Abstract
Inter-individual variation in cytosine modifications has been linked to complex traits in humans. Cytosine modification variation is partially controlled by single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), known as modified cytosine quantitative trait loci (mQTL). However, little is known about the role of short tandem repeat polymorphisms (STRPs), a class of structural genetic variants, in regulating cytosine modifications. Utilizing the published data on the International HapMap Project lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs), we assessed the relationships between 721 STRPs and the modification levels of 283,540 autosomal CpG sites. Our findings suggest that, in contrast to the predominant cis-acting mode for SNP-based mQTL, STRPs are associated with cytosine modification levels in both cis-acting (local) and trans-acting (distant) modes. In local scans within the ±1 Mb windows of target CpGs, 21, 9, and 21 cis-acting STRP-based mQTL were detected in CEU (Caucasian residents from Utah, USA), YRI (Yoruba people from Ibadan, Nigeria), and the combined samples, respectively. In contrast, 139,420, 76,817, and 121,866 trans-acting STRP-based mQTL were identified in CEU, YRI, and the combined samples, respectively. A substantial proportion of CpG sites detected with local STRP-based mQTL were not associated with SNP-based mQTL, suggesting that STRPs represent an independent class of mQTL. Functionally, genetic variants neighboring CpG-associated STRPs are enriched with genome-wide association study (GWAS) loci for a variety of complex traits and diseases, including cancers, based on the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) GWAS Catalog. Therefore, elucidating these STRP-based mQTL in addition to SNP-based mQTL can provide novel insights into the genetic architectures of complex traits.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell JT, Pai AA, Pickrell JK, Gaffney DJ, Pique-Regi R, Degner JF et al (2011) DNA methylation patterns associate with genetic and gene expression variation in HapMap cell lines. Genome Biol 12:R10. doi:10.1186/gb-2011-12-1-r10
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple Testing. J Roy Stat Soc B Met 57:289–300. doi:10.2307/2346101
Berto G, Camera P, Fusco C, Imarisio S, Ambrogio C, Chiarle R et al (2007) The Down syndrome critical region protein TTC3 inhibits neuronal differentiation via RhoA and Citron kinase. J Cell Sci 120:1859–1867. doi:10.1242/jcs.000703
Bibikova M, Barnes B, Tsan C, Ho V, Klotzle B, Le JM et al (2011) High density DNA methylation array with single CpG site resolution. Genomics 98:288–295. doi:10.1016/j.ygeno.2011.07.007
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19:185–193
Bolton KA, Ross JP, Grice DM, Bowden NA, Holliday EG, Avery-Kiejda KA et al (2013) STaRRRT: a table of short tandem repeats in regulatory regions of the human genome. BMC Genom 14:795. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-795
Borevitz JO, Liang D, Plouffe D, Chang HS, Zhu T, Weigel D et al (2003) Large-scale identification of single-feature polymorphisms in complex genomes. Genome Res 13:513–523. doi:10.1101/gr.541303
Brahmachary M, Guilmatre A, Quilez J, Hasson D, Borel C, Warburton P et al (2014) Digital genotyping of macrosatellites and multicopy genes reveals novel biological functions associated with copy number variation of large tandem repeats. PLoS Genet 10:e1004418. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004418
Conrad DF, Pinto D, Redon R, Feuk L, Gokcumen O, Zhang Y et al (2010) Origins and functional impact of copy number variation in the human genome. Nature 464:704–712. doi:10.1038/nature08516
Cooper GM, Coe BP, Girirajan S, Rosenfeld JA, Vu TH, Baker C et al (2011) A copy number variation morbidity map of developmental delay. Nat Genet 43:838–846. doi:10.1038/ng.909
Du P, Zhang X, Huang CC, Jafari N, Kibbe WA, Hou L et al (2010) Comparison of Beta-value and M-value methods for quantifying methylation levels by microarray analysis. BMC Bioinform 11:587. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-11-587
Duan S, Huang RS, Zhang W, Bleibel WK, Roe CA, Clark TA et al (2008) Genetic architecture of transcript-level variation in humans. Am J Hum Genet 82:1101–1113. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.03.006
Ellegren H (2000) Heterogeneous mutation processes in human microsatellite DNA sequences. Nat Genet 24:400–402. doi:10.1038/74249
Ellegren H (2004) Microsatellites: simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat Rev Genet 5:435–445. doi:10.1038/nrg1348
Encode Project Consortium (2012) An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 489:57–74. doi:10.1038/nature11247
Ernst J, Kheradpour P, Mikkelsen TS, Shoresh N, Ward LD, Epstein CB et al (2011) Mapping and analysis of chromatin state dynamics in nine human cell types. Nature 473:43–49. doi:10.1038/nature09906
Fraser HB, Lam LL, Neumann SM, Kobor MS (2012) Population-specificity of human DNA methylation. Genome Biol 13:R8. doi:10.1186/gb-2012-13-2-r8
