Genome-wide identification and molecular expression profile analysis of FHY3/FAR1 gene family in walnut (Juglans sigillata L.) development
- PMID: 37940838
- PMCID: PMC10634098
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09629-2
Genome-wide identification and molecular expression profile analysis of FHY3/FAR1 gene family in walnut (Juglans sigillata L.) development
Abstract
Background: Juglans sigillata L. (walnut) has a high economic value for nuts and wood and has been widely grown and eaten around the world. Light plays an important role in regulating the development of the walnut embryo and promoting nucleolus enlargement, which is one of the factors affecting the yield and quality of walnut. However, little is known about the effect of light on the growth and quality of walnuts. Studies have shown that far red prolonged hypocotyl 3 (FHY3) and far red damaged response (FAR1) play important roles in plant growth, light response, and resistance. Therefore, FHY3/FAR1 genes were identified in walnuts on a genome-wide basis during their growth and development to reveal the potential regulation mechanisms involved in walnut kernel growth and development.
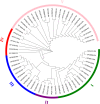
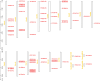
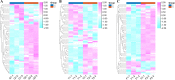
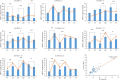
Results: In the present study, a total of 61 FHY3/FAR1 gene family members in walnuts have been identified, ranging in length from 117 aa to 895 aa. These gene family members have FHY3 or FAR1 conserved domains, which are unevenly distributed on the 15 chromosomes (Chr) of the walnut (except for the Chr16). All 61 FHY3/FAR1 genes were divided into five subclasses (I, II, III, IV, and V) by phylogenetic tree analysis. The results indicated that FHY3/FAR1 genes in the same subclasses with similar structures might be involved in regulating the growth and development of walnut. The gene expression profiles were analyzed in different walnut kernel varieties (Q, T, and F). The result showed that some FHY3/FAR1 genes might be involved in the regulation of walnut kernel ripening and seed coat color formation. Seven genes (OF07056-RA, OF09665-RA, OF24282-RA, OF26012-RA, OF28029-RA, OF28030-RA, and OF08124-RA) were predicted to be associated with flavonoid biosynthetic gene regulation cis-acting elements in promoter sequences. RT-PCR was used to verify the expression levels of candidate genes during the development and color change of walnut kernels. In addition, light responsiveness and MeJA responsiveness are important promoter regulatory elements in the FHY3/FAR1 gene family, which are potentially involved in the light response, growth, and development of walnut plants.
Conclusion: The results of this study provide a valuable reference for supplementing the genomic sequencing results of walnut, and pave the way for further research on the FHY3/FAR1 gene function of walnut.
Keywords: FAR1; FHY3; Gene family; Kernel; Walnut.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A pair of light signaling factors FHY3 and FAR1 regulates plant immunity by modulating chlorophyll biosynthesis.J Integr Plant Biol. 2016 Jan;58(1):91-103. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12369. Epub 2015 Jul 24. J Integr Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 25989254 Free PMC article.
-
The FHY3 and FAR1 genes encode transposase-related proteins involved in regulation of gene expression by the phytochrome A-signaling pathway.Plant J. 2003 May;34(4):453-71. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2003.01741.x. Plant J. 2003. PMID: 12753585
-
Discrete and essential roles of the multiple domains of Arabidopsis FHY3 in mediating phytochrome A signal transduction.Plant Physiol. 2008 Oct;148(2):981-92. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.120436. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Plant Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18715961 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of FHY3 and FAR1 as System Integrators in Plant Development.Plant Cell Physiol. 2023 Oct 16;64(10):1139-1145. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcad068. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37384577 Review.
-
Multifaceted roles of FHY3 and FAR1 in light signaling and beyond.Trends Plant Sci. 2015 Jul;20(7):453-61. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2015.04.003. Epub 2015 May 5. Trends Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25956482 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive identification and expression analysis of FAR1/FHY3 genes under drought stress in maize (Zea mays L.).PeerJ. 2024 Jun 28;12:e17684. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17684. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38952979 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Li G, Gao S, Martinez C, He G, Zhou Z, Huang X, Lee JH, Zhang H, Shen Y, Wang H, Deng XW. Arabidopsis transcription factor ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL5 plays a role in the feedback regulation of phytochrome A signaling. Plant Cell. 2010;22(11):3634–49. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.075788. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 32070372/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31860215/The National Natural Science Foundation of China
- Qianlin ke [2022] 17/Innovation and Application of Guizhou Walnut Germplasm
- Qianlin J [2022] No. 05/Study on the Vitality and Stigma of Guizhou Wuren Walnut Pollen
- [2015] 4010/The Bridging Project for the Enterprises and the Local walnut R&D Groups in Guizhou Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

