151 (2000).
Nath, S.K. et al. A nonsynonymous functional variant in integrin-alpha(M) (encoded by ITGAM) is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 40, 152–154 (2008).
Gallant, S. & Gilkeson, G. ETS transcription factors and regulation of immunity. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. (Warsz.) 54, 149–163 (2006).
Georgopoulos, K. et al. The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 79, 143–156 (1994).
Wojcik, H., Griffiths, E., Staggs, S., Hagman, J. & Winandy, S. Expression of a non-DNA-binding Ikaros isoform exclusively in B cells leads to autoimmunity but not leukemogenesis. Eur. J. Immunol. 37, 1022–1032 (2007).
Coughlin, J.J., Stang, S.L., Dower, N.A. & Stone, J.C. RasGRP1 and RasGRP3 regulate B cell proliferation by facilitating B cell receptor-Ras signaling. J. Immunol. 175, 7179–7184 (2005).
Lee, J. et al. pH-dependent internalization of muramyl peptides from early endosomes enables Nod1 and Nod2 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 23818–23829 (2009).
Harley, I.T., Kaufman, K.M., Langefeld, C.D., Harley, J.B. & Kelly, J.A. Genetic susceptibility to SLE: new insights from fine mapping and genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 285–290 (2009).
Graham, R.R., Hom, G., Ortmann, W. & Behrens, T.W. Review of recent genome-wide association scans in lupus. J. Intern. Med. 265, 680–688 (2009).
Nair, R.P. et al. Genome-wide scan reveals association of psoriasis with IL-23 and NF-κB pathways. Nat. Genet. 41, 199–204 (2009).
Chu, J.Y. et al. Genetic relationship of populations in China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11763–11768 (1998).
Ke, Y. et al. Y-chromosome haplotype distribution in Han Chinese populations and modern human origin in East Asians. Sci. China C Life Sci. 44, 225–232 (2001).
Shi, Y. et al. Genetic structure adds power to detect schizophrenia susceptibility at SLIT3 in the Chinese Han population. Genome Res. 14, 1345–1349 (2004).
Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 40, 1725 (1997).
Zhang, X.J. et al. Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21. Nat. Genet. 41, 205–210 (2009).
Purcell, S. et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575 (2007).
Price, A.L. et al. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 38, 904–909 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank all study participants. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation (30972727), the Key Project of National Natural Science Foundation (30530670 and 30830089), the Anhui Provincial Special Scientific Program (2007-7) and the Anhui Skin Genetic Study Innovative Research Team Program (TD200701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.-J.Z. conceived of this study and obtained financial support. X.-J.Z., J.-J.L. and S.Y. designed the study. J.-W.H., H.-F.Z., Y.C. and L.-D.S. participated in the design and were responsible for sample selection, genotyping and project management. D.-Q.Y., Z.H., Jin-Hua Xu, Z.-M.C., H.-F.X., H.F., Q.-J.L., Jian-Hua Xu, X.-P.L., Y.-F.P., D.-Q.D., F.-Q.Z., Z.-Z.Y., X.-Y.Z., Q.-W.W., F.H., L.M., X.-X.Z., W.-F.Z., F.G., P.-L.Z., Q.G., B.L., M.G., F.-L.X., J.-L.H., S.-X.L., H.L., Z.-X.W., C.-J.Y., P.-G.W., W.-M.Z., A.-P.Z., D.L. and Z.-F.Z. conducted sample selection and data management. W.-H.D., J.-Q.Y., S.-K.S., J.L., Y.-J.S., K.-J.Z., Yang Li, D.-Y.H. and Y.-M.L. undertook recruitment, collected phenotype data, undertook related data handling and calculation, managed recruitment and obtained biological samples. W.H., G.-P.Z., F.-S.Z., Y.-L.C., C.Q., C.Z., Z.Z., W.-S.L., Y.-Q.R., S.-Q.Z., M.S. and Y.W. performed genotyping analysis. H.-F.Z., X.-B.Z., Yi Li, H.Q.L. and F.-Y.Z. undertook data processing, statistical analysis and bioinformatics investigations. All the authors contributed to the final paper, with X.-J.Z., J.-J.L., S.Y., J.-W.H., H.-F.Z., Y.C. and L.-D.S playing key roles.
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary figures 1–4 and Supplementary Tables 1–4 (PDF 1273 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, JW., Zheng, HF., Cui, Y. et al. Genome-wide association study in a Chinese Han population identifies nine new susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet 41, 1234–1237 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.472
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.472
This article is cited by
-
Chemoproteomic development of SLC15A4 inhibitors with anti-inflammatory activity
Nature Chemical Biology (2024)
-
Omics-based integrated analysis identified IKZF2 as a biomarker associated with lupus nephritis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Regulation of activated T cell survival in rheumatic autoimmune diseases
Nature Reviews Rheumatology (2022)
-
Ubiquitin-binding domain in ABIN1 is critical for regulating cell death and inflammation during development
Cell Death & Differentiation (2022)
-
Circular RNA expression profile of systemic lupus erythematosus and its clinical significance as a potential novel biomarker
Genes & Genomics (2022)