Gamazon ER, Badner JA, Cheng L, Zhang C, Zhang D, Cox NJ et al (2013) Enrichment of cis-regulatory gene expression SNPs and methylation quantitative trait loci among bipolar disorder susceptibility variants. Mol Psychiatry 18:340–346. doi:10.1038/mp.2011.174
Hattori E, Ebihara M, Yamada K, Ohba H, Shibuya H, Yoshikawa T (2001) Identification of a compound short tandem repeat stretch in the 5′-upstream region of the cholecystokinin gene, and its association with panic disorder but not with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 6:465–470. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4000875
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA, Ramos EM, Mehta JP, Collins FS et al (2009) Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:9362–9367. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903103106
Johnson WE, Li C, Rabinovic A (2007) Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics 8:118–127. doi:10.1093/biostatistics/kxj037
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:27–30
Kuroda S, Schweighofer N, Kawato M (2001) Exploration of signal transduction pathways in cerebellar long-term depression by kinetic simulation. J Neurosci 21:5693–5702
Li R, Hsieh CL, Young A, Zhang Z, Ren X, Zhao Z (2015) Illumina synthetic long read sequencing allows recovery of missing sequences even in the “finished” C. elegans genome. Sci Rep. 5:10814. doi:10.1038/srep10814
McCarroll SA, Kuruvilla FG, Korn JM, Cawley S, Nemesh J, Wysoker A et al (2008) Integrated detection and population-genetic analysis of SNPs and copy number variation. Nat Genet 40:1166–1174. doi:10.1038/ng.238
Mills RE, Luttig CT, Larkins CE, Beauchamp A, Tsui C, Pittard WS et al (2006) An initial map of insertion and deletion (INDEL) variation in the human genome. Genome Res 16:1182–1190. doi:10.1101/gr.4565806
Moen EL, Zhang X, Mu W, Delaney SM, Wing C, McQuade J et al (2013) Genome-wide variation of cytosine modifications between European and African populations and the implications for complex traits. Genetics 194:987–996. doi:10.1534/genetics.113.151381
Monkley SJ, Pritchard CA, Critchley DR (2001) Analysis of the mammalian talin2 gene TLN2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 286:880–885. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.5497
Morley M, Molony CM, Weber TM, Devlin JL, Ewens KG, Spielman RS et al (2004) Genetic analysis of genome-wide variation in human gene expression. Nature 430:743–747. doi:10.1038/nature02797
Murrell A, Heeson S, Cooper WN, Douglas E, Apostolidou S, Moore GE et al (2004) An association between variants in the IGF2 gene and Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome: interaction between genotype and epigenotype. Hum Mol Genet 13:247–255. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddh013
Pai AA, Bell JT, Marioni JC, Pritchard JK, Gilad Y (2011) A genome-wide study of DNA methylation patterns and gene expression levels in multiple human and chimpanzee tissues. PLoS Genet 7:e1001316. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001316
Payseur BA, Jing P (2009) A genomewide comparison of population structure at STRPs and nearby SNPs in humans. Mol Biol Evol 26:1369–1377. doi:10.1093/molbev/msp052
Payseur BA, Place M, Weber JL (2008) Linkage disequilibrium between STRPs and SNPs across the human genome. Am J Hum Genet 82:1039–1050. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.02.018
Payseur BA, Jing P, Haasl RJ (2011) A genomic portrait of human microsatellite variation. Mol Biol Evol 28:303–312. doi:10.1093/molbev/msq198
Perry GH (2008) The evolutionary significance of copy number variation in the human genome. Cytogenet Genome Res 123:283–287. doi:10.1159/000184719
Pumpernik D, Oblak B, Borstnik B (2008) Replication slippage versus point mutation rates in short tandem repeats of the human genome. Mol Genet Genomics 279:53–61. doi:10.1007/s00438-007-0294-1
Ram D, Leshkowitz D, Gonzalez D, Forer R, Levy I, Chowers M et al (2015) Evaluation of GS Junior and MiSeq next-generation sequencing technologies as an alternative to Trugene population sequencing in the clinical HIV laboratory. J Virol Methods 212:12–16. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.11.003
Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J, Phan L, Smigielski EM et al (2001) dbSNP: the NCBI database of genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 29:308–311
Siegfried Z, Eden S, Mendelsohn M, Feng X, Tsuberi BZ, Cedar H (1999) DNA methylation represses transcription in vivo. Nat Genet 22:203–206. doi:10.1038/9727
Spielman RS, Bastone LA, Burdick JT, Morley M, Ewens WJ, Cheung VG (2007) Common genetic variants account for differences in gene expression among ethnic groups. Nat Genet 39:226–231. doi:10.1038/ng1955
St George-Hyslop P, Haines J, Rogaev E, Mortilla M, Vaula G, Pericak-Vance M et al (1992) Genetic evidence for a novel familial Alzheimer’s disease locus on chromosome 14. Nat Genet 2:330–334. doi:10.1038/ng1292-330
Stadler MB, Murr R, Burger L, Ivanek R, Lienert F, Scholer A et al (2011) DNA-binding factors shape the mouse methylome at distal regulatory regions. Nature 480:490–495. doi:10.1038/nature10716
Stark AL, Hause RJ Jr, Gorsic LK, Antao NN, Wong SS, Chung SH et al (2014) Protein quantitative trait loci identify novel candidates modulating cellular response to chemotherapy. PLoS Genet 10:e1004192. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004192
Stein JL, Hua X, Morra JH, Lee S, Hibar DP, Ho AJ et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis reveals novel genes influencing temporal lobe structure with relevance to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 51:542–554. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.02.068
Stranger BE, Forrest MS, Dunning M, Ingle CE, Beazley C, Thorne N et al (2007) Relative impact of nucleotide and copy number variation on gene expression phenotypes. Science 315:848–853. doi:10.1126/science.1136678
The International HapMap Consortium (2003) The International HapMap project. Nature 426:789–796. doi:10.1038/nature02168
The International HapMap Consortium (2005) A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437:1299–1320. doi:10.1038/nature04226
The International HapMap Consortium (2007) A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 449:851–861. doi:10.1038/nature06258
The International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409:860–921. doi:10.1038/35057062
Weber JL, Wong C (1993) Mutation of human short tandem repeats. Hum Mol Genet 2:1123–1128
Westfall P, Young S (1993) Resampling-based multiple testing: examples and methods for p-value adjustment. Wiley, New York
Wooster R, Cleton-Jansen AM, Collins N, Mangion J, Cornelis RS, Cooper CS et al (1994) Instability of short tandem repeats (microsatellites) in human cancers. Nat Genet 6:152–156. doi:10.1038/ng0294-152
Zhang W, Duan S, Kistner EO, Bleibel WK, Huang RS, Clark TA et al (2008) Evaluation of genetic variation contributing to differences in gene expression between populations. Am J Hum Genet 82:631–640. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.12.015
Zhang W, Duan S, Bleibel WK, Wisel SA, Huang RS, Wu X, He L, Clark TA, Chen TX, Schweitzer AC, Blume JE, Dolan ME, Cox NJ (2009) Identification of common genetic variants that account for transcript isoform variation between human populations. Hum Genet 125(1):81–93
Zhang DD, Cheng LJ, Badner JA, Chen C, Chen Q, Luo W et al (2010) Genetic control of individual differences in gene-specific methylation in human brain. Am J Hum Genet 86:411–419. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.02.005
Zhang X, Cal AJ, Borevitz JO (2011) Genetic architecture of regulatory variation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res 21:725–733. doi:10.1101/gr.115337.110
Zhang X, Mu W, Zhang W (2012) On the analysis of the Illumina 450 k array data: probes ambiguously mapped to the human genome. Front Genet 3:73. doi:10.3389/fgene.2012.00073
Zhang X, Moen EL, Liu C, Mu W, Gamazon ER, Delaney SM et al (2014) Linking the genetic architecture of cytosine modifications with human complex traits. Hum Mol Genet 23:5893–5905. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu313
Zhang W, Gamazon ER, Zhang X, Konkashbaev A, Liu C, Szilagyi KL et al (2015) SCAN database: facilitating integrative analyses of cytosine modification and expression QTL. Database (Oxford). doi:10.1093/database/bav025
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health: R21HG006367 (to WZ), R21CA187869 (to WZ and LH), and The Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center-Developmental Funds P30CA060553 (to WZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Hou and W. Zhang contributed equally to this work as senior authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
439_2015_1628_MOESM1_ESM.png
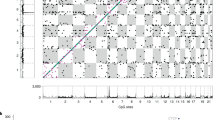
Supplementary material 1 Fig. 1 Pearson’s correlation coefficients (ρ) of STRPs and cytosine modifications in local scans between CEU and YRI samples. Scatter plot for Pearson’s correlations (ρ) of STRP length and M-values of local CpGs within ± 1 Mb windows of STRPs for CEU and YRI. (PNG 269 kb)
439_2015_1628_MOESM2_ESM.png
Supplementary material 2 Fig. 2 QQ-plots of the observed p -values for trans -acting STRP-based mQTL. P-values are binned and displayed as hexagons. Different grey scales of each hexagon represent different counts of p-values. A total of > 200 million observed p-values from the whole-genome scan are shown. (a) CEU; (b) YRI. (PNG 204 kb)
439_2015_1628_MOESM3_ESM.png
Supplementary material 3 Fig. 3 Enrichment of GWAS loci among cis -acting STRP-based mQTL. The null distributions of the numbers of SNPs overlapped with GWAS loci are displayed as histograms. The asterisk marks the true number of SNPs overlapped with GWAS loci within different windows: (a) ± 100 Kb; (b) ± 500 Kb; and (c) ± 1 Mb of cis-acting STRP-based mQTL (p-value < 10−3). (PNG 97 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zheng, Y., Zhang, X. et al. Linking short tandem repeat polymorphisms with cytosine modifications in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Hum Genet 135, 223–232 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1628-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-015-1628-4